Introduction
You’ve designed a new medical device. It could be a surgical tool or a component intended for use by patients. The design looks great on screen. But there’s a big problem. At the moment, it’s just not worth it to make a steel injection mould. The lead time of several months is also too long. You need real, functional parts for testing and clinical evaluations now. So, how can we bridge this gap?
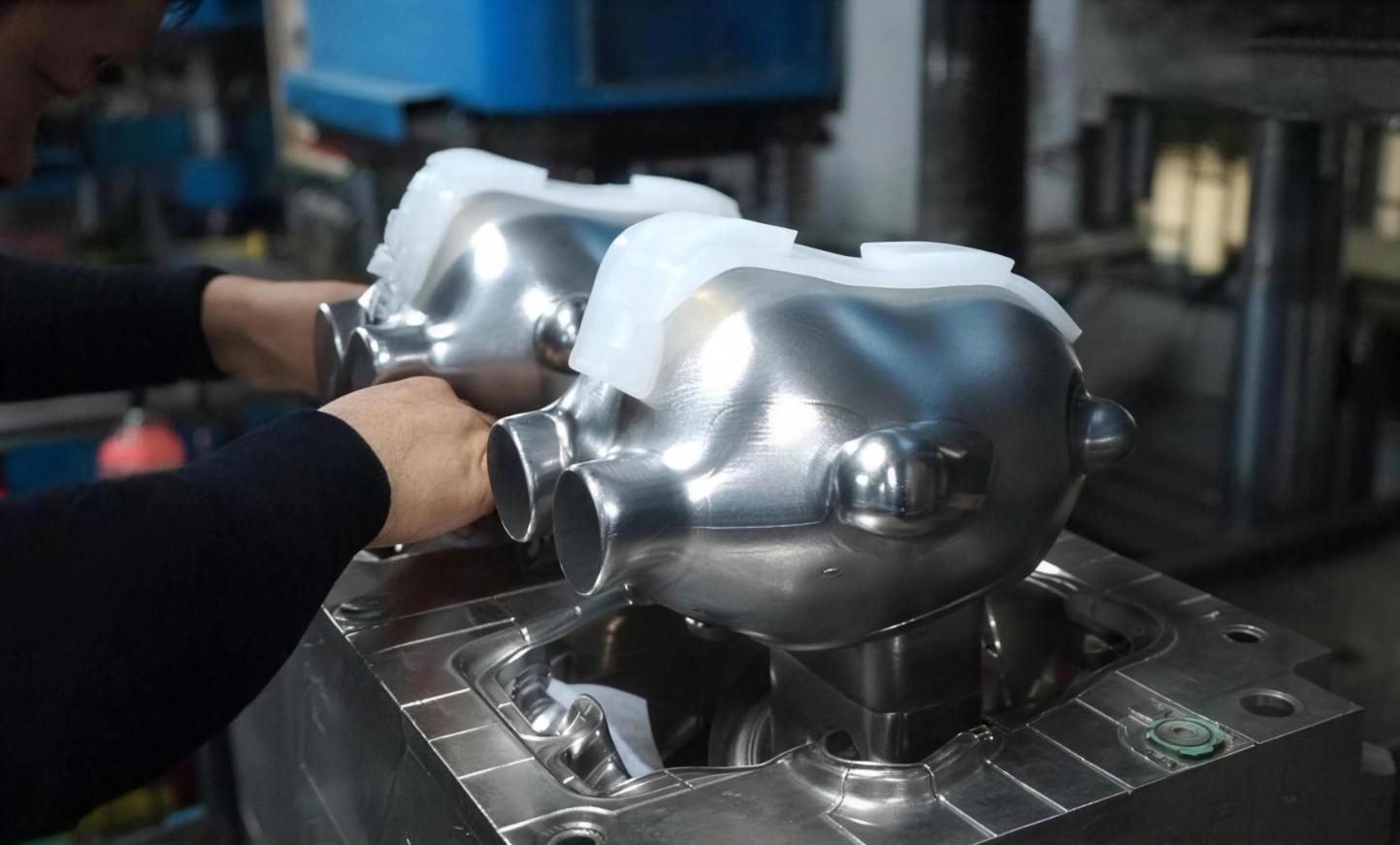

The answer is often a specific process: vacuum casting. This is a smart, cost-effective way to get medical devices from prototyping to full-scale production.
Here’s what you’ll learn. We’ll explain exactly how the vacuum casting process works. We’ll go through its unique selling points for medical applications, from how well it works with other materials to how it can create complex shapes. We’ll give you all the info you need to decide if it’s right for your project. And finally, we’ll compare it to the main options, so you can make an informed choice.
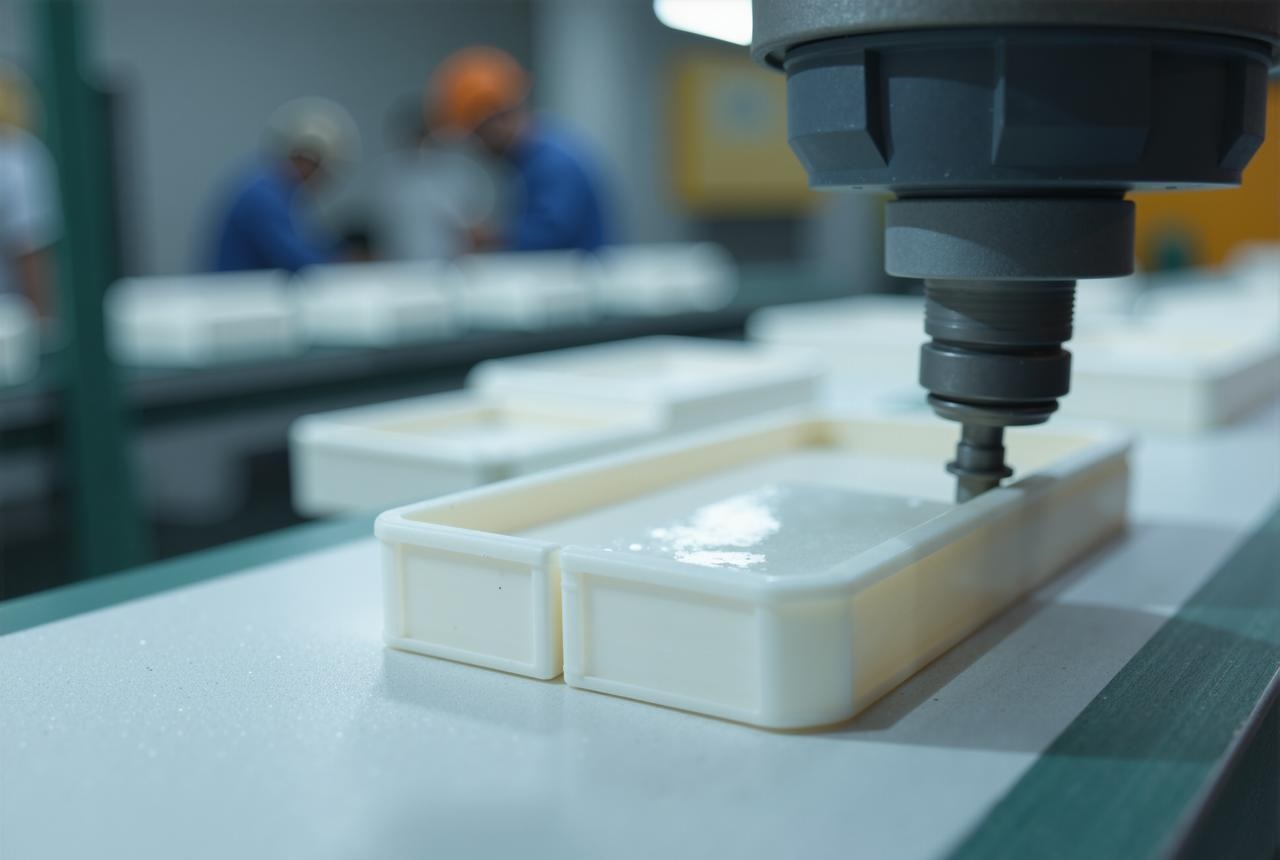

How Vacuum Casting Works?
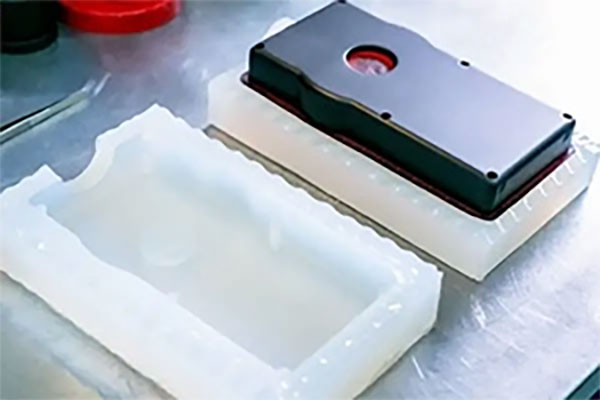
So, vacuum casting for medical devices is pretty much how we make high-quality, flexible silicone moulds from a master model. Then, we use vacuum pressure to cast parts with medical-grade materials, making sure there are no air bubbles. This process is perfect for creating prototypes or small batches of detailed, precise components, like patient-specific surgical guides or device housings.
Here’s how the vacuum casting process breaks down into five key stages, from your initial digital design to the final part:
Master Pattern Creation
We’ll create a high-resolution master pattern (positive model) of your medical parts design, often using 3D printing technologies like Stereolithography (SLA) for its excellent surface finish and detail.
The quality of the finished parts depends on the quality of the pattern. Any surface flaw or inaccuracy on the master will be replicated.
Silicone Mold Making
The master pattern goes in a box and you pour liquid silicone over it. Once the silicone block is set, it’s just a case of cutting it open and removing the master.
The idea is to create a flexible, detailed negative mould that can capture even the most complex undercuts of your design.
Degassing (The “Vacuum”)
The liquid casting resin is mixed and then put in a vacuum chamber to get rid of any air bubbles. You can also place the silicone mould under vacuum before casting.
This is really important for medical parts because it gets rid of any defects (porosity) that could mess up the part’s structural integrity or create surfaces where bacteria could grow.
Casting
The liquid resin, which has been degassed, is carefully poured into the silicone mould. The whole setup is usually kept under vacuum or at low pressure.
The vacuum makes sure the resin fills every nook and cranny of the mould properly and all the way through, so there’s no air trapped in there.
Curing & Demolding
The resin is left to cure and harden. Once the silicone mould has been cured, it can be peeled away from the new plastic part.
The idea is that the silicone’s flexible, so you can take it off without damaging the product. Then, your medical parts might get some post-processing like cleaning, support removal, or a bit of sanding.
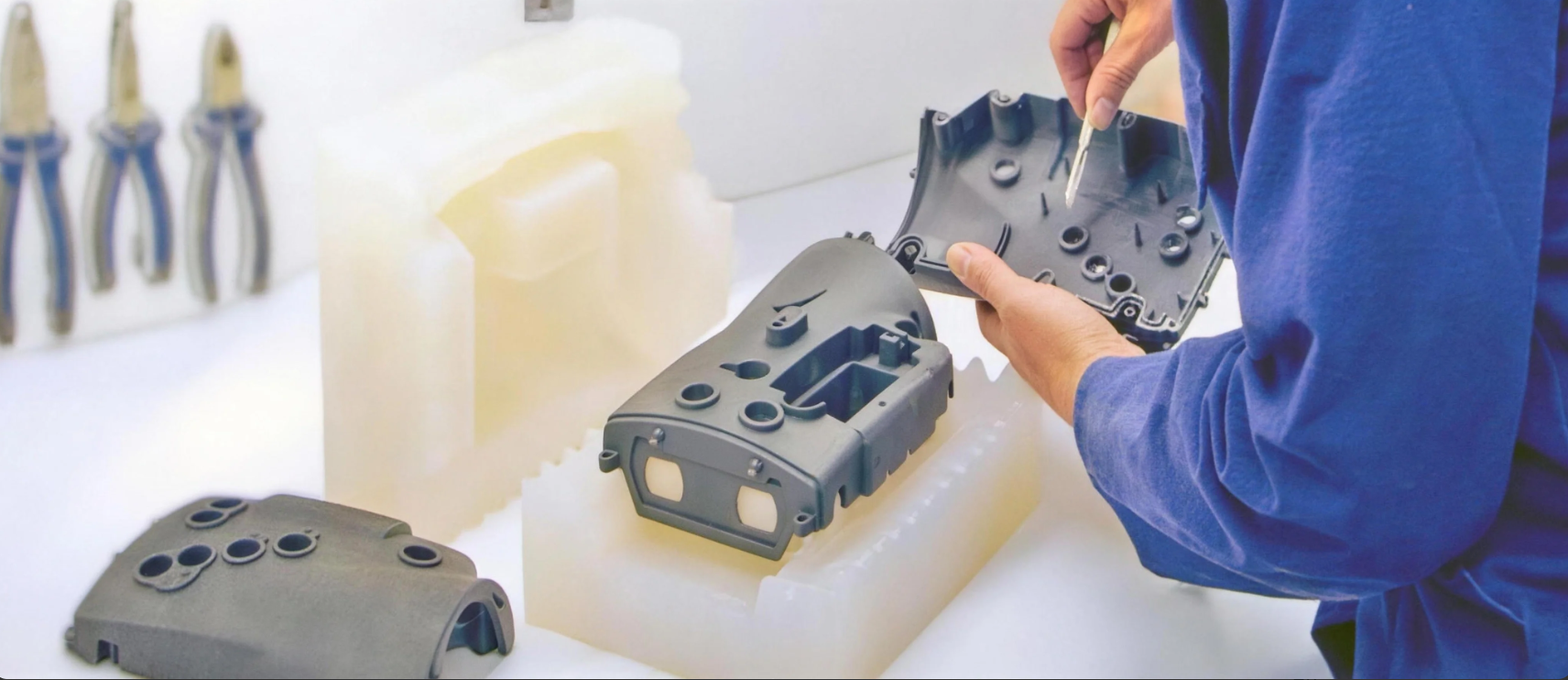

Why Vacuum Casting is a Strategic Powerhouse for Med-Tech
For medical device innovators, vacuum casting is more than just a way to make prototypes – it’s a key part of the strategy that speeds up development, reduces risk, and helps get products to market more quickly.
Unmatched Speed and Cost-Efficiency for Low Volumes
Vacuum casting is a really powerful tool because it changes the whole low-volume production economic model.
Lead Time and Cost vs. Injection Molding
When you’re dealing with batches of 10-500 units, vacuum casting sidesteps the biggest hurdle: the use of hard steel tooling. An injection mould can take anywhere between 8 and 16 weeks and cost tens of thousands of dollars to produce, whereas a vacuum-cast silicone mould will be ready in 1 to 3 days at a fraction of the cost. While the per-part cost in vacuum casting is higher, the near-elimination of upfront investment makes the total project cost for low volumes a lot lower.
The Bridge Production Concept
This economic profile makes it the ultimate “bridge production” method. It lets you supply top-quality, functional parts for clinical trials, market testing or early surgical use without the risk of capital outlay or delay of final tooling. You can validate your design, gather user feedback, and even generate early revenue while you wait for regulatory clearance or commit to high-volume production tooling.
Medical-Grade Material Performance
Vacuum casting isn’t just about shape; it’s about creating functional, compliant prototypes.
Biocompatible and Sterilizable Resins
Modern vacuum casting systems offer a wide range of biocompatible resins that meet standards like ISO 10993 and USP Class VI. You can sterilise these materials using standard methods (EtO, gamma, autoclave for specific grades), which makes the medical parts suitable for real-world functional testing and short-term use.
Mimicking Final Production Materials
These materials are just like the ones used for final production. The resins that are available are designed to closely copy the mechanical, thermal and chemical properties of the final production thermoplastics like Polypropylene (PP), ABS, Polycarbonate (PC) and flexible TPEs/TPUs. This means you can do accurate performance testing in simulated use conditions.
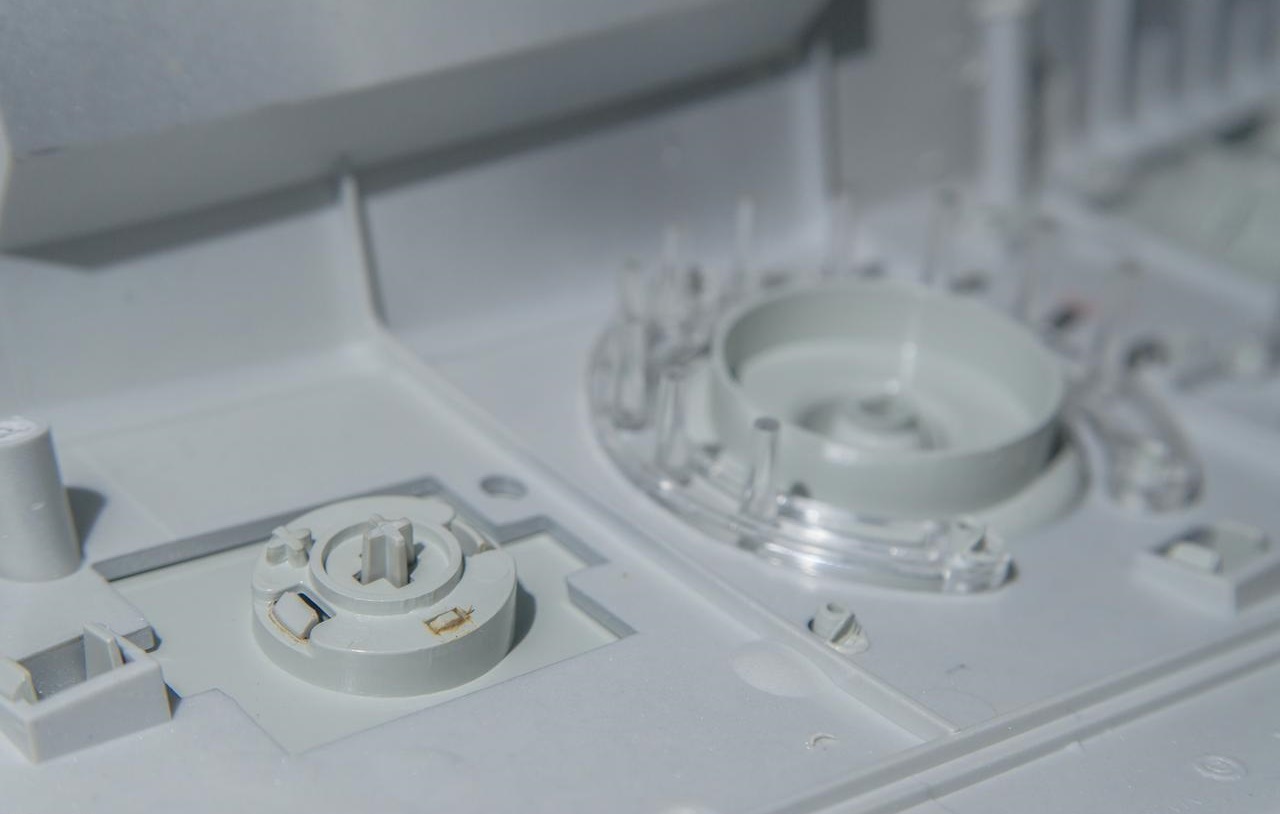

High Fidelity and Zero-Defect Quality
When it comes to medical devices, quality is non-negotiable, and vacuum casting is all about precision.
Surface Finish and Detail
vacuum casting is based on the quality of the 3D-printed master pattern. Using high-resolution technologies like SLA or DLP, it can replicate features down to ~30 microns with excellent, injection-molding-like surface finishes, often requiring no post-processing for visual or fit-check prototypes.
The Non-Negotiable Vacuum
It’s the degassing step that makes it more than just a casting method – it’s a precision medical process. If you get rid of all the air bubbles in the resin before and during casting, you’ll end up with parts that are fully dense and have no voids. This is really important for things like fluid-handling components, airtight seals, transparent parts for visualisation, and any part where internal porosity might affect its structural integrity or sterility.
Enabling the Regulatory Pathway
Vacuum casting’s biggest selling point is that it can help you de-risk and speed up getting to market.
Parts for Validation and Trials
Vacuum-cast parts are good enough to use in design validation testing, animal studies (as long as there’s the right biocompatibility paperwork) and even early human clinical trials. This means you can make improvements to the design bit by bit using medical parts that are the same as the final product, which will make your regulatory submission stronger.
The Critical Partner
The quality of the part depends on the system that makes it. It’s really important to team up with a supplier that’s got a certified Quality Management System (QMS), like ISO 13485. This makes sure you can follow the materials and processes from start to finish, and that you have the right documentation for your regulatory Technical File.
Key Medical Device Applications & Use Cases
As well as the tech side of things, vacuum casting is really important because it helps to make huge progress in medical device innovation. It’s the go-to way to turn early designs into real, top-notch assets that take a product from concept to market.
Here are the main medical device applications where vacuum casting really shines.
Functional Prototypes for Testing
This is the main application where vacuum casting comes into its own, producing prototypes that look far better than the models you can just see.
Form, Fit, and Function Testing
We put our medical products through a few tests to make sure they’re form, fit and function-wise sound. We can use medical-grade and engineering-grade resins to test prototypes for mechanical strength, chemical resistance and durability under simulated use. You can put the parts together to make working mechanisms to test how they work.
Ergonomic & User Studies
Ergonomic and User Studies The surface finish is great, so surgeons, clinicians and patients can use it to see how easy it is to use in studies, which is really important for human factors engineering.
Rapid Design Iterations
Fast design changes If a test shows that your medical part design needs to be changed, a new silicone mould can be made from a revised master in a few days. This means that changes can be made quickly and cheaply without wasting money on hard tooling.
Parts for Regulatory Submission & Clinical Use
Vacuum casting is perfect for clinical and regulatory steps because it provides the quality and traceability needed.
First-in-Human Trials
They’re made from biocompatible (ISO 10993) and sterilisable resins, so the vacuum-cast parts are great for producing limited batches of devices when you’re trying out the idea or doing a pilot clinical study.
Surgical Planning & Training Models
Surgeons use highly accurate, patient-specific anatomical models (cast in materials that mimic tissue or bone) to plan complex procedures, reducing operative risk and time.
Custom Surgical Guides/Jigs
For custom instrumentation, vacuum casting is great for making sterilisable, rigid guides that are used in the operating room to direct bone cuts or implant placement, because it’s precise and fast.
End-Use Components in Low-Volume Devices
For some market segments, vacuum casting moves from being a way to make prototypes to a proper way to manufacture stuff.
Niche Diagnostic Device Housings
For high-value, low-volume diagnostic equipment (e.g. for rare diseases), vacuum casting can produce the final housing with the required aesthetics, finish and material properties without the prohibitive cost of an injection mould.
Components for Robotic Surgery Systems
It’s perfect for making custom grips, covers, or non-structural parts for complex robotic systems where you’re producing hundreds, not millions.
Wearable Medical Sensors
If you’re working on wearable patches or monitor housings that need to be flexible or see-through, then vacuum casting with special silicones or clear resins lets you make small batches that match the final material specs.
The Alternatives: A Comparative Analysis
Picking a manufacturing method isn’t a matter of guesswork. There are options available. You’ve got to match the tool to the task.
Have you thought about the other options? Each one has a different job at a different time on your project. 3D printing is perfect for fast, complex projects. Injection moulding is for the final mass production stage. Vacuum casting is a great option for that middle ground. Let’s compare them directly.
| Method | Best For | Volume Range | Key Advantages | Key Limitations |
| Vacuum Casting | Working prototypes, pre-production batches. | 10 – 50 parts | Great surface finish, medical-grade resins, cheap molds for small runs. | Silicone wears out. Not for huge numbers. |
| Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) | One-off models, patient-specific guides, complex shapes. | 1 – 10 parts | Total design freedom. Fastest for a single piece. | Layer lines on surface. Can be weaker. Material limits. |
| Injection Molding | Mass-producing the final product. | 1,000+ parts | Cheapest per part at volume. Every plastic available. Strong. | Massive upfront cost for the steel mold. Very slow to start. |
| Die Casting (Metal) | High-volume metal components. | 1,000+ parts | Makes strong, precise metal parts fast. | Huge tooling cost. Only for certain metals. |
Additive Manufacturing: The Direct Competitor
3D printing fights for the same early-stage work. The choice depends on the printer type.
- You can use SLA/DLP for a quick look. Need a smooth, detailed model for a show? This is it.
- Just use SLS/MJF for the function. Need a tough plastic part to test? These printers make stronger, more reliable pieces.
- Use DMLS for metal. Need a custom bone implant or a tough tool? This prints directly onto metal.

The End Goal: Injection Molding and Die Casting
Forget prototypes. These are for the final product.
When it comes to plastic devices, injection moulding is like the finishing line. You use it when the design is perfect and you need to make a million units. It’s only then that the cost starts to make sense. Die casting is the same for metal. It’s for the final housing of a monitor or a surgical hand tool when you’re building by the thousands.
The path is clear. Start with 3D printing for ideas. Then move on to vacuum casting for real-world testing. Use injection or die molding for the final, market-ready device.

Decision Framework: How to Choose the Right Process
Picking the right process saves you time and money. If you make the wrong choice, you’ll end up with delays and wasted budget. Just follow a simple logic based on four key factors.
The four main things to think about when making a decision.
- Volume & Timeline: How many medical units are needed? When do you need the first one? We can’t do injection molding because there’s a deadline next week.
- Material & Performance:Is it necessary for the part to be sterile? Does it need to be as flexible as silicone or as rigid as polycarbonate? The material you need to use will determine the processes you can use.
- Design Complexity:Are there any deep undercuts or textured surfaces? There are loads of ways to make a simple block. A complex housing situation can make things tricky.
- Here’s the budget: What’s the total for the project? But what’s even more important is how it’s split. Can you afford a $50,000 steel mould (injection moulding) for a cheaper per-part cost, or do you need a $500 silicone mould (vacuum casting) with a higher per-part price?
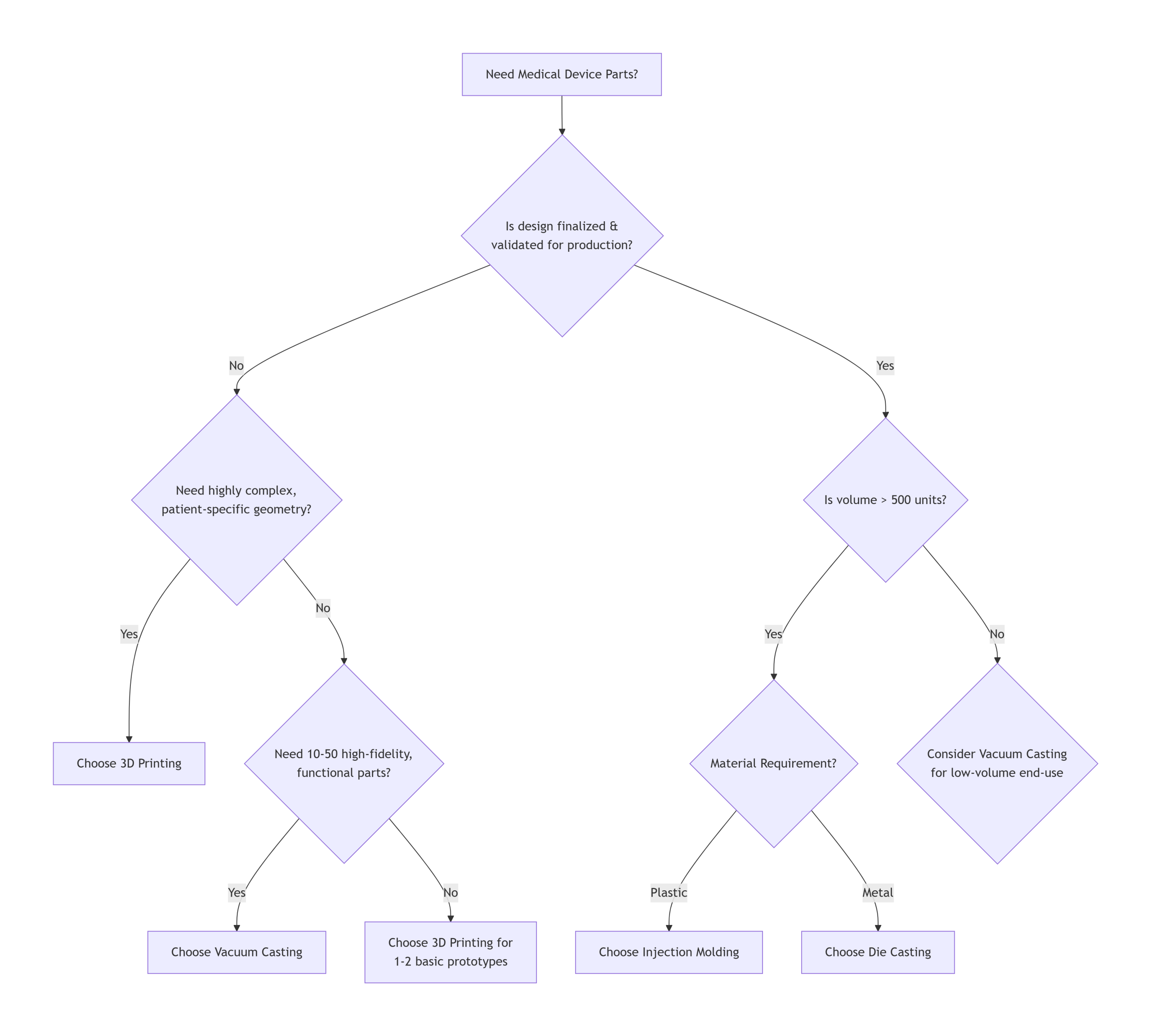
Picking the right process saves you time and money. If you make the wrong choice, you’ll end up with delays and wasted budget. Just follow a simple logic based on four key factors. Here’s a simple decision tree put together by NOBLE engineers that might help.
This framework helps you to separate the wheat from the chaff. It makes you match your project needs with the process to solve them. The idea is to keep things simple and not go overboard when it comes to the manufacturing process.
NOBLE: Your Trusted Partner in Medical Device Manufacturing
Here at NOBLE, we know that the journey from a concept to a cleared medical device can be challenging. Prototypes don’t always work. Timelines slip. Budgets are tight. We’re here to solve these specific problems.
We’re the ones who help you get your designs out there and into the hands of customers. Our job is to make sure your project is safe and on track, and to get it done faster by using the right tools at the right time.
Our process is based on a certified foundation. We’re certified to both ISO 9001 and ISO 13485 standards. This isn’t just a certificate for the wall. So, every project – from one prototype to a clinical batch – runs under a Quality Management System that’s certified for medical use. You’ll get full traceability and controlled documentation for your technical file.

Why should you choose to work with NOBLE?
- End-to-End Guidance: We’ll start by looking at your first CAD model to see if it’s easy to manufacture. We’ll be with you every step of the way, from picking the materials to making the prototypes and getting them into production. We’ll take care of the whole journey.
- Certified Materials for Medical Use: Our vacuum casting uses resins that have been tested to ISO 10993 standards and are biocompatible according to USP Class VI. The parts we make are great for testing and meet the standards for clinical trials.
- The right tool for every stage: Vacuum casting is one of our specialities, and we can produce 10-50 high-fidelity parts. When your project grows, we’ll make the move to injection molding for mass production or 3D printing for those tricky one-offs. We’ve got all the tools we need.
- A Strategic Engineering Partner: We’re like your R&D team’s right-hand man. We’re here to help you reduce technical risks, keep your project costs in check, and make sure your device is built to perform safely.
The next step is a chat. Get in touch with our engineering team today for a confidential chat and quote. So, let’s chat about how to make your design a reality and make it work.
FAQ
What’s the main benefit of using vacuum casting over 3D printing for medical prototypes?
They’re both great for prototyping, but vacuum casting usually makes parts with a better surface finish, isotropic mechanical properties, and true thermoplastic-like performance. It’s perfect for when you need a small batch (10-50 units) of high-quality, functional parts for design validation, ergonomic testing, or early regulatory submissions.
How your ISO 13485 certification can help out with my project?
Our ISO 13485 certification is all about medical devices. Basically, this means that every step of the process is done under a Quality Management System that’s been certified. So, everything from reviewing orders and handling materials to production, inspection, and documentation is done under one certified system. This gives you the audit trails, lot traceability and controlled documentation you need for your own regulatory submissions (FDA, CE) and makes sure you get the highest level of quality and safety.
What info do you need to get a quote?
To give you a quote that’s both fast and accurate, we usually need:
- 3D CAD model (STEP or IGES format preferred).
- Desired material specifications (e.g., rigidity, color, biocompatibility).
- Estimated quantity required.
- Any critical tolerances or post-processing needs (e.g., painting, assembly).
What if my project needs something more than vacuum casting can offer?
We’re your strategic manufacturing partner, so we can help you with your transition. Once your device design has been approved and production volumes are up, we can smoothly transition to injection molding for high-volume production. This ensures your design integrity is maintained and your product gets to market faster.








