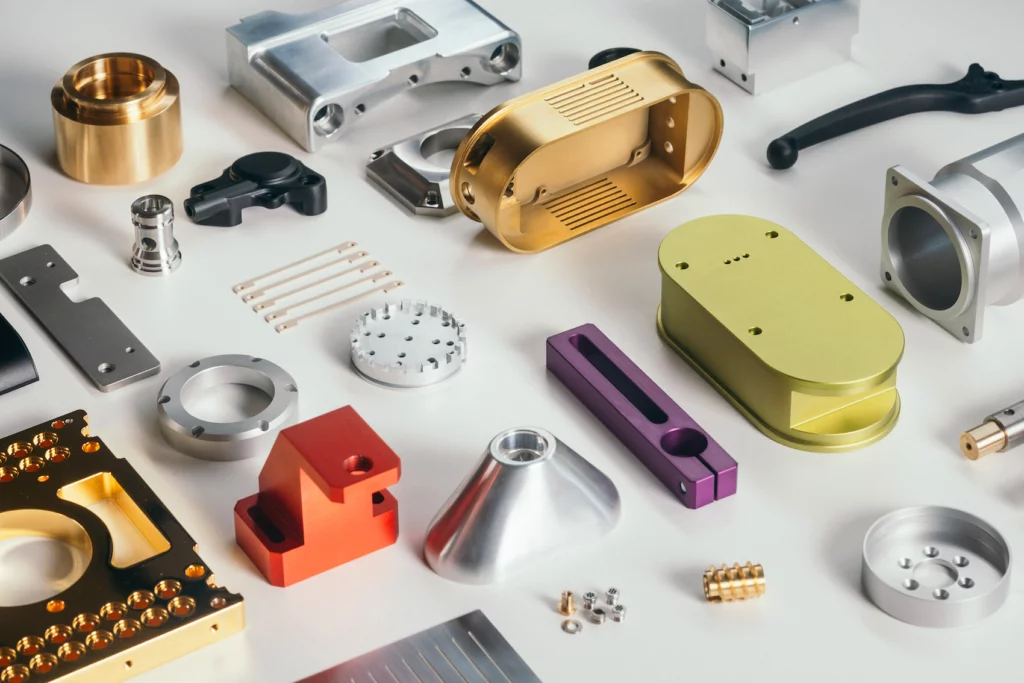
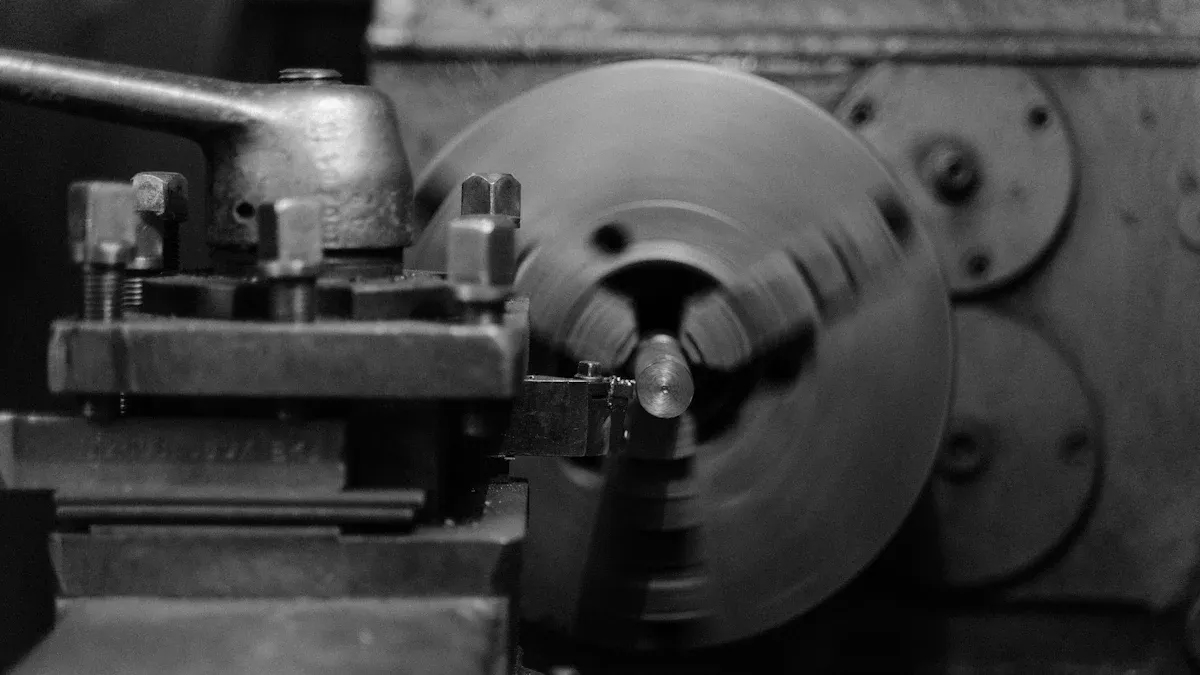
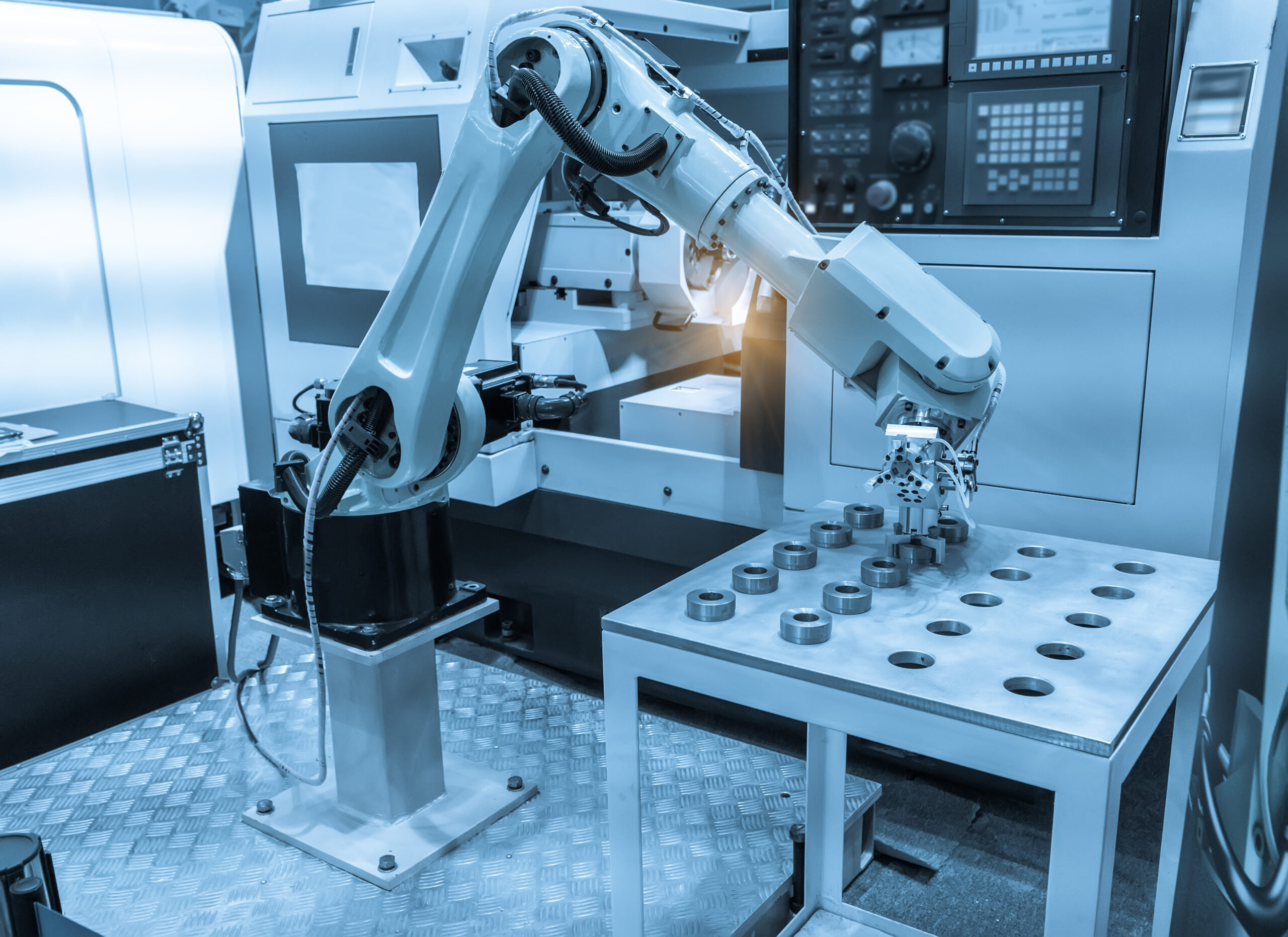
In the fast-paced world of today’s manufacturing, being able to produce top-notch, precise parts is a must if you want to stay ahead. And leading the charge in this industrial evolution is CNC machining, a groundbreaking technology that’s changing the way we think about making complex products.
So, what exactly is CNC? It stands for Computer Numerical Control. This cool process uses computer software and high-tech machines to automate the creation of all sorts of parts. Whether it’s complex aerospace pieces or the sleek cases for our latest gadgets, CNC machining has become essential for manufacturers and engineers alike.
In this guide, we’ll take a closer look at CNC machining—what it’s all about, the different ways it works, and the industries that rely on it to drive innovation and stay ahead of the curve.

Understanding CNC Machining
At its core, CNC machining is a computer-controlled manufacturing process that uses a variety of specialized tools and equipment to precisely shape, cut, and modify raw materials, such as metal, plastic, or wood, into desired components or parts.
The heart of a CNC machining system is the CNC machine, which is typically composed of a computer control unit, a tool carousel or magazine, and one or more axes of motion that allow the machine to move the cutting tool or the workpiece with incredible accuracy and repeatability.
The CNC machine is programmed using specialized software that translates the design specifications of a part or component into a series of numerical commands, which the machine then executes to create the desired shape or form. This level of automation and precision is what sets CNC machining apart from traditional, manually operated machining processes.

Key Features of CNC Machining
Precision and Accuracy
CNC machines are super precise—they can make parts with incredibly tight tolerances, often down to just a few thousandths of an inch. Thanks to advanced motion control systems and cutting tools, they can create complex shapes and intricate details with amazing repeatability.
Increased Efficiency
CNC machining speeds things up big time. By automating the manufacturing process it cuts down on the time and effort needed to make parts, meaning less manual work is involved. Plus, since CNC machines can run 24/7 with minimal downtime, they really boost productivity.
Versatility
CNC machines are incredibly flexible. They can handle all kinds of materials, from metals to plastics to composites, which makes them perfect for a ton of different applications. With interchangeable tools and customizable programming, you can create all sorts of parts and designs.
Improved Safety
Because CNC machining minimizes the need for operators to handle dangerous tools, it reduces the risk of injury. Many machines also come with cool safety features like automated tool changes and protective guarding, making the whole process safer overall.
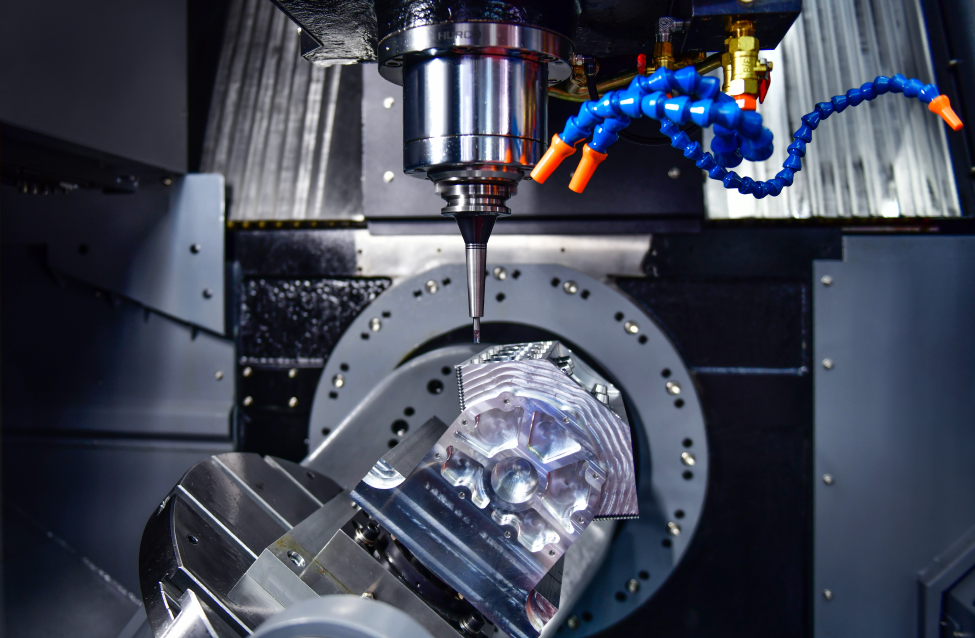
Common CNC Machining Processes
CNC Milling
Milling is all about using a rotating cutting tool to shave off material from a workpiece, shaping it into the part you need. CNC milling machines can be set up to do a ton of different jobs, like face milling, end milling, and pocket milling, just to name a few.
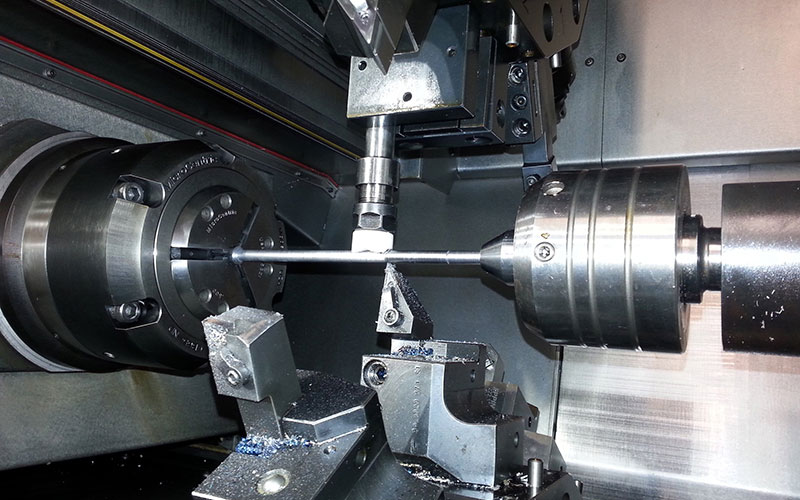
CNC Turning
Turning is a process where the workpiece rotates while the cutting tool stays still, shaping the part into something cylindrical or conical. CNC turning centers can handle a bunch of tasks, like threading, grooving, and parting, all with incredible precision and speed.
CNC Drilling
Drilling is the process of creating circular holes in a workpiece using a rotating drill bit. CNC drilling machines can handle all sorts of advanced drilling operations, including countersinking, tapping, and hole-making in different materials.
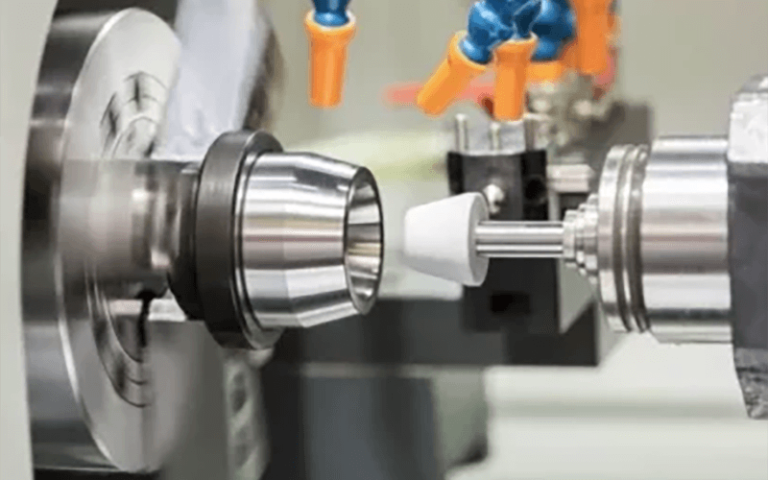
CNC Grinding
Grinding uses abrasive cutting tools to remove small amounts of material, giving the part a smooth, polished finish. CNC grinding machines are perfect for making high-precision parts like bearings, gears, and other critical components.
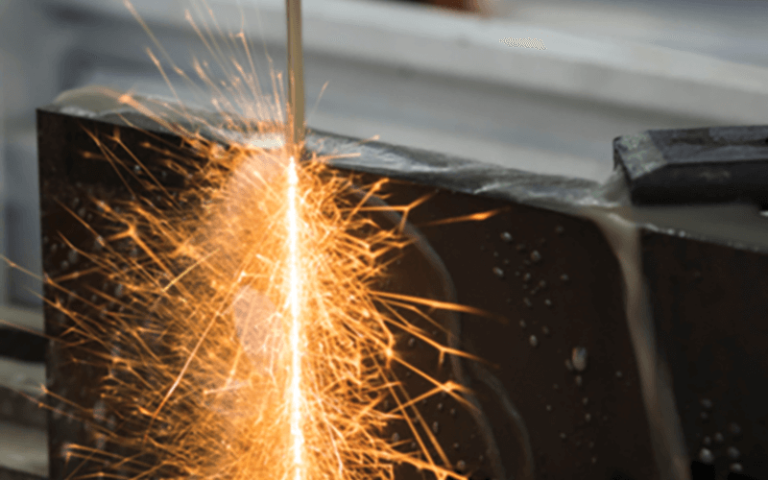

EDM-Cutting
EDM is a non-contact process that uses electrical discharges to remove material from a workpiece, allowing for the creation of complex shapes and features. CNC EDM machines can be programmed for different techniques, like wire EDM and sinker EDM.
These are just a few of the many CNC machining processes used in modern manufacturing, each with its own set of advantages and applications. Let me know if you’d like any tweaks!
Industries Benefiting from CNC Machining
Aerospace and Defense
The aerospace and defense industries depend on CNC machining to make crucial parts for aircraft, spacecraft, and military gear, where precision and reliability are absolutely essential. CNC machining is used to create complex parts like engine components, landing gear, and avionics housings.

Automotive
In the automotive industry, CNC machining is a key player, helping manufacturers make high-quality, custom parts for everything from engines and transmissions to body panels and interior trim. The speed, accuracy, and flexibility of CNC machining help manufacturers meet the ever-changing demands of the automotive market.

Medical and Surgical
The medical and surgical fields rely heavily on CNC machining for creating life-saving devices and implants. CNC machines are used to produce highly precise components for medical equipment, prosthetics, and surgical instruments, ensuring the highest standards of quality and safety.
Electronics and Telecommunications
CNC machining is essential in the electronics and telecommunications industries, where it’s used to create complex housings, enclosures, and components for our digital devices and infrastructure. The ability of CNC machines to produce tiny, precise parts with tight tolerances is key for making cutting-edge electronics and communication gear.

Energy and Industrial
CNC machining is also a huge asset in the energy and industrial sectors. It’s used to make parts for power generation equipment, industrial machinery, and other heavy-duty systems. The precision and durability of CNC-machined parts are vital for ensuring the reliable performance of critical industrial equipment.
As the examples above illustrate, the versatility and precision of CNC machining have made it an indispensable tool across a vast array of industries, driving innovation, improving product quality, and enhancing manufacturing efficiency.
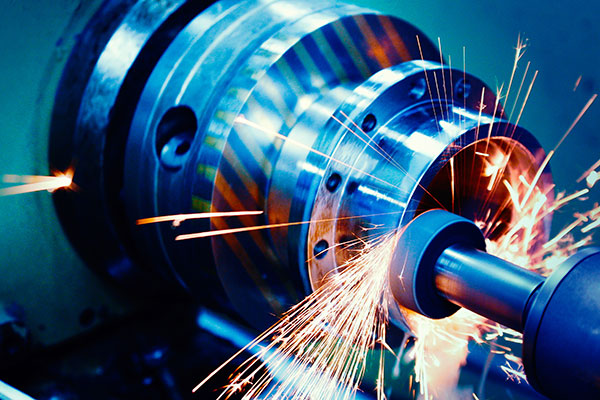

The Future of CNC Machining
As technology continues to evolve, the future of CNC machining holds exciting possibilities. Advancements in areas such as machine learning, additive manufacturing, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are poised to further enhance the capabilities and efficiency of CNC machining systems.

The integration of smart, connected CNC machines with advanced data analytics and predictive maintenance technologies will enable manufacturers to optimize their production processes, reduce downtime, and improve overall equipment effectiveness. Additionally, the convergence of CNC machining and additive manufacturing (3D printing) is opening up new frontiers in the design and fabrication of complex, customized parts and components.

As the world becomes increasingly interconnected and demand for high-quality, precision-engineered products continues to grow, the importance of CNC machining will only continue to rise. By staying at the forefront of these technological advancements, manufacturers and engineers can unlock new opportunities to drive innovation, boost productivity, and maintain a competitive edge in the global marketplace.







