The best CNC machining material is the one your project needs. You should think about a few things before you choose. These things are strength, hardness, toughness, machinability, cost, and how well it handles heat or chemicals. Dimensional tolerance and finish are important, too. One material might be good for one project but not for another. You might have a tricky design or need very exact sizes. Sometimes, you need to think about how many parts you need or if your manufacturer knows the material well. Metals like aluminum or steel are strong and last a long time. Plastics like ABS can save money for easy jobs. What you pick changes how well it works, how much it costs, and the quality.

Key Takeaways
Choose the right CNC machining material to match your project’s specific needs. At NOBLE, our engineering team helps you evaluate key factors like strength, heat resistance, cost, and precision to make the best choice. Metals such as aluminum and steel offer durability and longevity, but they require more complex machining—something NOBLE’s advanced production capabilities are well equipped to handle. For projects prioritizing ease of machining and cost efficiency, plastics like ABS and PEEK are ideal; they resist chemicals and are quicker to work with. By selecting materials that align with your part’s intended function, and working with NOBLE’s experienced coordinators and engineers, you can reduce time, save costs, and guarantee high-performance results—especially for challenging or critical applications.
Key Comparison Factors
Mechanical Properties
When you pick a CNC machining material, look at its mechanical properties. These are things like tensile strength, hardness, and toughness. These properties show how much force a material can withstand before it breaks. They also show how well it resists scratches and how it handles impacts. If you want to compare materials, here is their basic information in this table:
| Material Type | Specific Material/Grade | Tensile Yield Strength (MPa) | Hardness (HRB/HRC) | Toughness / Impact Resistance | Typical Applications |
| Metals | Aluminum 6061 | 200-400 | Medium | Good machinability, moderate toughness | General purpose, aircraft, automotive |
| Aluminum 7075 | 400-600 | Medium | High fatigue resistance, heat-treatable | Aerospace, sports equipment | |
| Stainless Steel 304 | 400-600 | Medium | High toughness, corrosion-resistant | Medical, marine, and food industry | |
| Stainless Steel 2205 Duplex | 400-600 | High | Very high toughness and corrosion resistance | Oil & gas, marine | |
| Mild Steel 1018 | 200-400 | Medium | Excellent toughness and weldability | General-purpose, machinery parts | |
| Alloy Steel 4140 | 200-400 | High | Good toughness and wear resistance | Industrial machinery, tooling | |
| Tool Steel D2 | 400-600 | Very High (above 50 HRC) | Exceptionally tough, wear-resistant | Cutting tools, dies | |
| Brass C36000 | 200-400 | Medium | Good machinability, corrosion-resistant | Mechanical parts, valves | |
| Plastics
|
ABS | 30-60 | Medium (50-90 HRB) | Moderate toughness, used in enclosures | Automotive, consumer products |
| Nylon | 60-100 | Medium | High toughness, mechanical parts | Automotive, fasteners | |
| PEEK | 60-100 | Medium | High toughness, chemical resistance |
Metals like stainless steel and tool steel are strong and hard. Plastics like ABS and PEEK are not as strong, but they can still be tough. They work well for many parts. If your part needs to hold heavy weights or take hits, pick a material with high tensile strength and toughness.
Machinability
Machinability means how easy it is to cut or drill a material. If a CNC machining material has high machinability, you can make parts faster. Your tools will also last longer. Aluminum and brass are some of the easiest metals to machine. Stainless steel and titanium are harder to cut. They can wear down tools quickly. Plastics are usually easy to machine, but heat can melt or change their shape.
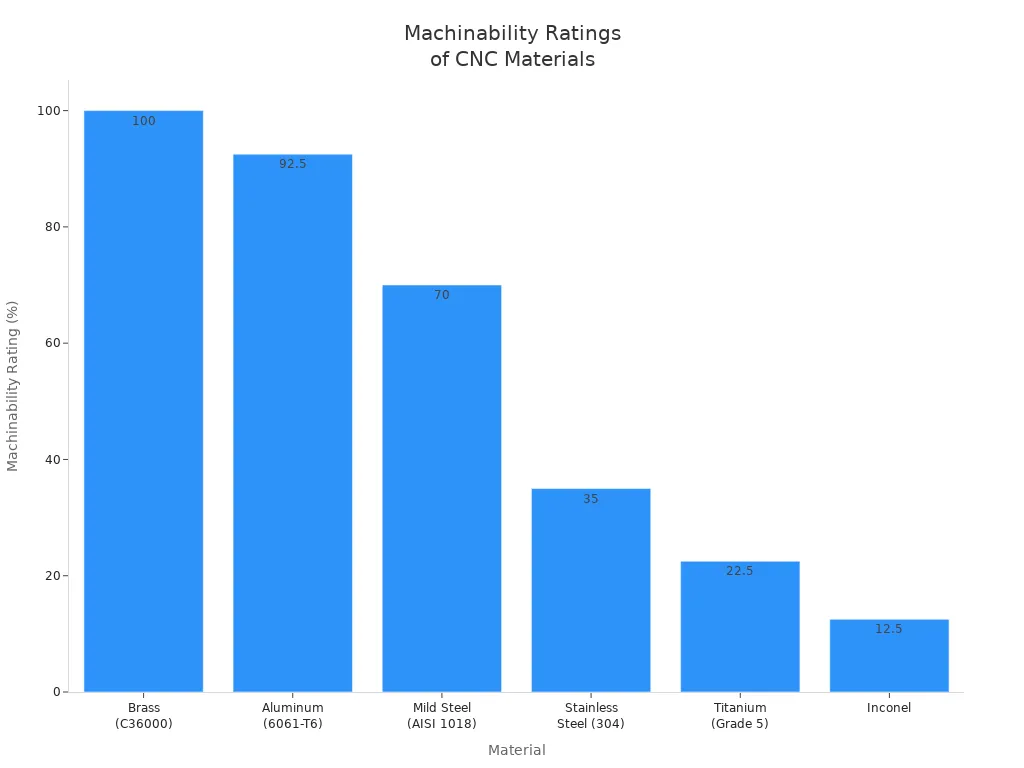
Cost
The price of your CNC machining material changes your project cost. Some materials, like aluminum 6061, are cheap and easy to find. Others, like PEEK or stainless steel, cost a lot more. The price also depends on how hard the material is to machine. It also depends on how much it wears down your tools.
With NOBLE’s expert engineering team and advanced machining capabilities, we help you choose the most cost-efficient material without compromising performance. Whether you need high strength, chemical resistance, or industry-specific compliance—like in aerospace or medical sectors—NOBLE delivers precision and value at every step.
Resistance
Resistance means how well a material stands up to heat, chemicals, or rust. If your part will get hot or touch harsh chemicals, you need a CNC machining material that can handle it. Metals like stainless steel work well in hot or wet places. Plastics like PEEK and PTFE resist many chemicals and do not rust. But they cannot take as much heat as metals. With its expert engineering team and deep material knowledge, NOBLE ensures the right material is chosen for every environment, no matter how extreme.
| Material | Max Operating Temperature (°C) | Corrosion Resistance | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Density (g/cm³) |
| Stainless Steel (304) | 870-925 | Good (can corrode in some environments) | 16.2 | 16.2 |
| PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) | 260 | Excellent | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) | 260 | Excellent | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide) | 200 | Excellent | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| PI (Polyimide) | 400 | Excellent | 3.0 | 3.0 |
Tolerance and Load
Tolerance means how close the finished part is to your design. Load means how much weight or force the part can take. Most CNC machining materials can reach tight tolerances. Some are better for very precise work.
| Tolerance Type | Tolerance Value (inches) | Tolerance Value (mm) | Notes |
| Standard Prototype & Production | ±0.005 | ±0.13 | Applies broadly to feature location, width, length, thickness, and diameter |
| Standard Precision or Production | ±0.002 | ±0.051 | Higher accuracy option available |
| Reamed Holes | ±0.0005 | ±0.0127 | Tight tolerance achievable on reamed holes |
| Feature Locations (same side) | ±0.002 | ±0.051 | Applies when features are machined on the same side of the part |
Metals Overview
Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum alloys are the material of choice when CNC machining for NOBLE. They are light and strong. They are also easy to cut and shape. Many industries use aluminum because it does not rust. It also looks nice when finished. Aluminum is easier to machine than most other metals. Look at this table:
| Aluminum Alloy | Machinability Characteristics | Comparison to Other Metals |
| 2011 | Great for fast, accurate work; tools last long | Easier than steel and titanium |
| 6061 | Simple to machine; strong | Easier to cut than steel and titanium |
| 6082 | Very strong; needs careful cutting | Still easier than steel and titanium |
| 7075/2024 | Very strong; wears tools faster | Not as easy as soft aluminum, but better than steel/titanium |
| MIC 6 | Very stable and smooth finish | Easier than many metals for molds and plates |
Aluminum alloys help you save time and money. They cut quickly and do not wear out tools like steel or titanium.
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel does not rust easily. It works well in wet or rough places. Here are some reasons to use stainless steel:
- Very strong for hard jobs
- Stays strong in hot or cold places
- Shiny look that does not rust
- Lasts a long time and needs little care
- It can be recycled and is good for the planet
The most used types for CNC machining are 303, 304, and 316. Grade 303 is easiest to cut. Grades 304 and 316 resist rust better.
Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is strong and not too expensive. You can pick low, medium, or high carbon types. Here is a quick chart:
| Steel Grade | 1018 | 1045 | 1060 |
| Carbon (%) | ~0.18 | ~0.45 | ~0.60 |
| Hardness (BHN) | ~126 | 163-190 | 163-190 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 440-790 | 570-700 | >900 |
| Machinability | Good | Good | Harder |
| Cost & Use | Cheap; used for shafts and rods | Medium price; used for gears and axles | More expensive; used for tools and blades |
Carbon steel is easier to cut than stainless steel. But it is not as easy as aluminum.
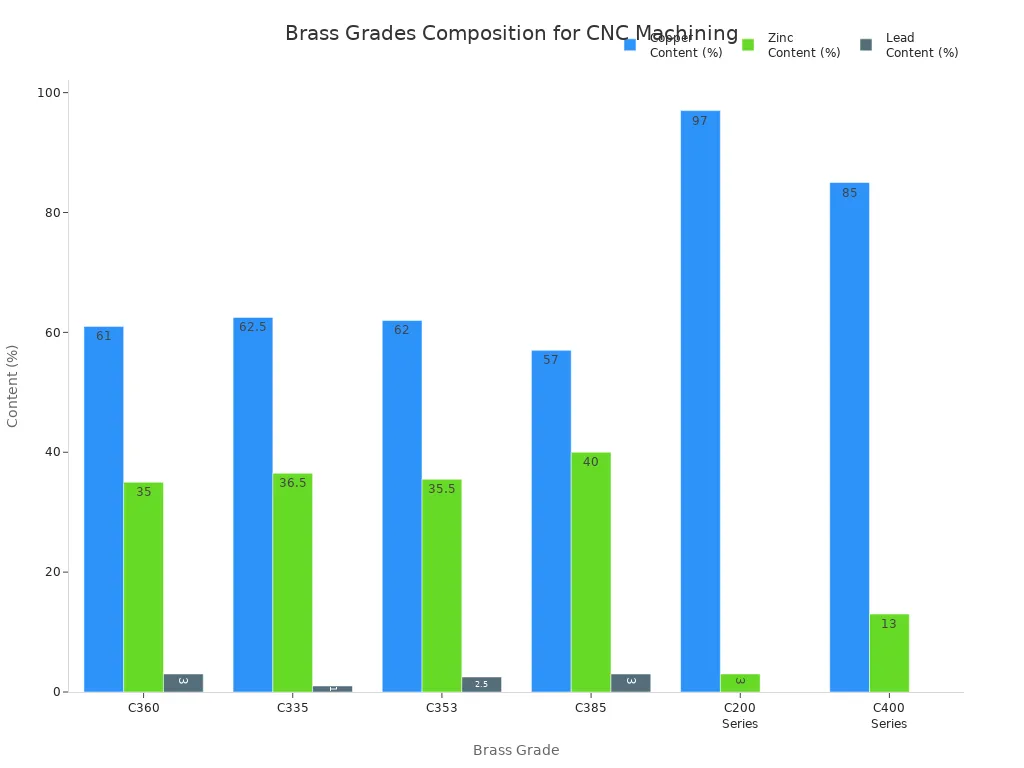
Brass and Copper
Brass and copper are good for parts that need to carry electricity. They also give a smooth finish. Brass, like C360, is very easy to cut. Copper is softer but carries electricity very well. Here is a chart with their main features:
| Brass Grade | C360 | C335 | C385 |
| Copper (%) | 61 | 62.5 | 57 |
| Zinc (%) | 35 | 36.5 | 40 |
| Lead (%) | 3 | 1 | 3 |
| Key Properties | Very easy to cut, strong | Easy to cut, okay strength | Super easy to cut, medium strength |
Titanium
Titanium is very strong for its weight and does not rust. It is used for planes or medical parts. It works well in tough places. But titanium is hard to cut. It gets hot and wears out tools fast. It also costs more than other metals. You need special tools and must go slowly when cutting titanium.
Plastics Overview

ABS
ABS is used a lot in CNC machining. It is tough and easy to work with. ABS can take hits and keep its shape well. It is good for parts that need to last but do not get very hot. You can use ABS for making prototypes, covers, and car parts. It costs less than many other plastics. ABS does not handle heat as well as polycarbonate. It is also not as strong as polycarbonate. But ABS is cheaper and still strong enough for most jobs. Pick ABS if you want strength, easy machining, and low cost for normal parts.
With NOBLE’s design expertise and streamlined production capabilities, we help clients get the most out of materials like ABS — balancing cost, strength, and manufacturability.
PPA
PPA is a high-performance plastic. It gives good chemical resistance and strength. PPA can take more heat than regular nylon. It works well in car engines, electrical parts, and machines. Use PPA when you need a plastic that will not break down in tough places.

Nylon
Nylon is strong and bends without breaking. You can use it for gears, bushings, and fasteners. Nylon does not wear out fast and can take shocks. It also handles chemicals and water better than many plastics. Nylon is a good pick if you need a part that can bend and not snap.

PEEK
PEEK is known for its strength and how it handles heat and chemicals. You can use PEEK in planes, medical tools, and car parts that must last. PEEK keeps its shape in hot water or steam. It does not soak up much water. Some types are safe for medical use. PEEK costs more than most plastics because it is special. But you get parts that last long and are made very exact.
| Category | Advantages of PEEK |
| Material | Great chemical resistance, does not soak up water, wears well, safe for the body |
| Process | Very accurate, repeatable, tight sizes, high melting point for faster machining |
Delrin
Delrin, also called acetal, is easy to machine and keeps its shape. You get strong parts that can take hits and heat. Delrin is good for gears, bearings, and moving machine parts. It is a top choice when you need plastic parts that are tough and exact.

Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate is very tough and almost never breaks. You can use it for clear and strong parts, like safety shields or light covers. Polycarbonate can take heat and sunlight, but it scratches more easily than some plastics. It costs more than ABS but gives you better strength and see-through parts.
| Property | ABS (Machined) | Polycarbonate (PC) (Machined) |
| Heat Deflection Temp | ~214°F (101°C) | ~280°F (138°C) |
| Tensile Strength | ~6,100 psi (42 MPa) | ~8,000 psi (55 MPa) |
| Elongation at Break | ~40% | ~50% |
CNC Machining Material Comparison
Metals vs. Plastics
When you pick a material, you must choose between metals and plastics. Each one has good and bad points. Metals like aluminum, steel, and titanium are very strong. They can hold heavy things and keep their shape. Plastics like ABS, Delrin, and PEEK are lighter. They are better at handling chemicals. NOBLE’s engineering team works closely with clients to select the ideal material for each project, ensuring the right balance of performance, durability, and cost. Look at the table below to see how they are different:
| Aspect | Metals (Aluminum, Steel, Titanium) | Plastics (ABS, Nylon, PEEK) |
| Material Cost | Costs more for each pound; special metals cost even more | Most plastics cost less; some special plastics cost more |
| Strength & Rigidity | Very strong and stiff; good for heavy things | Not as strong; light; can bend; good for stopping electricity |
| Machinability | Needs tough machines and tools; goes slow; needs coolant | Easier and faster to cut; can melt from heat; needs sharp tools |
| Tolerances | Can be made very exact (±0.001″ to ±0.005″) | Not as exact (±0.002″ to ±0.010″); can change with heat or water |
| Machining Time | Takes longer because it is hard and wears out tools | Faster, but heat can ruin parts |
| Post-Processing | May need extra steps like smoothing or coating | Usually needs little finishing; sometimes needs heat treatment |
Application Fit
You should always pick a CNC machining material that fits your project. Not sure what material is right for your project?NOBLE’s team of experts can help! We’ll match the right material to your design, performance, and production needs – saving time and minimizing costly mistakes. Here are some examples to help you choose:
- High-Strength Parts:
Pick metals like steel or titanium if your part must hold a lot of weight or take hard hits. These metals stay strong and last longer. - Lightweight Needs:
Use aluminum or plastics like nylon if you want your part to be light. Aluminum is strong and light. Plastics are good for covers or parts that do not need to be strong. - Chemical Exposure:
Choose plastics like PEEK or PTFE if your part will touch strong chemicals. These plastics do not rust or break down. Stainless steel is also good in wet or harsh places. - Cost-Sensitive Projects:
Use plastics like ABS or Delrin for cheap and simple parts. Aluminum 6061 is a good metal if you want to save money but still need some strength. - Tight Tolerances:
Pick metals if you need very exact parts. Metals keep their shape better and can be made more exact. Plastics can change size with heat or water. - Electrical Insulation:
Use plastics if your part should not carry electricity. Plastics like nylon and PEEK stop electricity and keep electronics safe.
Here is a checklist to help you choose:
- How strong does your part need to be?
- Will your part get hot, touch chemicals, or get wet?
- How exact do your parts’ sizes need to be?
- Do you need to save weight or money?
- Does your part need to stop electricity?
When you answer these questions, you can pick the best CNC machining material for your project. If you need any help, please feel free to contact us, NOBLE’s excellent team of engineers can give you the best answer!
Choosing the Right Material
Decision Steps
You can follow a simple process to pick the best material for your project. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Define what your part needs. Think about strength, heat, electricity, and the place where you will use the part.
- Make a list of materials that fit these needs and match your design.
- Compare these materials. Look at how easy they are to machine, how much they cost, and if you can get them quickly.
- Think about the job your part will do. Check if it needs to be light, strong, or work in tough places.
- Look at how the material acts during machining. Some materials wear out tools fast or need slow speeds.
- Plan for the finish. Make sure the material works with any surface treatment you want.
- Check the main features of each material. Look at strength, hardness, how much it bends, and how it handles heat or electricity.
- Think about how easy it is to buy the material. Check the price, how long it takes to get, and if it is easy to find.
Expert Tips
- Pick strong metals like stainless steel or alloy steel for parts that take a lot of stress or move often.
- Use corrosion-resistant metals for wet or chemical environments. Choose titanium or PEEK for high heat or harsh spots.
- Start with easy and cheap materials like aluminum or ABS for test parts. Use special materials like titanium or PEEK for final parts that need top performance.
- Match your choice to your industry. Medical parts need safe and rust-free materials. Planes need light and strong materials. Cars need tough and low-cost options.
- Use the right tools and speeds. Metals need good cooling and strong tools. Plastics need sharp tools and slow speeds to stop melting or bending.
If your project is complex or very important, NOBLE’s team of engineers and materials experts can provide trusted guidance to ensure your project starts right and stays on track. They can help you avoid mistakes and save time.

Why Choose NOBLE for CNC Machining Services?
At NOBLE, we combine precision engineering, advanced design expertise, and seamless project coordination to deliver exceptional CNC machining solutions. Our team of highly skilled engineers and technicians works across a wide range of materials — from metals like titanium and aluminum to performance plastics like PEEK and Delrin — ensuring every part meets exact specifications and performance demands.
Our capabilities include:
- Advanced Design & Prototyping
Rapid, high-accuracy prototyping supported by CAD/CAM integration and DFM (Design for Manufacturability) insights. - High-Precision Machining
3-, 4-, and 5-axis CNC machining with tight tolerances and excellent surface finish quality. - Material Expertise
In-depth knowledge of metals and plastics, helping clients choose the best material for strength, cost, heat resistance, or chemical durability. - Scalable Production
From one-off prototypes to full-scale production runs, NOBLE ensures consistent quality and on-time delivery. - Cross-Functional Project Support
Our integrated team bridges engineering, production, and quality control — optimizing timelines and minimizing errors.
NOBLE is not just a manufacturer — we are your strategic partner in precision machining.
FAQs of CNC Machining Materials
What is the easiest material to machine with CNC?
Aluminum is the easiest material for CNC machining. You can cut it quickly and get a smooth finish. Your tools last longer with aluminum. Brass is also easy to machine and gives you good results.
How do you know if a material is strong enough?
You should check the tensile strength and hardness of the material. These numbers show how much force the material can take before it breaks or bends. Always match the strength to your part’s job.
Can you use plastics for high-precision parts?
You can use plastics for many precise parts. Some plastics, like Delrin, hold tight tolerances. Plastics may change shape with heat or moisture, so check if your part needs to stay exact in tough conditions.
What if you need a part that resists chemicals?
Pick materials like PEEK, PTFE, or stainless steel. These materials stand up to harsh chemicals and do not rust. Always check the chemical resistance chart for your chosen material.










