What are CNC Turning Parts?
CNC turning is a machining process that shapes a rotating workpiece using a cutting tool. The workpiece rotates on the spindle, while the cutting tool moves along the surface of the workpiece to remove the material. This cutting process of CNC turning can produce cylindrical parts such as shafts, pins, and rods.

Principle of CNC Turning Process
CNC turning works by rotating a workpiece on a spindle. The material is fixed on the main shaft and rotates at high speed. This rotation allows the cutting tool to remove material evenly from the surface.
The cutting tool moves along the workpiece in precise directions. It can move parallel or perpendicular to the axis of rotation. The variation of the tool’s running path can produce different shapes, such as cylinders, cones, or threads.
The CNC turning process is controlled by a computer program. Computer programs ensure the high precision and repeatability of processing by controlling the movement of the cutting tool, the rotational speed of the workpiece, and the cutting depth.
CNC turning can produce smooth surfaces and strictly control tolerances, and is suitable for both simple and complex cylindrical parts.
What is a CNC Turning Center?
A CNC turning center is an advanced type of CNC lathe designed for producing precise cylindrical parts. Unlike traditional lathes, turning centers are equipped with computer numerical control systems that automate the machining process. They can perform multiple operations such as turning, facing, drilling, threading, and even milling, all in a single setup. This improves efficiency, reduces production time, and ensures high accuracy. CNC turning centers are widely used in industries like automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and electronics, where consistent quality and tight tolerances are essential.
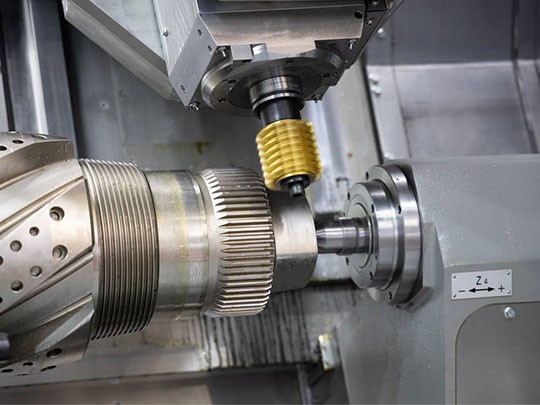

How Does Precision CNC Turning Work?
Material Preparation
The first step in CNC turning is preparing the raw material. The workpiece, usually a metal rod or bar, is cut to the required length. The materials also need to be cleaned to remove dirt, oil, or rust that may affect machining.
The material is checked for defects to ensure it is suitable for precise machining. Appropriate materials can ensure that the workpiece is firmly fixed on the spindle.
Workpiece Mounting
After preparation, the workpiece is mounted onto the machine spindle. It is clamped firmly using a chuck or collet to prevent any movement during rotation. Proper alignment is checked to ensure the axis of the workpiece matches the machine’s spindle.
The step of installing the cutting tool is of vital importance, as any mistake can lead to uneven cutting, poor surface finish or exceeding the tolerance size.
Tool Selection and Setup
Select the cutting tool based on the material and shape of the part, then install the tool on the tool rest and carefully adjust its position. Set the cutting speed, feed rate, and cutting depth according to the material and design requirements.
Machining Process
The CNC turning operation begins with the programmed tool movements. The forming of a workpiece is achieved through the movement of the cutting tool along the surface of the workpiece. Rough cuts remove most of the material, followed by finishing cuts to achieve the exact dimensions and surface quality.
Depending on the design, the machining process may include turning, threading, slotting, or sharpening.
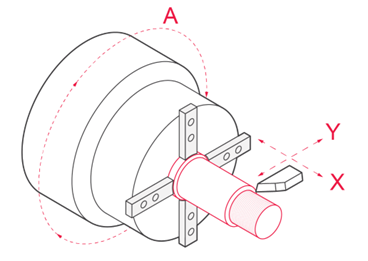
Inspection and Finishing
After machining, the parts are removed from the spindle and cleaned, and then the dimensions, tolerances, and surface finish are verified. The need for adjustments or secondary processes depends on the customer’s requirements.
After machining, the parts are inspected to make sure they meet the design specifications. This step guarantees the reliability and quality of the CNC-turned part in its intended application.
What Are The Main Parameters in the CNC Turning Process?
In CNC turning, several key parameters affect the quality, efficiency, and results of the process.
The Key Parameters of the CNC Turning Process
- Cutting Speed:Cutting speed is how fast the surface of the workpiece moves against the cutting tool. The spindle speed and the diameter of the workpiece will affect the cutting speed.
- Feed Rate: The feed rate is the distance the cutting tool moves along the workpiece in one rotation. It affects surface quality and machining time. A higher feed rate removes more material faster. A lower feed rate gives a finer finish.
- Depth of Cut: Depth of cut is the thickness of material removed in one pass of the tool. A larger depth of cut makes machining faster but increases tool wear and vibration.
- Spindle Speed: Spindle speed is the rate at which the spindle rotates the workpiece. The correct speed depends on the material and the type of tool used.
- Tool Geometry: Tool geometry is the angles, edges, and shapes of the tool. The right geometry controls cutting forces, reduces wear, and improves precision. The right tool design is chosen based on the material and part requirements.
Surface Finishing of CNC Turning Parts
CNC turning leaves noticeable tool marks as the block’s surface is removed to create the desired shape. Please select the appropriate surface finish for your custom part. NOBLE offers a variety of common surface finishes to enhance both the functionality and aesthetics of your part.
1. Anodizing
An electrolytic process mainly for aluminum parts that increases corrosion resistance, improves surface hardness, and allows coloring.
Anodizing is durable, lightweight protection; available in clear, black, red, blue, and other colors.
2. Powder Coating
Dry powder is electrostatically sprayed onto the part, then cured under heat to form a durable, protective coating.
3. Electroplating
A metallic coating (nickel, chrome, zinc, gold, etc.) is applied to the part surface using an electrochemical process.
4. Polishing
Mechanical or chemical methods are used to smooth the surface and improve reflectivity.
5. Brushing
A linear abrasive finishing that creates fine, consistent texture lines on the surface.
Brushing can provide a satin or matte look, hide scratches, and enhance decorative appearance.
Summarize the features of CNC turning
| Surface Finishes | Features | Option |
| Anodizing | Anodizing improves corrosion resistance, enhancing wear resistance and hardness, and protecting the metal surface. Widely used in mechanical parts, aircraft, and automobile parts, precision instruments, etc. | Materials: Aluminum
Color: Clear, black, grey, red, blue, gold.
Texture: Smooth, matte finish |
| Sand Blasting | Sand blasting results in parts with a smooth surface with a matte texture. Used mainly for visual applications and can be followed by other surface treatments. | Materials: ABS, Aluminum, Brass
Color: N/A
Texture: Matte |
| Powder Coating | Powder coating is a type of coating that is applied as a free-flowing, dry powder. Unlike conventional liquid paint, which is delivered via an evaporating solvent, powder coating is typically applied electrostatically and then cured under heat or with ultraviolet light. | Materials: Aluminum, Stainless Steel, Steel
Color: Black, any RAL code or Pantone number
Texture: Gloss or semi-gloss |
| Electroplating | Electroplating can be functional, decorative or corrosion-related. Many industries use the process, including the automotive sector, in which chrome-plating of steel automobile parts is common. | Materials: Aluminum, steel, Stainless Steel
Color: N/A
Texture: Smooth, Glossy finish |
| Polishing | Polishing is the process of creating a smooth and shiny surface, either through physical rubbing of the part or by chemical interference. The process produces a surface with significant specular reflection, but in some materials, it is able to reduce diffuse reflection. | Materials: Aluminum, Brass, Stainless Steel, Steel
Color: N/A
Texture: Glossy |
| Brushing | Brushing is a surface treatment process in which abrasive belts are used to draw traces on the surface of a material, usually for aesthetic purposes. | Materials: ABS, Aluminum, Brass, Stainless Steel, Steel
Color: N/A
Texture: Satin |
Advantages of the CNC Turning Process
Precision Finish
CNC turning process, by virtue of its digital control characteristics, can achieve ultra-precision machining; conventional machining accuracy is stably controlled in the range of ± 0.01mm, high-end models can even reach the accuracy level of ± 0.005mm.
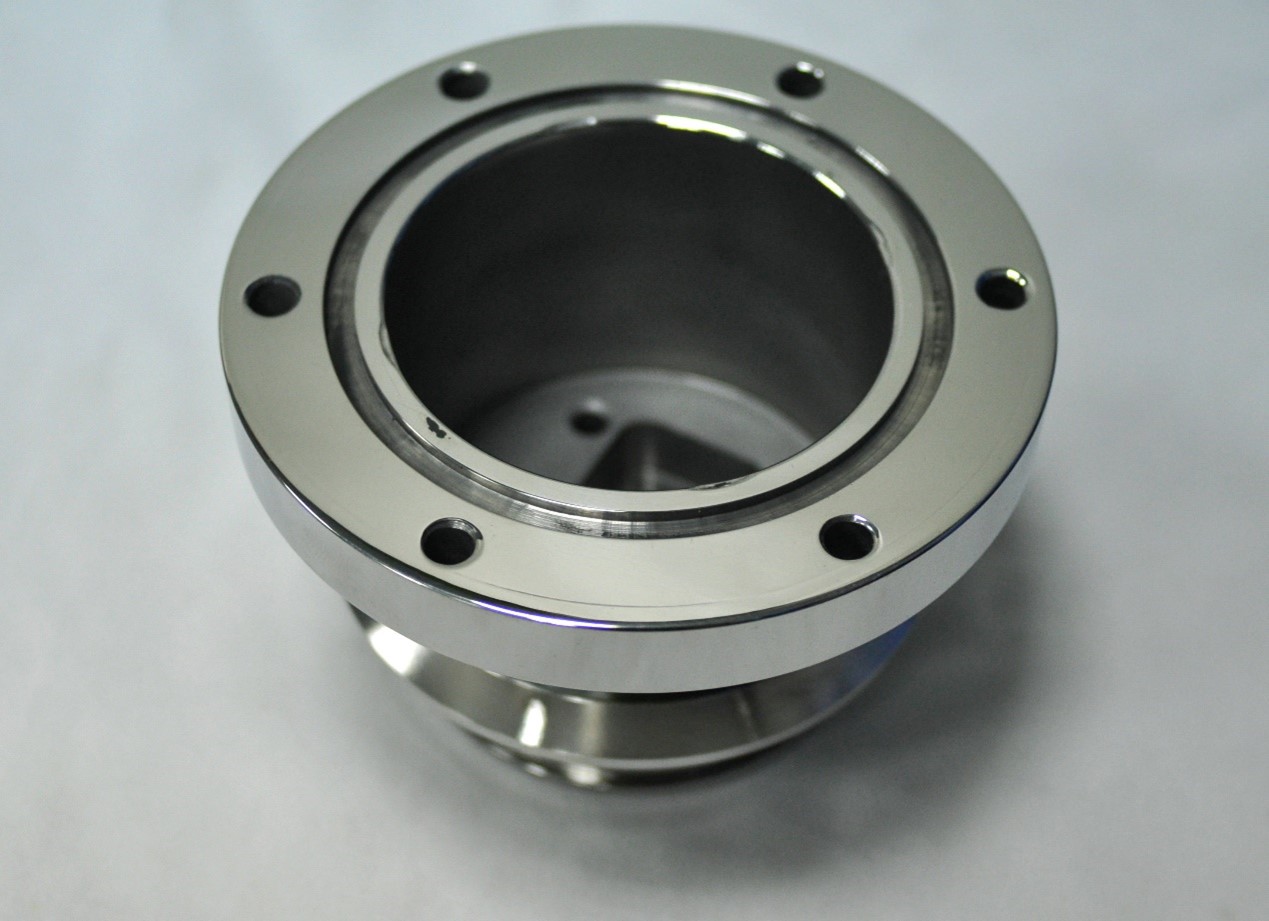

Stable Consistency
Each CNC turning part follows the same process, which ensures repeatability. Even in large quantities, the parts keep the same precision and surface finish. The stability of CNC turning processing makes CNC turning reliable for industries with high standards.
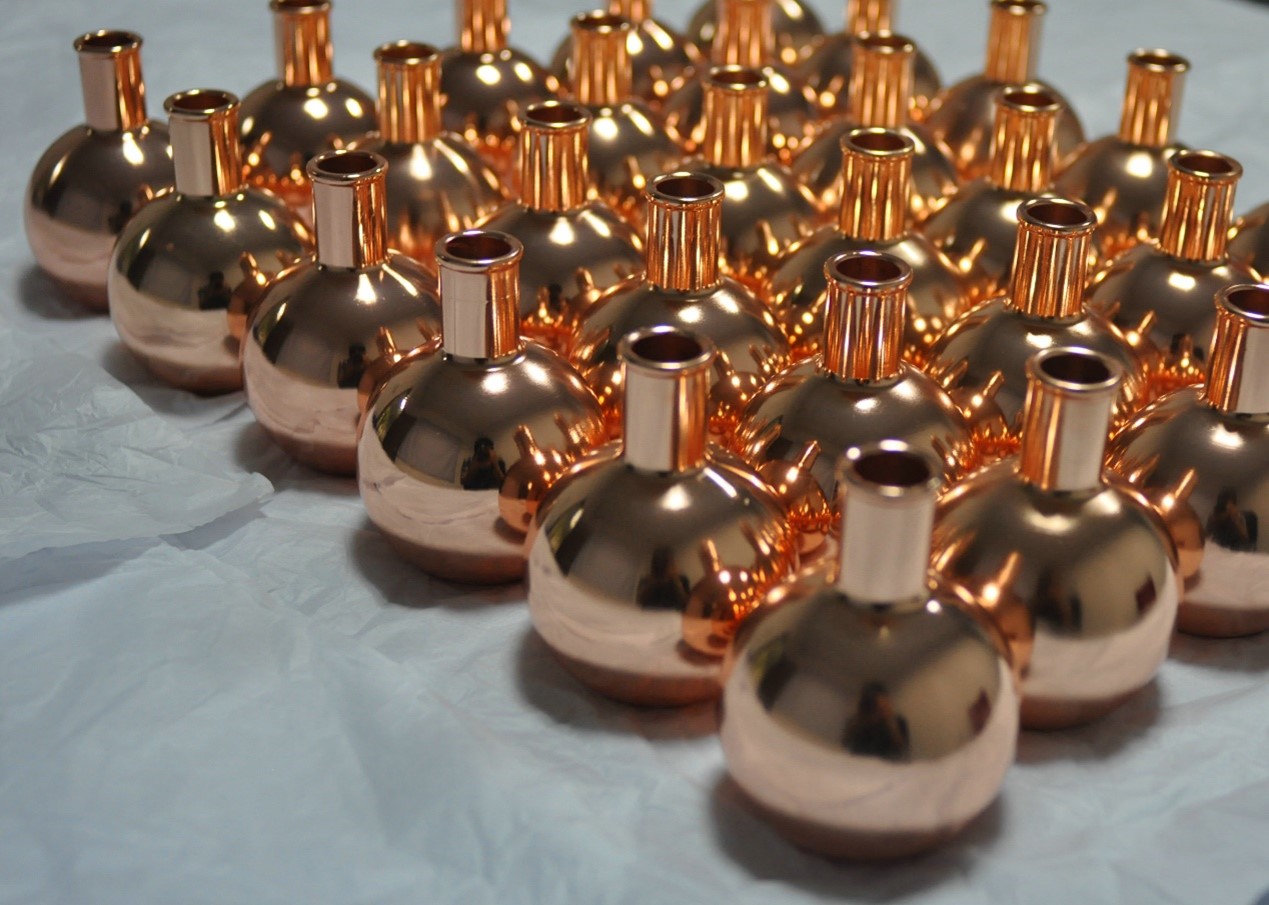

Automated Efficiency
The process is fully automated, controlled by computer programs. Once the turning process is programmed, the machine can run with minimal human input. This reduces labor needs, lowers errors, and boosts productivity for both small and large-scale production.
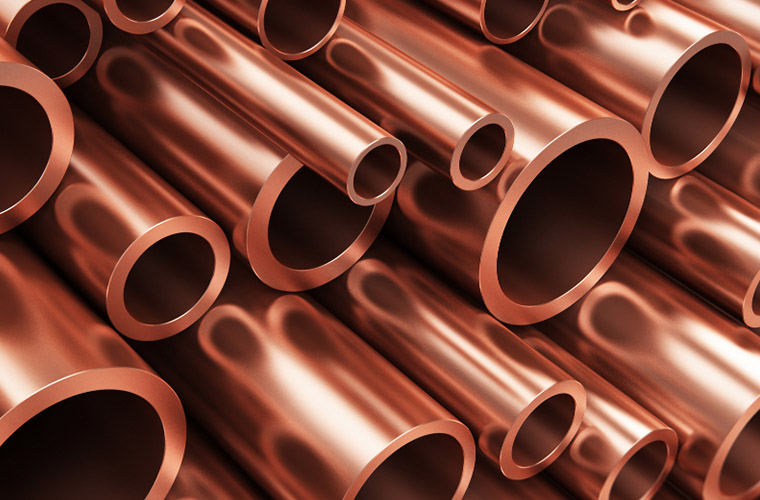

Material Variety
CNC turning technology can machine almost all engineering materials:
Metals
- Aluminum
- Stainless steel
- Carbon steel
- Alloy steel
- Brass
- Copper
- Titanium
- Magnesium
- Zinc

Plastics
- ABS
- POM
- Nylon (PA)
- Polycarbonate (PC)
- Polyethylene (PE)
- Polypropylene (PP)
- PTFE (Teflon)
- PVC
- Acrylic (PMMA)
The ability to machine different materials lets manufacturers make parts for many industries, from automotive to aerospace and medical. They can do this without changing the core processes.
Complex Structure
CNC turning can produce not only simple cylindrical shapes but also more complex features. It can also efficiently and precisely manufacture various complex geometric features, such as threads, tapers, grooves, and complex contours with fine details.
This machining method allows greater freedom in product design. It enables more innovative structures and functions. It also meets the high technical demands and complex applications of modern engineering.
Smart Flexibility
CNC turning allows quick changes in design and setup. It can quickly switch to machining different parts with simple program changes, cutting preparation time, and reducing delays.
Disadvantages of the CNC Turning Process
High Initial Cost
CNC turning machines are expensive to purchase and set up. This investment covers not only the cost of the machines but also the software and the cost of training or hiring skilled operators.
Programming Requirement
CNC turning is highly dependent on precise programming to control the operation of the equipment. Any error that occurs during the programming process may directly lead to machining defects in parts or even cause equipment failure.
Limited Shapes
CNC turning is mainly suited for cylindrical or round parts. For workpieces with complex internal cavities, deep concave features, or asymmetric, irregular geometric shapes, the processing capacity of this technology is often limited.
Slower for High Volume
For very large production runs, CNC turning can be slower and more costly compared to processes like die casting or injection molding.
What Are the Common Problems in the CNC Turning Process?
Tool Wear
Cutting tools will gradually wear out during continuous machining, especially when dealing with hard materials, and the wear is more significant. This kind of wear will directly lead to an increase in the surface roughness of the workpiece, a decrease in processing accuracy, and dimensional deviations. Regularly checking cutting tools and replacing worn ones is essential.
Dimensional Inaccuracy
During the numerical control machining process, programming deviations, tool calibration errors or incorrect equipment parameter Settings may all lead to part dimensions exceeding the design tolerances. Even small measurement errors can cause defects in components.
Surface Finish Issues
The quality of a part’s surface is influenced by cutting speed, feed rate, or tool geometry. By optimizing the system and carefully adjusting these parameters, surface finish and overall product quality can be improved.
CNC Turning vs. CNC Milling Comparison
Tolerance
| Process | Typical Tolerance |
| CNC Turning | ±0.005 mm to ±0.02 mm for general parts; ±0.001 mm to ±0.01 mm for high-precision parts |
| CNC Milling | ±0.01 mm to ±0.05 mm for general parts; ±0.002 mm to ±0.02 mm for high-precision parts |
Workpiece Movement
The main difference between CNC turning and CNC milling lies in the workpiece motion.
In CNC turning, the workpiece rotates while the cutting tool stays mostly still.
In CNC milling, the workpiece is fixed, and the cutting tool moves in different directions to cut the material.
Shape Capability
The flexibility of CNC turning and CNC milling varies greatly, especially in terms of part geometry.
CNC turning is best for cylindrical or round parts, such as shafts, pins, and rods, because the workpiece rotates while the tool cuts.
CNC milling is more versatile for complex and irregular shapes, flat surfaces, slots, and cavities, since the tool rotates and moves across the fixed workpiece.

Applications
CNC turning and CNC milling are applied in different ways based on their machining capabilities.
CNC turning is commonly used for producing rotational parts such as bolts, nuts, shafts, and bushings, making it ideal for industries like automotive, aerospace, and machinery.
In contrast, CNC milling is widely applied to create complex components with flat surfaces, slots, holes, and intricate 2D shapes, which are often required in mold making, electronics, medical devices, and precision engineering.
| Item | CNC turning | CNC Milling |
| Machining method | Workpiece rotation, tool movement | Tool rotation, workpiece fixed or moving |
| Applicable parts | Round, shaft parts | Flat surfaces, complex geometries |
| Tool type | Single-point turning, boring, threading tools, etc. | End mills, ball end mills, saw blade mills, etc. |
| Machining characteristics | Efficient machining of symmetrical bodies | Suitable for complex contours, cavities |
Key Applications of CNC Turning Parts
Automotive Industry
CNC turning is widely used to make engine shafts, gear parts, bushings, and fasteners. Automotive parts need high precision and smooth surfaces to ensure a proper fit and reliable performance in vehicles.

Aerospace Industry
Aircraft parts such as turbine shafts, landing gear pins, and hydraulic components are often made with CNC turning. CNC turning ensures tight tolerances and material strength.

Medical Industry
CNC turning produces surgical tools, orthopedic implants, and dental components. Medical components need to meet medical standards.
Electronics Industry
Connectors, pins, and housings used in electronic devices are often made using CNC turning.
Industrial Equipment
CNC turning is applied to produce rollers, valves, couplings, and machine shafts. Industrial components need durability and precision to perform well in heavy-duty industrial applications.

NOBLE: CNC Turning Services Provider
NOBLE offers professional CNC turning services tailored to meet the demands of modern industries. We have advanced CNC lathes to ensure the high precision, smooth surface, and consistent quality of each batch of products.
NOBLE can machine a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and composite materials etc., providing more flexibility for the application of parts.
NOBLE’s CNC turning services are suitable for both prototyping and mass production. NOBLE can ensure the timely delivery of high-quality parts, helping you bring your projects to market faster and more effectively.
FAQs of CNC Turning
What materials can be used in CNC turning?
CNC turning works with many materials, including metals such as steel, aluminum, and brass, as well as plastics and composites. The material is chosen based on the part’s use, strength needs, and surface finish requirements.
What are the advantages of CNC turning?
CNC turning offers high precision, consistent results, and a smooth surface finish. It allows automated production, handles complex cylindrical shapes, and works with a wide range of materials. It is suitable for both prototyping and large-scale manufacturing.
What are the limitations of CNC turning?
CNC turning is mainly suited for cylindrical or round parts. It is less efficient for producing complex internal shapes or intricate geometries. Very high production volumes may be slower and more costly compared to other methods like injection molding or stamping.
How do CNC turning and CNC milling differ?
CNC turning rotates the workpiece while the tool stays mostly still. It is best for cylindrical parts. CNC milling keeps the workpiece fixed while the tool moves in many directions. It works well for flat, angled, and complex 2D shapes.
How to ensure the high quality of parts during CNC turning?
High-quality parts require appropriate materials, precise programming, stable machine setup, and regular tool maintenance. Work with experienced CNC turning suppliers to ensure the precision, consistent tolerances, and finish of each part.












