Introduction
A part made by CNC machining is not really finished until it goes through proper post-processing.
The CNC machining process shapes materials with high accuracy. But even a well-machined part can have small issues like burrs or rough spots. That’s why CNC machining post-treatments matter. They help fix surface problems, improve corrosion resistance, and make the part stronger and better-looking. With good machined part finishing, the part becomes ready to handle real use. In this guide, we’ll explore the various CNC machining post-treatments and finishes, why they matter, and how they enhance both the performance and aesthetics of the final product.
Why Post-Processing Matters: 3 Key Perspectives
1. Engineering: Dimensional stability
CNC machining post-processing plays a big role in keeping parts dimensionally stable. It helps parts hold their shape and size, especially when they’re under pressure. For example, in aerospace, parts like brackets go through stress relief to stop any warping caused by the machining process. Skipping this can make the machined part finishing less accurate, and it might fail during operation, leading to expensive or even dangerous results.
Treatments like annealing or normalizing are key here. They make sure the part can deal with heat and pressure over time. In industries like aerospace and automotive, even small-sized errors can cause serious trouble. That’s why proper CNC machining post-processing and careful machined part finishing matter so much.

2. Economics: Cost of Skipping Treatments vs. ROI
CNC machining post-processing isn’t just a technical step—it’s a smart investment. Sure, skipping treatments might cut costs upfront, but it usually leads to bigger problems down the road. Take aluminum parts used near the ocean, for example. If they’re not anodized, they can corrode fast. That means shorter lifespans and more money spent fixing or replacing them.
On the other hand, spending a bit more on things like anodizing, coating, or passivation often pays off. These treatments make the part last longer and perform better over time.
Post-processing also saves money on maintenance. Adding a corrosion-resistant layer to a machined steel part can stop rust before it starts. That means fewer breakdowns and less time spent on repairs. When you invest in proper CNC machining, post-processing, and solid machined part finishing, you get parts that last longer, work better, and cost less to keep running.
3. Aesthetics: Visual and Tactile Value of Machined Parts
Looks matter—especially when the part is something customers will see or touch. CNC machining post-processing can take a plain part and make it look sharp and refined. Think about the MacBook from Apple. Those clean, chamfered edges don’t just look great—they show how much effort went into making the product feel premium.
In areas like cars, electronics, or high-end goods, appearance is just as key as performance. Machined part finishing techniques like polishing, brushing, or chroming help parts look sleek and professional. And it’s not just about looks. The right surface finish can also make a part feel smoother and more pleasant to hold, which adds to the overall user experience.

3. Commonly used surface treatments
Deburring and Edge Radiusing
Deburring is one of those CNC machining post-processing steps that you don’t want to skip. It gets rid of sharp edges, burrs, and small leftover bits from machining. Depending on the job, it can be done by hand, with machines like tumblers, or even by blasting it with high-temperature gas. The point is simple: smoother edges mean a safer, better-looking, and more functional part. It also makes the machined part finishing more complete and professional.
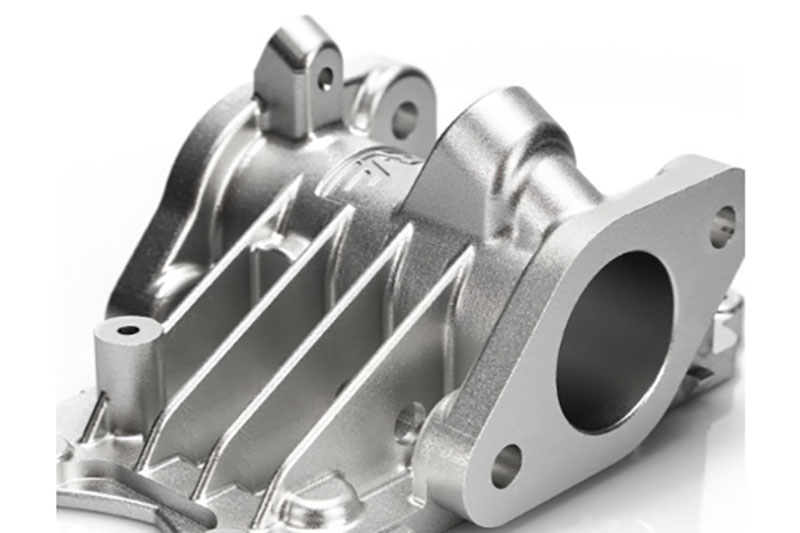

Polishing
Polishing takes things a step further. It’s all about making the surface smooth and shiny—almost like a mirror. This can be done with polishing wheels and compounds, or through electropolishing, which uses electricity and chemicals to clean up the surface. The result looks great, but it’s not just for show. A polished part also slides more easily, wears down less, and holds up better against corrosion. So, good polishing is more than just a final touch—it’s part of what makes the whole machined part finishing process work.

Glass Bead Blasting
Glass bead blasting is a great CNC machining post-processing step for cleaning up a part and giving it a nice, even texture. It works by shooting fine glass beads at the surface to smooth out any small flaws. It’s especially useful when you want a consistent surface without changing the part’s dimensions. This kind of machined part finishing adds a lot of visual appeal without messing with the function.
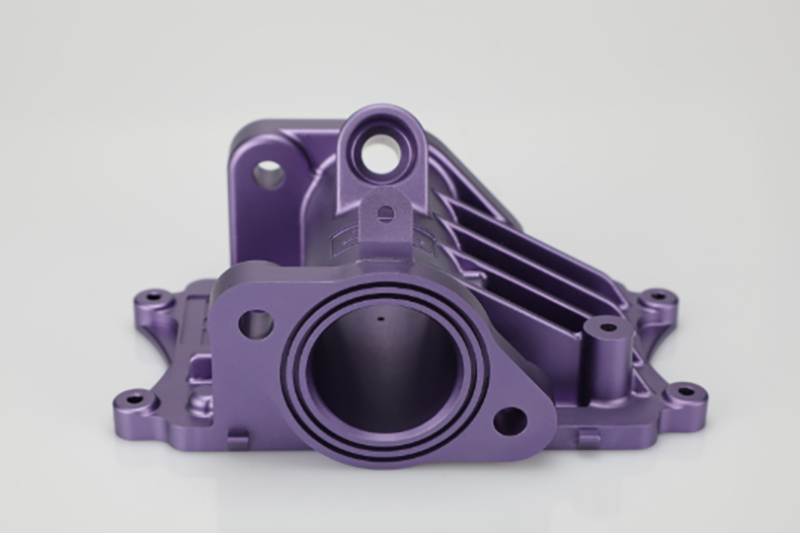

Anodizing (Oxygenation)
Anodizing—known as oxygenation—is a go-to CNC machining post-processing technique for aluminum parts. It uses electricity to build up a thicker oxide layer on the metal’s surface. That layer helps the part resist corrosion and wear, and it also holds dye well if you want to add color. Anodizing is common in industries like aerospace, automotive, and architecture, where parts need strong protection and solid machined part finishing to handle rough conditions.
Laser Engraving
Laser engraving is a go-to CNC machining post-processing step when you need sharp, permanent markings. It uses a focused laser to etch things like logos, serial numbers, or barcodes right into the surface. It’s super precise and doesn’t mess with the material itself. If you want your machined part finishing to include clean, professional labeling that lasts, this is a solid option.

Chemical Etching
Chemical etching is a clever way to shape or mark a part without touching it with a tool. Instead, chemicals remove tiny layers of material to create fine designs or adjust thickness. It’s great for parts that need complex detail, like in electronics or aerospace. As part of CNC machining post-processing, it adds high-level detail to the surface while keeping the finish smooth and stress-free. It’s another way to take machined part finishing to the next level.
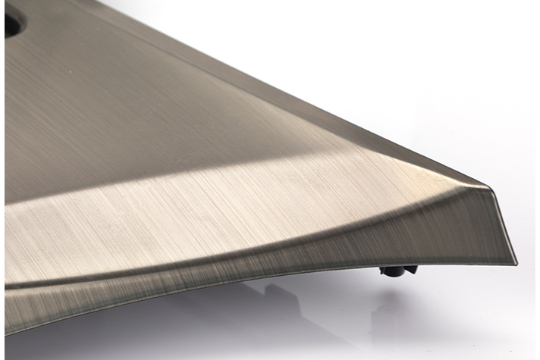
Brushing
Brushing is a simple but effective CNC machining post-processing technique that adds a clean, directional texture to metal surfaces. It’s done with abrasive pads or brushes that leave a soft, satin finish. This not only makes the part look better, but it also helps cover up small flaws and cuts down on glare. You’ll often see brushed finishes on aluminum or stainless steel parts where both looks and performance are important. It’s a reliable way to take machined part finishing up a notch.
Spray painting is a great option when you want a part to look good and hold up over time. It’s a CNC machining post-processing method that sprays paint or coating across the surface in a fine mist, giving it a smooth and even finish. It works well on big parts or complicated shapes. Besides offering a wide range of colors and finishes, spray painting also adds a layer of protection—like corrosion resistance—depending on the coating used. It’s a popular choice in industries like cars, electronics, and appliances where strong, attractive machined part finishing is key.

Electroplating
Electroplating is a well-known CNC machining post-processing step that adds a thin metal layer to a part using electricity. The part goes into a special solution, and metal from the solution sticks to its surface. This boosts things like corrosion resistance, durability, and even electrical conductivity. Metals like gold, silver, nickel, and copper are commonly used, depending on what the part needs. Whether it’s for electronics, auto parts, or just to give something a polished look, electroplating is a solid choice for strong machined part finishing.

Chrome Plating
Chrome plating is one of those finishes that makes a part stand out. It uses electroplating to add a thin layer of chrome to the surface, giving it a shiny, mirror-like look. But it’s not just about style—it also makes the part harder, easier to clean, and more resistant to wear and corrosion. There are two types: decorative chrome, which is mostly for looks and goes over nickel, and hard chrome, which is built for performance in heavy-use parts. It’s a go-to CNC machining post-processing method for everything from car parts to aerospace and industrial tools where durable machined part finishing matters.

Acid Pickling
Acid pickling is a helpful CNC machining post-processing step for cleaning up metal parts before they move on to other treatments. It works by soaking the part in an acid solution—usually something like hydrochloric or sulfuric acid—to strip away rust, scale, and surface oxides. It gets the part ready for things like electroplating or painting by giving it a clean base. Just keep in mind, it might slightly etch the surface, which can affect tight tolerances. It’s especially common in prepping stainless steel and other steel components for solid machined part finishing.
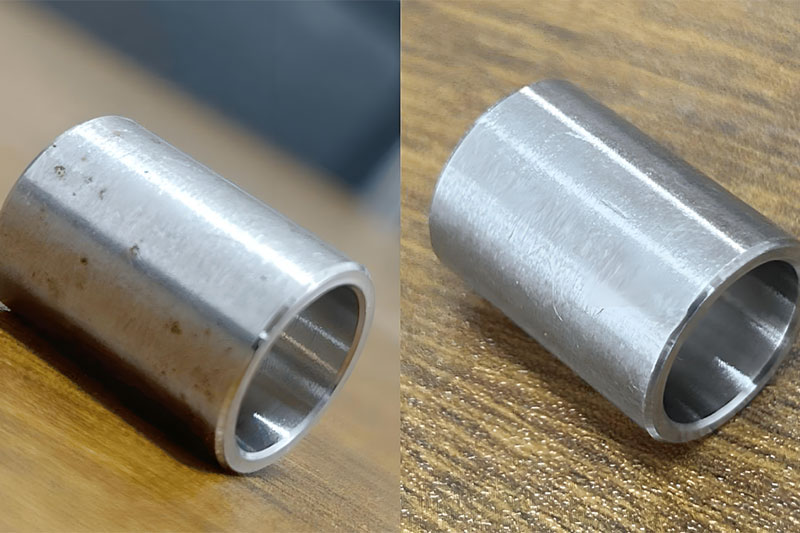

Passivation
Passivation is another smart CNC machining post-processing technique, especially for stainless steel. The part goes into an acid bath—often with citric or nitric acid—to clean off surface iron and contaminants. That reaction helps build a protective oxide layer, which boosts corrosion resistance. It’s great for parts that will be used in tough conditions, like marine gear, food equipment, or pharma machinery. With proper passivation, the machined part finishing holds up longer and needs less upkeep over time.

Silk-Screen Printing
Silk-screen printing is a flexible CNC machining post-processing step for adding graphics to metal parts. It works by pushing ink through a screen, with blocked areas keeping the design clean and sharp. It’s great for logos, labels, or patterns on flat or slightly curved surfaces. You get bold colors and durable prints, which makes this a smart choice when you want your machined part finishing to stand out and last.
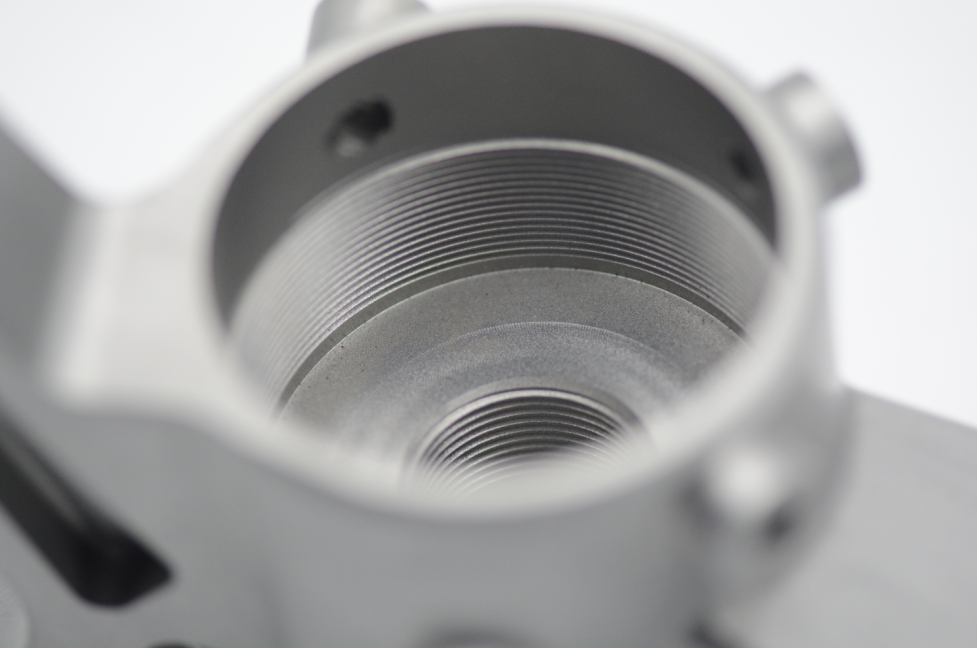

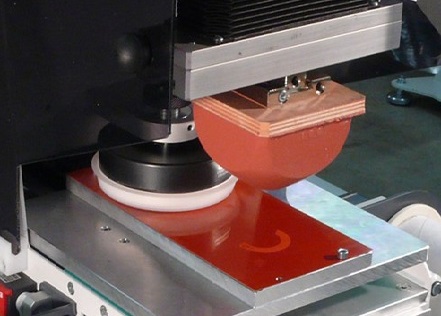
Pad Printing
Pad printing is perfect for those tricky, not-so-flat parts. It’s a CNC machining post-processing method that uses a soft silicone pad to stamp designs onto uneven or curved surfaces. The image is picked up from a printing plate and transferred onto the part. This is super handy for printing on things like pens, golf balls, or medical tools. It’s used a lot in industries that need clean, consistent markings on complex shapes. If you’re looking to add branding or functional labels as part of your machined part finishing, pad printing gets the job done where other methods can’t.

4. Common Mistakes to Avoid
In CNC machining post-processing, there are a few common mistakes that can affect part quality and add unnecessary costs:
- Inadequate Machine Setup and Calibration: If the machine is not set up or calibrated correctly, it can cause dimensional issues and poor finishes.
- Ignoring Material Properties: Every material behaves differently. Using the wrong tools or settings can lead to tool wear, part damage, or less-than-ideal finishes.
- Neglecting Tool Maintenance: Worn-out or dull tools can damage the surface quality and slow down the machining process. It’s important to keep tools checked and maintained regularly.
- Improper Cutting Parameters: Incorrect speeds, feeds, or cut depths can cause tool wear, surface imperfections, or even distortion of the part.
- Poor Design for Manufacturability: When designs don’t take machining constraints into account, it can lead to more complex and costly processes.
To avoid these problems, careful planning is key. Understand the material properties, keep tools in good shape, and design with manufacturing limits in mind to improve CNC machining post-processing and ensure high-quality machined part finishing.

5. Future Trends
The CNC machining industry is constantly changing, with a few big trends leading the way:
Advanced Automation and Robotics: Collaborative robots (or cobots) are stepping in to handle tasks like material loading, secondary operations, and quality checks. This makes the whole process faster and helps minimize downtime.
Internet of Things (IoT) and Industry 4.0: Thanks to better connectivity, it’s now easier to monitor machines in real-time, predict maintenance needs, and optimize processes, making production smoother and more efficient.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI is helping analyze CNC machining data to make smarter decisions. It can optimize tool paths, predict tool wear, and improve precision, all while cutting down on waste.
Additive and Hybrid Manufacturing: By combining additive manufacturing with traditional CNC machining, manufacturers can create more intricate designs and structures with better flexibility and efficiency.
Enhanced Software and Simulation Tools: CAD/CAM software is getting better and better, allowing for more accurate simulations, better designs, and optimized tool paths. This helps reduce errors and cuts down on the time spent in CNC machining.
These trends are pushing the CNC machining industry toward smarter, more efficient, and sustainable manufacturing practices, which is great for both productivity and the environment.
6. Conclusion
CNC machining post-processing is crucial for achieving the desired part quality and performance. By understanding and avoiding common mistakes, staying informed about emerging trends, and selecting appropriate post-processing methods, manufacturers can enhance efficiency and product quality.

NOBLE-Your Trusted CNC Machining Partner
At NOBLE, we specialize in providing comprehensive CNC machining services, including precision post-processing solutions to meet the diverse needs of our clients.
Provide perfect CNC machining solutions for complex geometric parts at competitive prices. With many years of rich CNC machining experience, we provide customers with unparalleled high-precision CNC machining parts. Get a quote in minutes and parts in days.









