What is 5-Axis CNC Machining?
5-Axis machining is an advanced manufacturing technology in which the cutting tools can move synchronously on five independent axes, thus completing the machining of workpieces with highly complex geometries in a single clamping.
This technology combines three linear axes (X, Y, and Z) with two rotational axes (such as A and B, or B and C) to achieve machining from multiple angles. It removes the limits of traditional machining, which often requires several setups and manual adjustments of the workpiece. This capability not only improves machining accuracy and boosts production efficiency but also greatly reduces the overall manufacturing time. Because of these benefits, it is widely used in demanding industries such as aerospace, medical devices, and oil and gas.
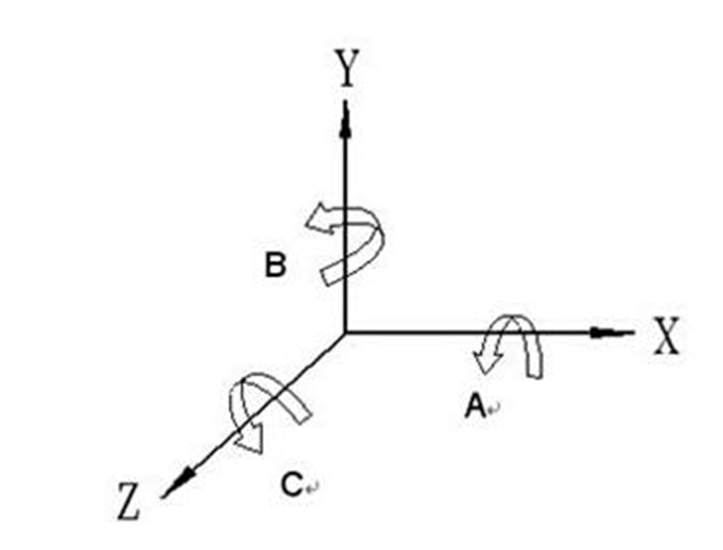
How Does 5-Axis CNC Machining Work?
Multi-Axis Linkage
The core of multi-axis linkage is that the numerical control system of the machine tool can precisely control the five axes to perform coordinated interpolation movements simultaneously.
This enables the cutting tool to move along complex spatial trajectories and approach the workpiece from any direction, thereby forming a geometric shape with a complex curved surface in one go.
Tool Control
To ensure accuracy, the 5-axis system is equipped with a tool tip control function. It can compensate in real time for the changes in the position of the tool tip caused by the movement of the rotating axis, always ensuring that the tool tip moves along the programmed path.

Optimize Cutting Tools
Through two rotating axes, the Angle of the cutting tool relative to the workpiece can be dynamically adjusted during the machining. This not only enhances the efficiency and lifespan of the cutting tools but also ingeniously avoids the interference between the tool holder and the workpiece and fixture, thereby enabling the machining of complex features such as deep cavities and inverted turns.
One-Time Clamping
After the workpiece is clamped, the machining of all five surfaces except the bottom surface can be completed by rotating the worktable or the spindle head. This eliminates the reference conversion error caused by multiple clamping, greatly improving the overall dimensional accuracy and positional accuracy of the parts, and saving the auxiliary time for repeated clamping.

Types of 5-axis CNC Machining
3+ 2-Axis Positioning Machining
This method is not a true 5-axis linkage. Instead, it uses two rotating axes to tilt and fix the tool at an optimal Angle before performing 3-axis milling. It is equivalent to a “universal fixture”, allowing the cutting tool to process the side or complex cavity of the workpiece at a fixed inclination Angle, thus completing multi-faceted machining in a single clamping. Its precision is higher than multiple clamping, but its efficiency is not as good as continuous 5-axis linkage.
5-axis Continuous Machining
During the cutting process, the five axes move simultaneously and continuously in coordination, causing the center point of the tool and the direction of the tool axis to constantly change in space.
This enables the cutting tool to always maintain the best cutting posture with the complex surface and avoid interference.
Cutting Tool Side Edge Machining
This process focuses on cutting by using the side edge of the tool rather than the tip. The tool is tilted at a certain Angle through the 5-axis function, allowing the stronger and longer side cutting edge to come into contact with the workpiece.
This can significantly enhance the material removal rate, achieve better surface quality, effectively avoid the low-speed cutting zone at the center of the tool tip, and extend the tool life.
Material can be used in 5-Axis CNC Machining
Aluminum
Aluminum alloy is one of the most common materials in 5-axis machining. It is light in weight, moderate in strength and easy to machine.
5-axis machining, with its high rotational speed and continuous multi-angle machining capabilities, can quickly and efficiently mill complex parts such as aerospace components, automotive frames, and electronic casings, while achieving excellent surface finish.
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is highly favored for its corrosion resistance and strength, but its tendency to work harden poses challenges to processing.
5-axis machining can effectively control cutting force and heat by maintaining constant contact between the tool and the workpiece and the optimal cutting Angle, avoiding work hardening, and thus stably produce precision parts for medical devices and chemical equipment.

Titanium Alloy
Titanium alloys are of high strength, light weight, and corrosion resistance, but they are difficult-to-machine materials.
5-axis machining avoids severe wear at the tool tip and the formation of a built-up edge by using the side edge of the tool and maintaining a constant chip load.
This is crucial for manufacturing aerospace and medical implants that must take into account both complex geometries and structural integrity.

Plastics
Plastics such as PEEK, nylon, and ABS are also often machined by 5-axis machining. These materials have relatively low rigidity and are sensitive to heat.
5-axis machining can use sharp tools and optimized cutting parameters to achieve clean and crisp cuts, avoiding material melting, deformation or burrs. It is perfectly suitable for machining medical device prototypes and corrosion-resistant industrial components.

Composite Material
5-axis machining is crucial for machining carbon fiber materials. Its high-precision path control can reduce delamination and burrs.
The sharp sp, special cutting tools, in combination with 5-axis linkage, can cleanly cut fibers and perfectly machine complex curved surface structural components required for aerospace and high-end sports goods.
Die Steel
5-axis machining is the preferred choice for machining injection molding and die-casting molds. It can efficiently mill complex cavities and deep cavities of die steel, avoid interference through tool inclination, and improve the consistency and efficiency of large curved surfaces by using side edge machining, significantly reducing the polishing time of fitters.
Material Selection Guide for 5-Axis CNC Machining
Functional Requirements
The materials must meet the core requirements of the parts in the working environment.
For instance, aerospace parts require a high strength-to-weight ratio; Medical implants need to be biocompatible.
Ensure that the physical, chemical, and mechanical properties of the materials match the product life cycle.
Material Machinability
Processability directly affects cost, efficiency, and quality. Aluminum alloy and other free-cutting materials can be machined quickly and have low tool costs. Titanium alloys and superalloys can cause significant wear to cutting tools, require special parameters, and are very costly.
A balance needs to be struck between performance and processability to avoid poor economy or quality risks caused by overly difficult material machining.
Geometric Complexity of Parts
5-axis excels in machining complex curved surfaces, deep cavities and irregular structures. For such parts, materials that can maintain good stability during machining should be selected.
If the geometric shape is complex and high strength is required, materials such as titanium alloys should be given priority. These materials can not only bear complex loads but also adapt to the characteristics of 5-axis multi-angle cutting.
Cost Control
Cost is not merely the unit price of materials, but the comprehensive cost. Including material costs, machining time consumption, tool wear and tear, and post-finishing requirements.
A comprehensive manufacturing cost analysis must be conducted.
Surface Finishing
If the parts eventually require anodizing, electroplating, or other finishing treatments, their applicability must be taken into account when selecting materials.
For instance, different series of aluminium alloys have a direct impact on the anodizing effect. The surface treatment plan should be determined at the initial design stage, and compatible materials should be selected.

Advantages of 5-Axis CNC Machining
Manufacturing Complex Geometric Shapes
The biggest advantage of 5-axis machining is its flexibility. The cutting tool can move in five directions at the same time, which allows it to handle complex curved surfaces, deep cavities, and irregular shapes that 3-axis machines cannot process.
It can easily machine parts like turbine blades and precision molds. This greatly increases the design freedom and makes it possible to create more advanced and detailed products.
High Machining Accuracy
5-axis machining allows a workpiece to complete the machining of multiple surfaces in a single clamping.
This avoids the reference conversion error caused by multiple re-clamping, greatly ensuring the overall dimensional accuracy of the parts and the positional tolerance between different features, and achieving a higher overall manufacturing quality.

High Efficiency
By adjusting the workpiece to the optimal machining position through the rotating axis, 5-axis machine tools can use shorter tools and achieve greater cutting line speeds.
Meanwhile, multi-faceted machining eliminates the auxiliary time of repeated clamping, resulting in a higher material removal rate and a significant reduction in the production cycle.
Good Surface Quality
5-axis machining can adjust the direction of the tool axis to enable the side edge of the tool to perform cutting and always maintain the best contact state between the tool and the machined surface.
This can achieve more consistent cutting force, lower surface roughness, and better surface quality.

Avoid Machining Interference
When machining deep cavities or complex structures, collisions are prone to occur between the cutting tool, tool holder, and the workpiece or fixture.
5-axis machine tools can create sufficient movement space for tool holders by flexibly adjusting the spatial posture of the cutting tools, ingeniously avoiding interference and completing machining tasks that are difficult for traditional methods to handle.
Extension of Cutting Tool Service Life
By tilting the tool at an Angle, the stronger side edge of the tool, rather than the fragile ti,p can undertake the main cutting work.
Meanwhile, the constant chip load and better chip removal conditions reduce the vibration and wear of the cutting tools, thereby effectively extending the service life of the cutting tools and lowering production costs.
Disadvantages of 5-Axis CNC Machining
High Equipment Cost
The structure of a 5-axis CNC machine tool is very complex. It requires high standards for its mechanical components, CNC system, and servo motors. Because of this, the cost of purchasing a 5-axis machine is much higher than that of a 3-axis machine.
In addition, the related maintenance, calibration, and supporting facility costs are also more expensive, and the initial capital investment requirements for enterprises are high.

Complex Programming
Programming for 5-axis machining is far more complex than that for 3-axis machining. Programmers must have a profound understanding of tool path planning, which requires the use of expensive professional CAM software and a large amount of post-finishing work.
At the same time, the requirements for the skills and experience of the operators are also extremely high.
Fixturing and Calibration Challenges
Even if a machine tool has 5 axes, precise tooling fixtures are still needed to stably support the workpiece. Complex part shapes and multi-angle cutting will generate greater forces and moments, posing strict requirements for fixture design.

Potential Vibration Risks
In dynamic machining, the movement of the rotating shaft may cause the spindle head or worktable to overhang, thereby reducing the system rigidity, triggering vibration and affecting surface quality.
In addition, the motion errors of the 5 axes may accumulate, posing more severe challenges to the precision compensation and calibration of the machine tool.
Limited Part Compatibility
5-axis machining is not suitable for many simple parts that mainly have vertical features. In such cases, its efficiency advantage cannot be fully shown.
On the contrary, the longer programming and setup time will increase the overall cost. As a result, it may become more expensive than 3-axis machining and offer lower cost performance.
Factors Influencing the Cost of 5-Axis CNC Machining
Geometric Complexity of Parts
The more complex the shape is, the longer the programming time and simulation verification time required will be. During machining, smaller tools, more tool passes, and lower feed rates may be required, and the tool axis direction needs to be adjusted frequently. All these significantly increase time and tool costs.

Selection of Materials
Materials directly affect machining efficiency and tool consumption. Difficult-to-machine materials require lower cutting parameters, more durable specialized tools, and longer machining times, all of which drive up costs. In addition, the purchase price of the material itself and the cost of the blank are also important components.
Precision Requirements
The stricter the tolerance requirements and the higher the surface finish requirements, the more sharply the cost will increase. This requires more precise machine tools, more refined machining strategies, longer machining times, and possibly additional subsequent procedures such as manual polishing or measurement.
Equipment and Operating Costs
5-axis machine tools themselves require a huge investment, and their depreciation, maintenance, and calibration costs are evenly distributed among each part.
Meanwhile, the power consumption during the machining, the licensing fees for high-value CAM software, and the maintenance costs of the workshop environment all constitute hidden operating expenses.

Post-processing
After 5-axis machining, parts usually still require subsequent machining, such as deburring, heat treatment, surface treatment, etc. These processes not only incur costs themselves, but may also become more complex and expensive due to the precision requirements of the previous processes.
Batch Size and Clamping Strategy
For small-batch prototypes, the high programming and preparation costs cannot be shared. For mass production, although the cost per piece decreases, it may be necessary to invest in the design and manufacture of dedicated tooling fixtures, which is another initial investment.
An efficient clamping strategy can reduce downtime and directly affect the total cost.
How 5-Axis Machining Improves Accuracy and Surface Finish
Improves Accuracy
- Minimizing the number of clamping operations: In traditional machining, the cumulative error brought about by multiple clamping operations is the main factor affecting accuracy.
- Consistent spatial positioning: With the precise fit of the A/C rotation axes, the cutting tool can approach the machining area at the optimal geometric Angle.
- Enhance process standards: Achieve automated control of the machining procedure through digital programming, significantly reducing the reliance on operators’ experience in traditional machining.
Improves Surface Finish
- Optimize tool-workpiece position: By adjusting the spatial Angle between the tool and the machined surface in real time, always keep the tool in the most ideal cutting geometry state.
- Continuous cutting mode: Compared with the discrete tool connection method of 3-axis machining, 5-axis technology achieves true continuous cutting through the smooth transition of tool paths.
- Stable cutting parameters: By intelligently adjusting the tool’s inclination Angle, the cutting edge is always operating within the optimal cutting line speed range.
Applications of 5-Axis CNC Machining
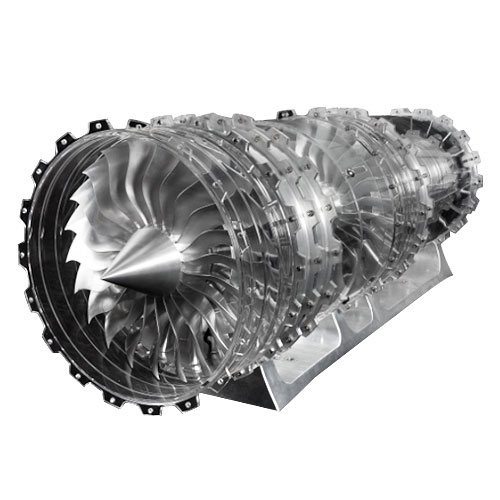
Aerospace Industry
This is the core application field of 5-axis machining. It is used for machining aircraft engine blades, blisks, fuselage structural components, etc. These parts are usually made of high-strength heat-resistant alloys.
5-axis machining can precisely form these lightweight and high-strength complex components in one go, and ensure their reliability and consistency.
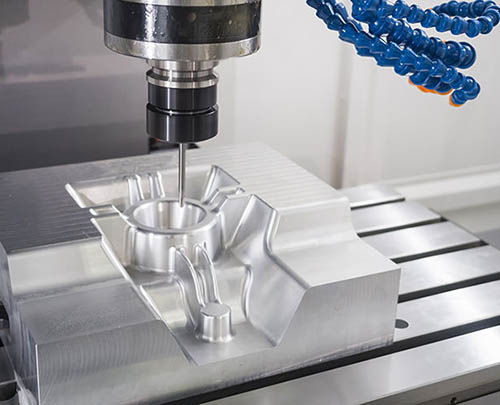

Precision Mold Manufacturing
5-axis machining is the industry standard for the machining of automotive injection molds, die-casting molds, and blow molding molds.
It can efficiently machine the complex cavities, deep grooves, and inverted structures of molds.

Medical Industry
It is used for machining surgical guides, orthopedic implants, and dental restorations. These implants need to perfectly match the patient’s unique bone structure, have complex shapes, and have extremely high requirements for biocompatibility.
5-axis machining can precisely mill these personalized complex curved surfaces from materials such as titanium alloys, cobalt-chromium alloys or PEEK.
Heavy Industry
5-axis machining is applied in the manufacture of turbine blades, gas turbine components, oil and gas valves, and pump casings, etc. These parts are usually large in size, complex in shape, and need to withstand high pressure, high temperature, or corrosive environments.
5-axis machining can ensure that these key components have the required strength, sealing performance, and flow channel performance, meeting the demanding working conditions.

Scientific Research and National Defense
In optical equipment, precision measuring instruments, radar systems, and weaponry, many core components have special curved surfaces and fine structures, which have extremely high requirements for precision and reliability.
5-axis machining can achieve the manufacturing of these complex prototypes and small-batch key parts, and it is an important support for promoting technological research and development and ensuring national defense security.

The Automotive Industry
5-axis machining can manufacture automotive engine cylinder heads, complex prototype parts, as well as appearance and functional parts for high-end consumer goods.
5-axis machining can quickly achieve complex designs, provide excellent surface quality, and be used to manufacture the precision molds required for the production of these products, enhancing the overall texture and performance of the products.

NOBLE’s 5-axis Machining
NOBLE is your trusted one-stop custom manufacturing solution, from prototype design to manufacturing, with huge manufacturing resources, suitable technology, streamlined process, expert guidance, and a perfect quality inspection process to turn your ideas into reality.
NOBLE meets mass production needs through strict tolerance control, quality inspection, and a complete supply chain, and quickly delivers cost-effective, high-precision parts.
NOBLE combines first-class precision parts processing technology and excellent high-quality CNC processing services. Choose our premium 5-axis machining services to advance your CNC machining projects.
- ISO 9001 & ISO13485 Certified Factory
- Cost-Effective Price & Fast Lead Time
- 10+ years of CNC Machining Parts
- Tight Tolerance of 0.001 mm
- Fast Turnaround in 7 days
- 24/7 Engineering Support
FAQs
What are the main advantages of 5-axis machining?
It offers superior accuracy, higher efficiency, better surface finish, and the ability to manufacture complex geometries in a single setup, reducing production time and human error.
Which industries commonly use 5-axis machining?
It is widely used in aerospace, automotive, medical device, energy, and mold-making industries where precision, durability, and complex part shapes are critical.
What types of parts are ideal for 5-axis machining?
Parts with intricate surfaces, deep cavities, or multiple angles—such as turbine blades, impellers, aerospace components, and precision molds—are perfect candidates for 5-axis machining.
Is 5-axis machining more expensive than 3-axis machining?
Yes, it generally costs more due to higher machine investment and complex programming. However, it can reduce total production time and improve quality, often lowering overall project costs.
What are the limitations of 5-axis machining?
High equipment cost, complex programming, fixturing challenges, and limited suitability for simple parts are common limitations.








