The art of Sheet Metal Machining plays a pivotal role in contemporary manufacturing, serving as a fundamental pillar across industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and construction. Precision techniques—including cutting, bending, and forming—enable the transformation of flat metal sheets into complex components. This capability not only ensures the functional integrity of end products but also enhances their aesthetic value.
What is sheet metal?
Sheet metal is a versatile material that’s been flattened into thin, flexible pieces, typically measuring under 6 mm in thickness. It plays a key role in metalworking, allowing it to be shaped into countless configurations. Its thickness can vary, offering a range of possibilities for different uses and industries.
What is the purpose of sheet metal?
Sheet metal is essential in construction for holding architectural and structural elements together, ensuring they maintain their shape over time. It is frequently used as cladding on large areas such as roofs and partitions. Additionally, sheet metal is commonly combined with other materials to construct walls, floors, and ceilings.
How is sheet metal made?
The manufacturing process begins by selecting the appropriate metal and cutting it to the desired size and shape. Once the metal is prepared, various techniques such as rolling, extruding, and bending are used to shape it into the final product. Depending on the design, the result can range from flat panels to complex three-dimensional structures.

The Importance of Sheet Metal Machining
Known for its strength, versatility, and cost-efficiency, sheet metal is a favored material in industries that require both durability and precision. Its uses span from the creation of detailed automotive parts to the development of robust HVAC systems and the construction of precise electronic enclosures. Mastering Sheet Metal Machining techniques is vital for ensuring that products meet design standards, maintain high quality, and achieve optimal production efficiency.
What is Sheet Metal Forming?
Sheet metal begins as flat stock, which is then cut and shaped through a series of steps. The first operation in a typical project is sheet cutting, where tools like lasers, shears, and punch presses are used to create holes and edge features, a process known as blanking.
After blanking, the next step involves forming the sheet metal, usually using a brake press. The press, which can be either manual or automated, applies die inserts to bend the metal into the desired shape, transforming it from a two-dimensional sheet into a three-dimensional part. The bending process allows for multiple directions of formation, enabling the production of both simple and complex geometries, which may require custom die tooling. Once the necessary tools are in place, it becomes cost-effective to produce additional parts, making sheet metal fabrication a viable option for both low- and high-volume manufacturing.
Essential Techniques in Sheet Metal Fabrication
1. Cutting Techniques
Shearing: Shearing is a traditional metal cutting technique that applies shear forces to achieve straight cuts, commonly used in high-volume production environments where precision and efficiency are essential.
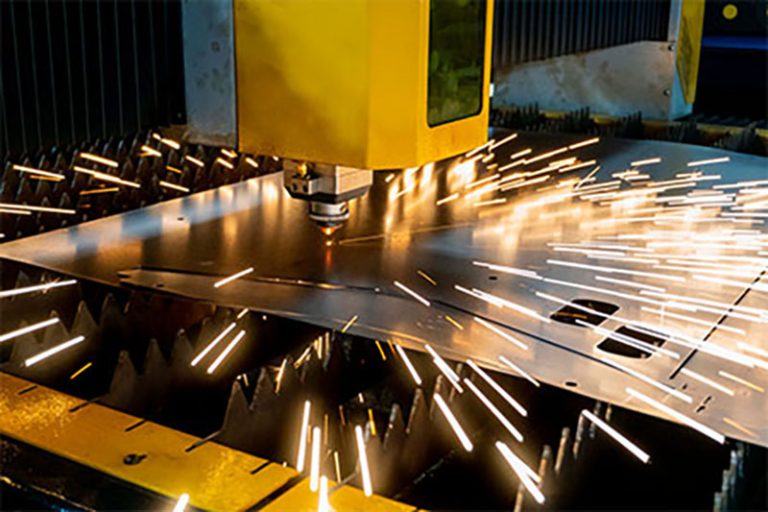
Sheet metal Laser Cutting: Laser cutting employs focused laser beams to achieve high precision and flexibility when cutting complex patterns in various metals. This technique is particularly useful for intricate designs and tight tolerances.

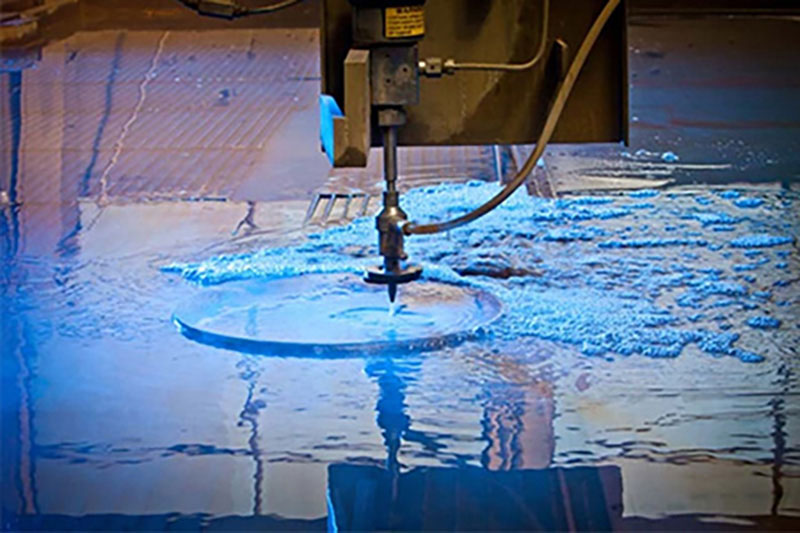
Waterjet Cutting: Waterjet cutting utilizes a high-pressure stream of water mixed with abrasives to cut materials, providing clean edges without the introduction of heat, making it suitable for heat-sensitive materials.

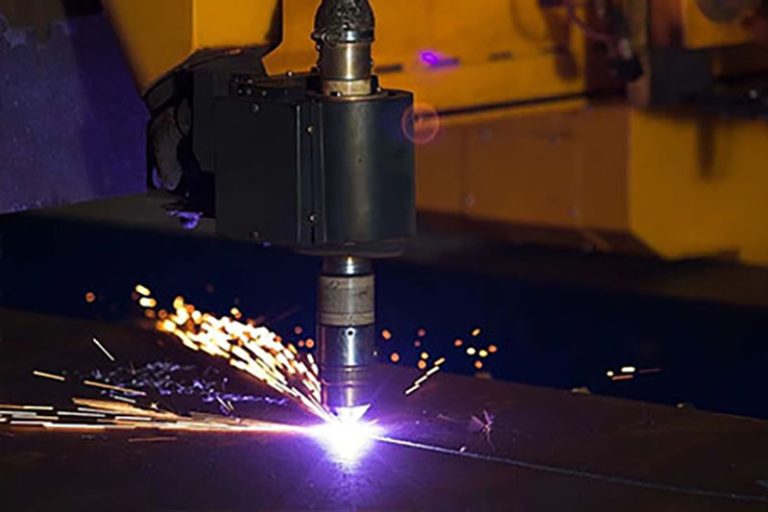
Sheet Metal Plasma Cutting: Sheet metal Plasma cutting is the process that uses a high-velocity jet of ionized gas (plasma) to melt and blow away material, usually metal. This method is commonly used for cutting electrically conductive materials like steel, aluminum, brass, and copper.

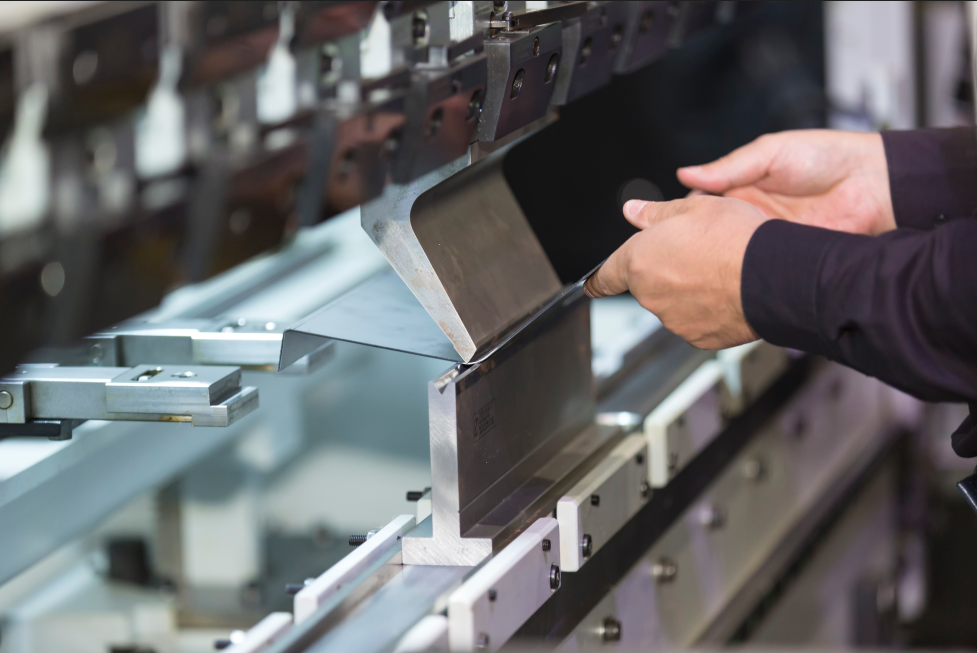
2. Sheet Metal Bending and Forming
Press Brake: Press brake bending employs a press and die set to create precise angular bends in metal sheets, a crucial process for fabricating components that require specific geometric shapes.

Sheet Metal Bending: Roll bending uses rollers to curve metal sheets into cylindrical or conical shapes, providing flexibility in the production of pipes, tubes, and other curved components.
Deep Drawing: Deep drawing is a process used to create three-dimensional shapes by drawing a sheet metal blank into a die cavity, resulting in seamless, structurally robust components.
3. Joining Methods
Sheet metal welding: Welding involves using heat to fuse metal sheets, creating strong, permanent joints that are crucial for structural applications in industries such as automotive and construction.
Fastening: Techniques such as riveting, screwing, and adhesive bonding are utilized to form temporary or detachable joints, providing flexibility for assembly and maintenance tasks.
Tips for Optimizing Sheet Metal Fabrication Efficiency
1. Material Selection and Preparation
Selecting the correct metal alloy based on key factors such as mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and cost is critical to ensuring both optimal product performance and longevity.
2. Design for Manufacturing (DFM) Principles
Implementing DFM principles early in the design phase helps reduce material waste, streamline manufacturing, and improve assembly efficiency, resulting in lower production costs and shorter lead times.
3. Tooling and Equipment Maintenance
Regular maintenance and calibration of cutting tools, dies, and molds are key to ensuring consistent precision and quality in Sheet Metal Machining. This routine practice helps extend equipment life and reduce downtime, leading to more efficient operations.
4. Quality Control Measures
Implementing stringent quality control measures at each phase of the manufacturing process, from raw material inspection to final product testing, ensures compliance with design specifications and aligns with customer expectations.
5. Embracing Technological Advancements
The implementation of advanced technologies such as automation, robotics, and CAD software plays a critical role in boosting production efficiency, accuracy, and scalability in Sheet Metal Machining operations.
Trends Shaping the Future of Sheet Metal Machining
1. Sustainability Initiatives
The growing emphasis on sustainability is leading to breakthroughs in eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient manufacturing processes, and enhanced recycling programs, all aimed at reducing environmental impact.
2. Digital Transformation
The integration of IoT-enabled monitoring, AI-driven predictive maintenance, and cloud-based analytics enhances operational visibility, boosts efficiency, and supports better decision-making capabilities.

3. Additive Manufacturing (AM)
The adoption of additive manufacturing (AM) technologies, including metal 3D printing, is transforming Sheet Metal Machining by enabling complex designs, quick prototyping, and the flexibility to produce parts on demand.
4. Customization and Personalization
As consumers want more personalized products, Sheet Metal Machining is shifting to focus on customization. Manufacturers are responding by offering more tailored solutions and flexible production methods.
Conclusion
Mastering Sheet Metal Fabrication isn’t just about technical know-how—it’s about blending expert craftsmanship with innovative technology and forward-thinking strategy. By embracing advanced methods, following best practices, and staying ahead of the curve with emerging trends, manufacturers can boost product quality, streamline their operations, and remain competitive in an ever-changing global market. Whether you’re a seasoned pro or just beginning your journey in sheet metal, staying informed, refining your processes, and embracing new technologies will unlock endless growth opportunities.







