What do the Boeing 787 Dreamliner, a modern tennis racket, and a Formula 1 car have in common? It’s not just about going for peak performance; it’s about the way they’re built. You interact with composite materials every day, probably without even knowing it.

This guide will demystify these advanced materials. NOBLE engineers will be happy to chat with you about the different types and their amazing benefits. We’ll chat about real-world applications that are shaking up the industry. Then check out what new ideas are coming up.
What Are Composite Materials?
The Core Concept
Think of a concrete sidewalk. By itself, cement is brittle. Mixed with sand and gravel, it gets tougher. But when you embed steel rebar inside, it transforms into a massively strong, durable material. That’s the core idea behind all composite materials: synergy. The whole becomes fundamentally greater than the simple sum of its parts. We engineer them by combining distinct materials to create something with superior properties that none of the components could achieve alone.
Breakdown of the Two Key Components
Every composite is a partnership between two essential components, each with a critical, non-negotiable role.
The Reinforcement (The Muscle)
This is the backbone. The reinforcement is the strong, load-bearing element that gives the composite its strength and stiffness. We typically use fibers—incredibly fine strands of carbon, glass, or aramid (like Kevlar). On their own, these fibers are flexible, but when locked into place, they become the primary structural element, carrying the load and defining the material’s mechanical performance.
The Matrix (The Glue)
If the reinforcement is the muscle, the matrix is the skeleton, and the skin. This is the binder, a continuous material—often a polymer resin like epoxy or polyester—that encapsulates the fibers. Its job is threefold: it holds the reinforcement in the optimal orientation, distributes stress evenly between the fibers, and protects them from environmental damage like impact, moisture, and chemicals.
Without the matrix, the fibers are useless; without the fibers, the matrix is typically weak. It’s the combination that creates a high-performance material.

Why Do We Use Composite Materials?
Unmatched Strength-to-Weight Ratio
This is the single biggest reason composite materials have revolutionized industries like aerospace and automotive. Picture a carbon fibre rod that can hold the same weight as a steel rod. The carbon fibre rod would be much lighter – often less than half the weight. For planes, this means they can use less fuel and fly further. For high-performance vehicles, that means faster acceleration, better handling, and better braking. When every gram matters and failure is not an option, we go for composite materials.
Superior Corrosion and Chemical Resistance
Unlike steel, composite materials simply do not rust. Pretty amazing, right? This is one of the ways composites do better than traditional metals – they can effectively resist corrosion even in harsh environments. As you can probably guess, they’re used in ship hulls and propellers, chemical storage tanks holding highly corrosive solvents, and the steel reinforcement inside concrete bridges.
Remarkable Design Flexibility
With metals, you are often limited by what you can machine from a block or weld from sheets. Composites are changing this. You can mould them into complex, seamless, and organic shapes that would be impossible or too expensive to create with metal. We can design one composite part to replace a whole bunch of welded or bolted metal components, cutting points of failure, and making production more efficient. This means engineers can come up with designs that are perfect for the job, not just easy to make.
High Fatigue Resistance
Fatigue -the gradual weakening of materials due to repeated stress cycles, which is often the primary cause of metal failure. Composite materials, especially carbon fibre, exhibit exceptional fatigue resistance. Aircraft wings undergo countless bending cycles during their service life. Over time, metal materials can develop cracks, which can pose safety hazards and increase replacement costs. But composite materials can handle these stresses better. In places where things could go wrong and have really bad consequences, the durability of composite materials ensures that components are safe and reliable in the long term.
Dimensional Stability
People discovered that materials expand or contract in response to changes in temperature. Subsequently, scientists identified the underlying patterns and named this property the ‘coefficient of thermal expansion’.
Metals typically have a high coefficient. Composites, especially those with carbon fiber reinforcement, can be engineered to have a coefficient that is nearly zero. This is fantastic news for precision instruments and satellite components made from carbon fibre, which can maintain their exact shape and dimensions across extreme temperature ranges. This means they can withstand the frigid depths of space and the intense heat of atmospheric reentry!

A Tour of Common Composite Types
Think of the world of composite materials like a team of specialists. Each member’s got their own unique set of skills, so they’re perfect for jobs that need a bit of something extra. You see these materials every day, but you might not realise the advanced engineering behind them.
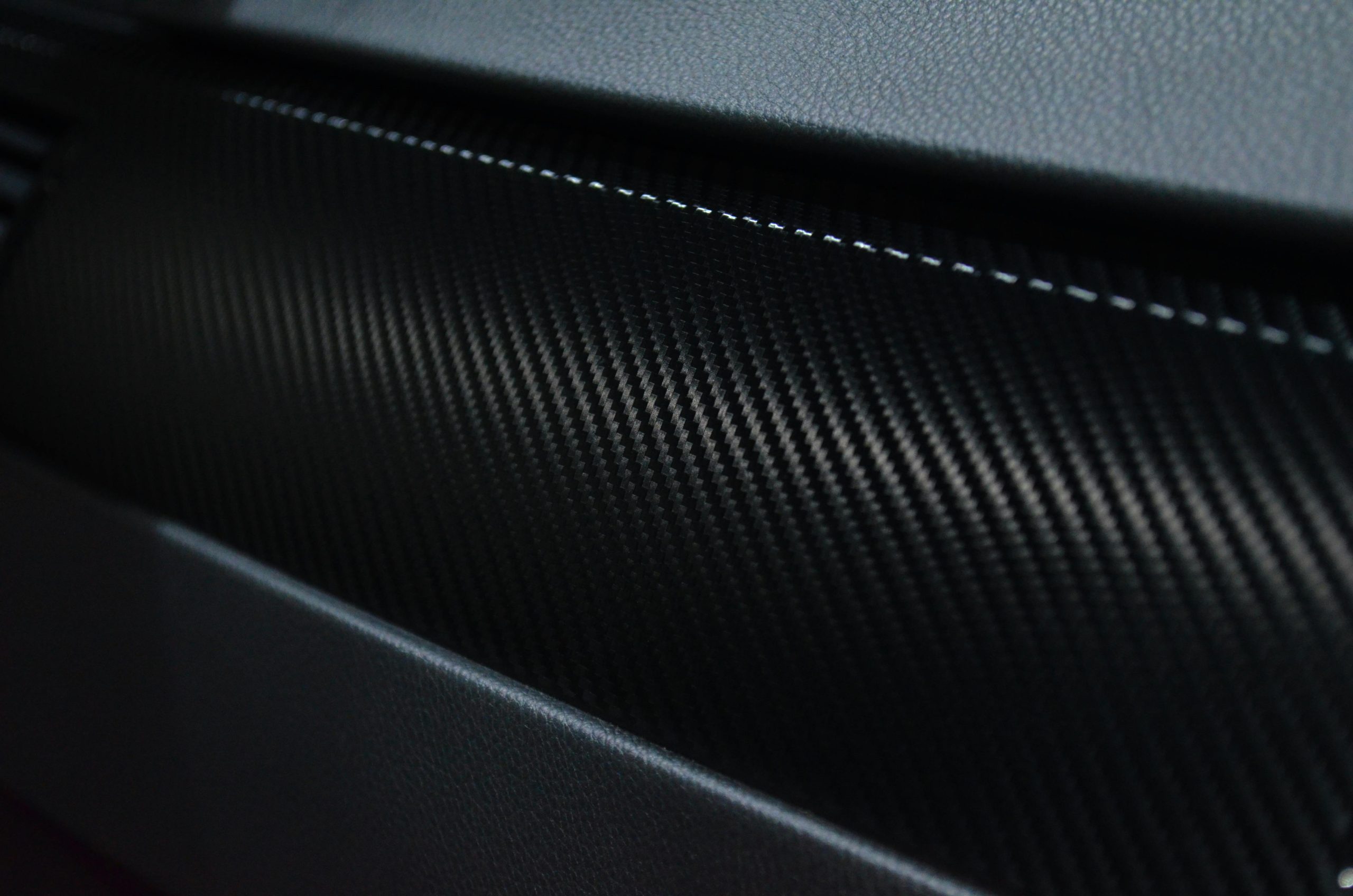
Carbon Fiber Composites: The High-Performance Champion
When a project needs a mix of lightness and strength, we go for this material. It’s the one we all know for pushing performance boundaries.
- Key Traits: Its reputation is based on how stiff it is compared to how light it is. The stuff is really rigid, but surprisingly light. But this top-tier performance does cost a bit more. The raw materials are expensive, and the layup and curing processes need to be precise and take time. You pay for the best performance.
- Common Uses: Carbon fibre is the go-to material for top-tier engineering. You’ll find it in the main fuselage structures of modern aircraft, like the Boeing 787; in the survival pods of Formula One race cars; and in critical body panels of luxury supercars. But there are so many other ways to use it. Even top-tier sports equipment relies on it, like professional bike frames, the most durable hockey sticks, and the best tennis rackets.

Fiberglass (GFRP): The Versatile Workhorse
If carbon fibre is the star athlete, fiberglass is the reliable, all-purpose workhorse. It’s the composite that brought the technology to the masses, offering a fantastic balance of performance and practicality.
- Key Traits: Fiberglass is widely favored by the public due to its high strength, low cost, and ease of manufacturing. Although it is less strong than carbon fiber, its affordability and durability make it a preferred material for numerous applications.
- Common Uses: You see it all the time. It’s the go-to material for ship hulls and loads of car body panels, and you’ll find it in everyday stuff like bathtubs, swimming pools, and lightweight industrial tanks.

Ceramic Matrix Composites (CMCs): The Heat Defiers
These composite materials are b They’re pros when it comes to dealing with extreme heat and cold, which can damage or break down other materials. built for environments that would be a death sentence for others.
- Key Traits: Their most outstanding feature is their incredible resilience to heat, wear, and corrosion. Amazingly, they retain their strength and shape at temperatures that would cause advanced superalloys to fail, often operating reliably above 1200°C (2200°F). These innovative solutions are game-changers in the field of thermal management.
- Common Uses: This is a total game-changer for jet engines. These days, you’ll find CMCs in the most intense parts of the engine, like the turbine blades, shrouds, and exhaust nozzles. They help to handle higher operating temperatures and make the engine more efficient. They are also critical for the heat shields on space re-entry vehicles and are used in ultra-high-performance brake systems for sports cars and aircraft.
Metal Matrix Composites (MMCs): The Heavy-Duty Performers
When plastic composites cannot withstand thermal or mechanical stresses, it is clear that traditional metals are the answer. But what if traditional metals aren’t strong enough? Metal-matrix composites are exactly what you need!
- Key Traits: Scientists have found that by mixing certain ceramic materials with base metals like aluminium, you can create new materials that are even better than the original metal. These new materials are stronger, stiffer, more heat-resistant, and less likely to change size when heated. But, as you’d expect, these materials are heavier than polymer-based composites.
- Common Uses: Metal matrix composites are stronger, stiffer, and more heat-resistant, so they’re a great replacement for traditional metals in engine components like piston rings, high-performance brake discs, and drive shafts. They’re also really stable, which makes them perfect for use in spacecraft and satellite parts, as well as top-quality bike frames and parts.

Composites in Action: Where You Find Them Every Day
We’ve already sung their praises, but how can we really understand the impact of composite materials? You’ve got to see their applications in action to get it. This isn’t just something you see in labs—it’s a material that’s actually changing the world around you, making the impossible possible.
Soaring through the Skies (Aerospace)
The aerospace industry is arguably where composite materials have made their most profound mark. Modern aircraft like the Boeing 787 and Airbus A350 are over 50% composite by weight. We use them for the entire airframe structure, the winglets that reduce drag, and even the interior panels and seating. The primary driver is weight. The Result? Every kilogram of weight saved translates directly into massive fuel savings over the life of the aircraft. This isn’t just about cost; it’s about range and environmental impact. A lighter plane can fly further on the same amount of fuel or burn significantly less for the same route, slashing carbon emissions.
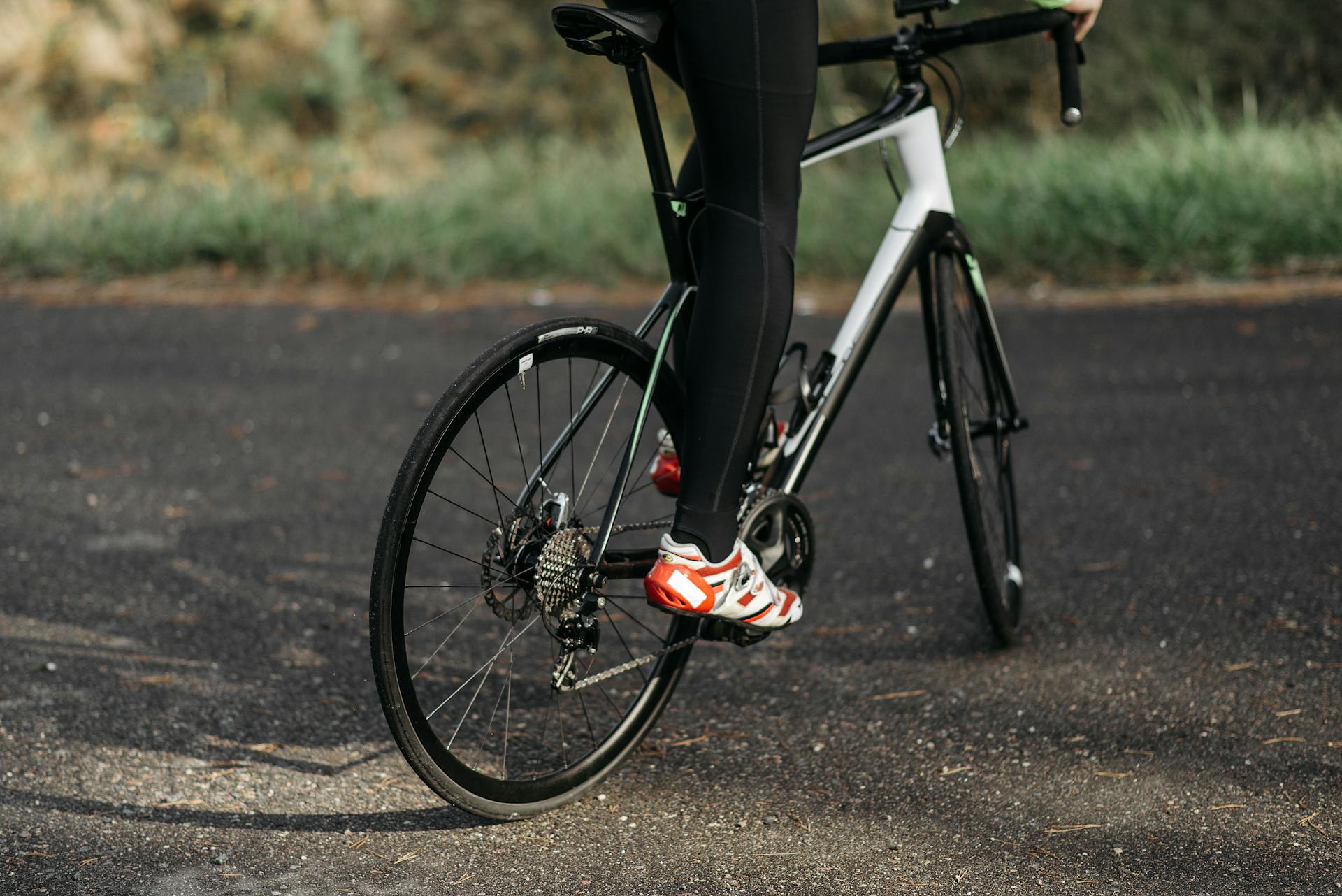

Pushing Human Limits (Sports & Recreation)
If you’ve ever swung a modern tennis racket or ridden a high-end road bike, you’ve felt the benefit of composite materials. We engineer these materials to create equipment that is simultaneously stronger, stiffer, and lighter. A carbon fiber bicycle frame absorbs road vibration while transferring more of your pedaling power directly to the pavement. A composite hockey stick provides a sharper “whip” for a faster shot. In fishing rods, golf clubs, and even running shoes, composite materials allow us to precisely control flex and energy return, giving athletes a tangible edge by enhancing their natural ability.
Building a Better World (Construction & Infrastructure)
The durability and corrosion resistance of composite materials are quietly revolutionizing our infrastructure. We are now building entire bridge decks from fiberglass composite materials that will last for decades longer than concrete without succumbing to road salt. We use carbon fiber rebar to reinforce concrete in corrosive environments and apply carbon fiber sheets to repair and strengthen aging structures like parking garages and building columns. Furthermore, the massive blades of modern wind turbines are almost entirely composite. Their ability to be engineered into long, strong, and fatigue-resistant airfoils is what makes large-scale wind power generation feasible. This is where composite materials move beyond high-tech gadgets and become essential for building a more resilient and sustainable future.

The Other Side of the Coin: Challenges and Limitations
I can’t promise that any one material will be a hit with everyone. While composite materials are great, they do have some practical challenges that engineers and manufacturers have to deal with. If you can understand these limits, it’ll help build trust and provide a good foundation for making informed decisions.
Higher Material and Manufacturing Costs
Why does that carbon fiber bicycle frame carry such a premium price? The answer’s in the whole production ecosystem. The raw materials themselves – carbon fibre precursors and high-performance epoxy resins – are more expensive than bulk metals. But the real cost driver is often in the manufacturing. You need a lot of energy for things like autoclave curing, and it takes ages, which is really different to how quickly you can stamp metal.
The truth is that the journey from raw fibre to a finished, high-performance part is complicated and expensive. This makes professional machining in composite materials a premium service.
Complex Repair Processes
While ordinary dents in car doors are manageable, repairing damage to composite structures presents an entirely different challenge. Even minor impacts—so small they’re invisible to the naked eye—can cause internal delamination. This can severely compromise the component’s strength. Such damage is harder to detect than metal cracks and typically requires specialized equipment like ultrasonic scanners, which is precisely why I call it difficult.
Repairs are no simple task. You can’t just weld it. If you’re trying to fix a carbon fibre panel, you’ve got to get the patch design right, make sure the surface is prepped properly, and then control the curing cycle. It’s a highly skilled process, not at all like traditional bodywork- See? This is truly beyond the capabilities of ordinary people.

Recyclability and Environmental Concerns
This could be the biggest challenge for composite materials. The thing is, composites are so durable because of their permanently cross-linked molecular structure, which comes from thermosetting polymer matrices. But that also makes them really tricky to recycle. Most composites can’t be melted down and reshaped like chocolate, unlike aluminium or steel. Most thermoset composites end up in landfills at the end of their service life.
We’re not quite there yet with making composites fully circular, but the industry is making good progress.

Choose NOBLE for Your Composite Materials Machining
You’ve seen the incredible potential of composite materials. Now’s the perfect time to find a trusted manufacturing partner! Our engineers are here to help you make your ideas a reality. Here at NOBLE, we get that composite processing isn’t just about cutting – it’s about precision, rigour, and technical know-how.
Why Partner with NOBLE for Your Composite Projects?
- Unmatched Expertise: We’re top of the class when it comes to: We’re all about the delicate art of composite machining. Our team knows a thing or two about carbon fibre, fiberglass and other advanced composite materials, so we can make sure you don’t get any nasty surprises like delamination, splintering, or heat damage.
- State-of-the-Art Technology: NOBLE puts money into the latest CNC machine tools, diamond-coated cutting tools, and advanced cooling technology, all specifically calibrated for composite materials. This makes sure every part gets a clean, precise, and high-quality surface finish.
- Commitment to Quality & Precision: From the first prototype to mass production, we keep a close eye on quality at every stage. After making constant improvements, we deliver components that fully meet your specifications and tolerance standards, ensuring they fit perfectly and function flawlessly in final assembly.
FAQ
What is the simplest definition of a composite material?
A composite material is created by combining two or more different substances to form a new material that is stronger and better performing than its individual components.
What is the biggest advantage of using composite materials?
Their best feature is their strength-to-weight ratio, which is second to none. They provide the structural strength of metals like steel but at a fraction of the weight. This means better fuel efficiency for vehicles and aircraft, and better performance for sports equipment.
Do you know if composite materials can be recycled?
This is a bit of a challenge. The most common composites use thermosetting resins, which are really hard to recycle. But the industry is coming up with new ways to do things, like using recyclable thermoplastic resins and better ways to get back valuable fibres, which makes things more sustainable.
What can NOBLE do for my project?
At NOBLE, we are a leading Chinese manufacturer specializing in the professional machining of advanced composite materials. We utilize our expertise in precision manufacturing to help you select the ideal materials and navigate complex fabrication processes. Our factory can do custom machining solutions, from making prototypes to mass production, so your project will get the most out of composite materials.








