What is Metal Die Casting Production?
Metal die casting is a metal casting process. Its essence is to inject molten metal into a precisely designed metal mold under high pressure, and then cool and solidify it to eventually form a casting of the predetermined shape and size.
The die-casting process mainly relies on three core elements: die-casting machines, die-casting molds, and die-casting alloys. The characteristic of metal die casting is to fill the mold with high pressure and high speed, which enables die casting to efficiently and in large quantities produce metal parts with complex structures, thin walls, precise dimensions, and smooth surfaces.
Die casting technology originated in the early 19th century. In 1838, an American named Bruce invented the first manual piston die-casting machine for printing lead type.
At the beginning of the 20th century, the successful application of aluminum alloy die-casting promoted the development of the automotive industry and marked the true beginning of modern die-casting technology.

How Metal Die Casting Production Works?
Mold Preparation
Before starting die-casting, the mold needs to be installed and preheated first. Then, the cavity should be cleaned and a mold release agent sprayed.
Mold release agents facilitate the ejection of castings and can also cool the molds. After the mold is prepared, the die-casting machine drives the moving mold to closely close with the fixed mold and applies a huge clamping force to prevent the molten metal from spilling out.
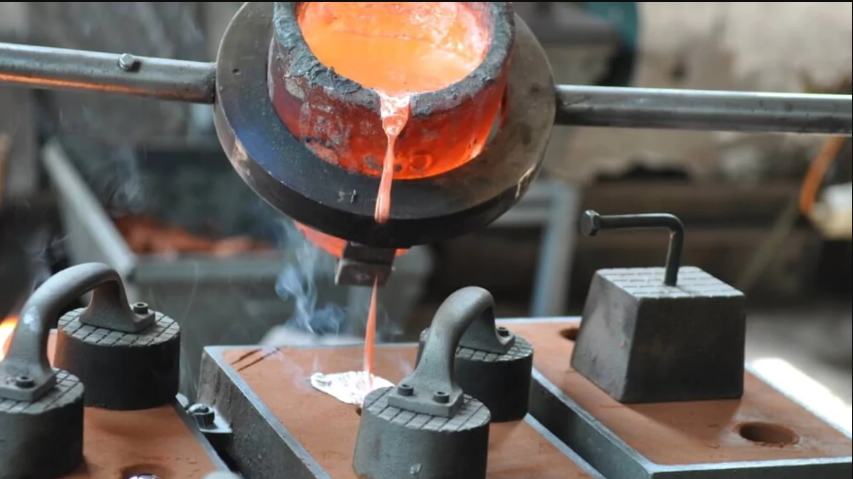
Material Casting
After the die-casting mold is prepared, the specific alloy is heated to a molten state in the furnace, and the composition is kept uniform. Then, use a measuring spoon to take the required amount of molten metal out of the furnace and smoothly pour it into the closed injection sleeve, preparing for injection.
Injection Process
The punch of the die-casting machine advances at an extremely high speed, instantly pressing the molten metal in the sleeve into the sealed mold cavity. The molten metal fills the entire cavity within a few hundredths of a second, ensuring the precise replication of thin walls and complex structures.
Cooling
After the molten metal fills the cavity, the punch does not immediately retreat but continues to maintain a huge pressure. This stage is called holding pressure. It forces the metal that is contracting and solidifying to receive additional replenishment, thereby reducing internal shrinkage cavities and defects and increasing the density of the casting.
Ejection
After the mold has been held under pressure for a period of time and the casting is basically set, the mold closing mechanism opens the mold.
The ejector mechanism inside the mold moves forward under the drive of the ejection cylinder, smoothly pushing the formed casting out of the mold and completing the demolding process.
Trimming
The castings ejected by die-casting usually have extra material edges, such as gating systems and vent slots. The castings need to have these material edges cut off by hand or with equipment and undergo necessary surface cleaning. After one casting is cleaned, the mold closes, and the next die-casting cycle begins.
The Types of Metal Materials Used in Metal Die-casting Production
Aluminium
Aluminum is the most widely used die-casting material. Aluminum is light in weight and has good mechanical strength, corrosion resistance and thermal and electrical conductivity.
Aluminum alloy has good casting fluidity and is suitable for producing thin-walled parts with complex structures. It is widely used in the automotive, electronic and aerospace industries.
Zinc
Zinc alloy is very easy to die-cast and can produce parts with extremely high dimensional accuracy and extremely smooth surfaces.
Zinc alloys have good mechanical properties and can undergo various electroplating treatments. Zinc alloy is often used to manufacture hardware parts, toy models, bathroom accessories and electronic casings, and other products.
Magnesium
Magnesium alloy is the lightest among practical metals, with high specific strength and specific stiffness, and it has excellent shock absorption and electromagnetic shielding properties.
Magnesium is often used in situations where weight is a strict requirement, such as laptop casings, camera bodies, car steering wheel frames, and aerospace components.
Copper
The copper alloys mainly used in die casting are brass and bronze. Copper has excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance.
Copper has a high melting point, causing significant wear and tear on molds and making die-casting more difficult and costly. Copper is typically used to manufacture special parts that require high strength and electrical conductivity, such as valves, gears, and electrical connectors.
Types of Metal Die Casting Production Process
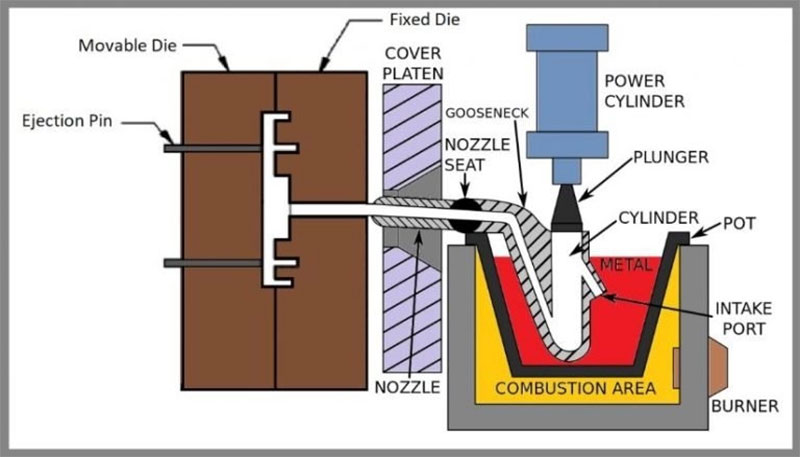
Hot Chamber Die Casting
In hot chamber die casting, the injection mechanism is immersed in molten metal, and the metal is directly injected into the mold through the injection chamber. The hot chamber die casting method is highly efficient and has a fast cycle speed, making it suitable for low-melting-point metals such as zinc, magnesium, and lead.
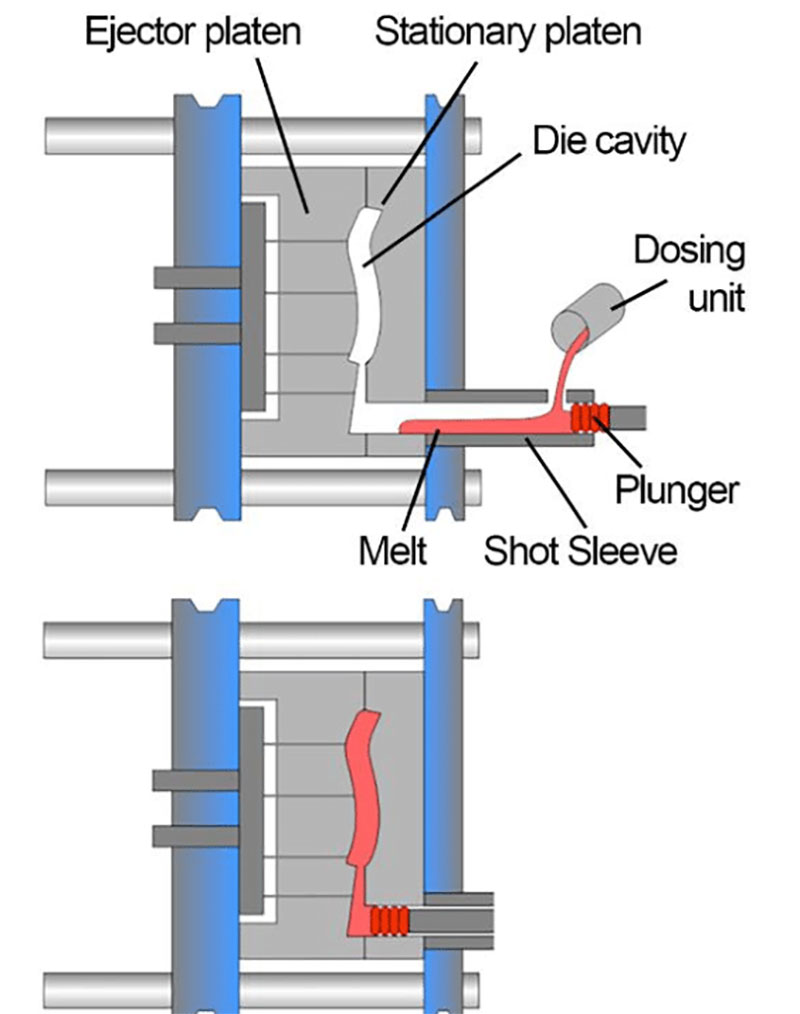
Cold Chamber Die Casting
In cold chamber die casting, the injection mechanism is separated from the furnace, and the molten metal needs to be injected into the injection chamber manually or mechanically.
Cold chamber die casting is suitable for high-melting-point metals such as aluminum and copper. Although cold chamber die casting is slightly less efficient, it can effectively prevent equipment corrosion and ensure product quality.
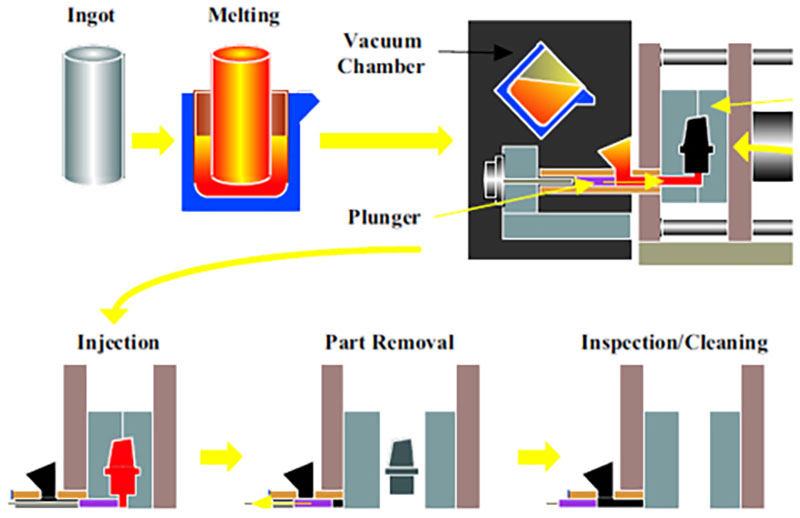
Vacuum Die Casting
Vacuum die casting involves evacuating the air during the die casting process to reduce the gas in the mold cavity, thereby minimizing porosity defects and enhancing density and mechanical properties.
Vacuum die casting is often used for products with high strength requirements, such as automotive structural parts and aviation components.

Low-Pressure Die Casting
Low-pressure die casting is a process in which molten metal is slowly pushed from a crucible into a mold by low-pressure gas, ensuring smooth metal filling and dense structure.
Low-pressure die casting is often used in the production of larger aluminum parts such as car wheels and engine blocks.
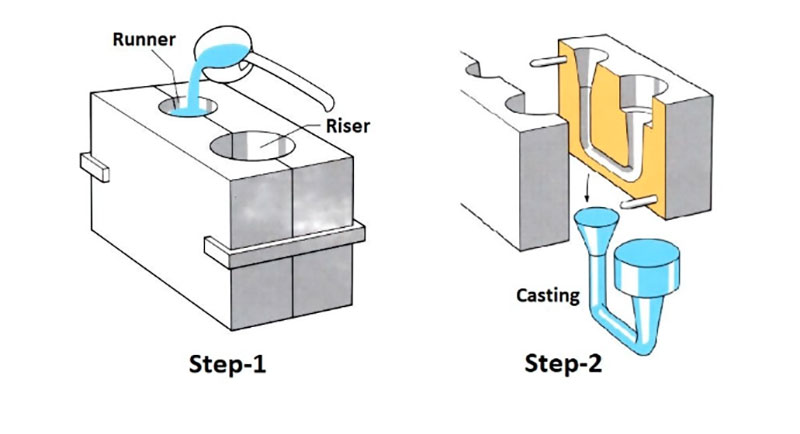
Gravity Die Casting
Gravity die casting uses the self-weight of the metal to inject molten metal into the mold without the need for external injection.
Gravity die-casting is a simple process and suitable for medium and small batch production, such as pump bodies, pipe fittings, mechanical housings, etc.
Advantages of Metal Die Casting Production
3-Dimensional Accuracy
Metal die casting can achieve high-precision products with complex shapes in a single forming process, featuring small dimensional tolerances and good repeatability.
The parts machined by metal die-casting have a smooth and fine surface, which can be directly painted, electroplated, or polished, greatly reducing the subsequent machining and surface finishing processes and costs.
Production Efficiency
The die-casting process has a short cycle, enabling rapid injection, cooling, and demolding, and is particularly suitable for batch and automated production.
Compared with traditional casting or machining methods, metal die casting can produce more highly consistent parts within the same period of time, significantly reducing the cost per piece.
Complex Forming
Metal die casting can form parts with complex geometries, thin-walled structures, and fine features, such as reinforcing ribs, threaded holes, and inserts, in a single mold, avoiding multiple processing or assembly procedures and achieving the manufacturing of products with high integration and high structural integrity.
Mechanical Strength
Metal die casting, due to high-pressure injection, causes the metal to rapidly fill the mold cavity and solidify. As a result, the internal structure of die castings becomes denser, with fewer pores and shrinkage cavities, and they have higher mechanical strength, hardness, and wear resistance.
After being treated by vacuum die-casting or semi-solid die-casting processes, the performance of the parts can approach that of forgings.
Material Utilization
The metal loss in the metal die-casting production process is extremely low. The gating system and overflow parts can be reused in the furnace, and the overall material utilization rate can reach over 90%.
Compared with traditional casting methods, metal die casting not only saves raw materials but also benefits environmental protection and cost control.

Disadvantages of Metal Die Casting Production
High Mold Cost
The design and manufacturing cost of metal die-casting molds is relatively high, especially for complex-structured or multi-cavity molds, which require precise machining and high-temperature resistant steel. Therefore, the initial investment is large.
For small-batch production or projects with frequent design changes, the mold cost of metal die casting is difficult to amortize and has poor economic efficiency.
Unsuitability for High-Melting-Point Metals
The temperature resistance limit of die-casting machines and molds is usually only applicable to medium and low melting-point metals such as aluminum, zinc, magnesium, and copper.
High-melting-point materials such as steel and iron cannot be formed by die-casting, which to some extent limits the application scope of this process.
High Maintenance Cost
Die-casting machines and their supporting systems (such as hydraulic, cooling, and spraying equipment) are expensive and have high maintenance requirements. If equipment malfunctions during production, it will cause damage to molds or lead to production halts, increasing the maintenance and operation costs of enterprises.
Challenges in the Metal Die Casting Production Process
Porosity and Shrinkage Issues
Porosity and shrinkage cavity problems are the most common challenges in die casting. When filling at high speed, if the air in the mold cavity is not discharged in time, it will be drawn into the molten metal and form pores. Meanwhile, when the thick walls of the casting are solidifying and contracting, if they are not replenished with sufficient molten metal, shrinkage cavities will form.
The defects of pores and shrinkage cavities can significantly reduce the mechanical properties and sealing performance of parts.
Complex Process Parameter Control
In the metal die-casting process, numerous parameters such as injection speed, pressure, temperature, and time need to be precisely matched. Even the slightest deviation of any parameter may lead to defective products.
For instance, insufficient pressure can lead to incomplete filling, while excessive speed will intensify entrainment, which poses extremely high demands on process control.
Deformation Control
Although die-castings have high precision, the shrinkage of the castings after demolding and the deformation caused by the release of residual stress are still issues that need to be strictly controlled.
Dimensional factors can affect the dimensional stability and assembly accuracy of parts, increasing the cost of subsequent processing or correction.

Applications of Metal Die Casting Production
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry is the largest application market for die-castings. Metal die casting can be used to manufacture engine blocks, transmission cases, clutch housings, steering gear assemblies, wheels, as well as various brackets and structural components.
Die casting can provide high-strength and lightweight parts, meeting the requirements of automobiles for safety and fuel economy.
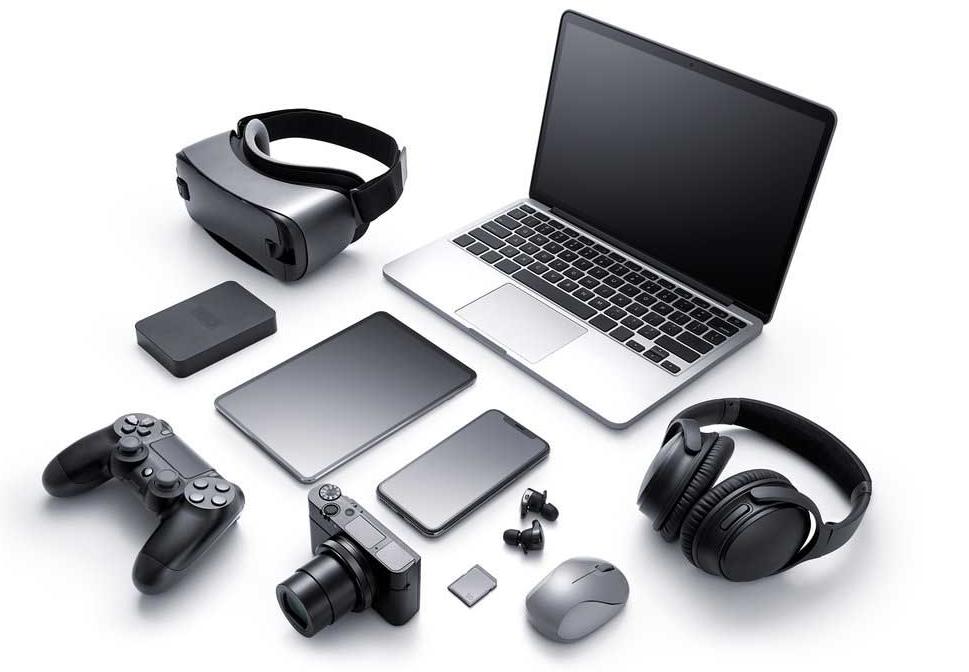

Electronic Products
Metal die casting can be used to manufacture electronic products, such as the middle frames of smartphones, the shells of laptops, heat sinks, connectors, etc.
Die-castings provide electronic products with excellent electromagnetic shielding, structural strength, and heat dissipation performance, while achieving an exquisite appearance and a thin and light design.
Household Appliances
The core components of many household appliances are manufactured by die-casting technology, such as the compressor casing of refrigerators, the blades of air conditioners, the shells of power tools, the valve bodies of faucets, door locks, and various kitchenware.
The advantages of metal die-casting lie in its durability, high production efficiency, and good surface treatment effect.

Aerospace
The aerospace field has extremely high requirements for the performance of parts. Die casting is used to manufacture aircraft engine parts, missile cabins, radar components, and the shells of military communication equipment etc.
Metal die casting usually employs high-performance aluminum alloys and magnesium alloys to meet the requirements of being lightweight and high-strength.

NOBLE’s Metal Die Casting Production Service
NOBLE is your trusted one-stop custom manufacturing solution, from prototype design to manufacturing, with huge manufacturing resources, suitable technology, streamlined process, expert guidance, and a perfect quality inspection process to turn your ideas into reality.
Providing high-precision and long-life die-casting mold services at competitive prices, combining cutting-edge die-casting mold technology with advanced production equipment, our expert engineers are dedicated to reducing cycle times by up to 50%+, with fast turnaround, obtaining in minutes Get a quote and getting your die casting mold within days.
- ISO 9001 & ISO13485 Certified Factory
- 10+ Years of Die Casting Mold Making
- Advanced Equipment & Competitive Price
- Get an Instant Die Casting Mold Making Quote
- Professional & Free DFM Report
- 24/7 Engineering Support
- Lead Time As Fast As 3 Days
FAQs of Die Casting
What Is the Difference Between Hot Chamber and Cold Chamber Die Casting?
Hot chamber die casting is suitable for low-melting-point metals like zinc and magnesium, while cold chamber die casting is used for higher-melting-point metals such as aluminum and copper.
Can Die Cast Parts Be Machined or Surface Treated?
Yes. Die-cast parts can undergo secondary processes such as CNC machining, anodizing, powder coating, and electroplating to achieve tighter tolerances or improved aesthetics and corrosion resistance.
Is Metal Die Casting Suitable for Low-Volume Production?
Traditionally, die casting is more economical for high-volume runs. However, with modern rapid tooling and prototyping technologies, it is now possible to produce small batches efficiently, especially for product testing or limited-edition parts.
What Factors Should Be Considered When Designing a Die-Cast Part?
Designers should consider wall thickness, draft angles, gate position, and cooling layout to ensure smooth filling and easy ejection. Proper design helps reduce defects and extend mold life.
How Much Does Metal Die Casting Cost?
The cost depends on factors such as mold complexity, production volume, part size, and material type.








