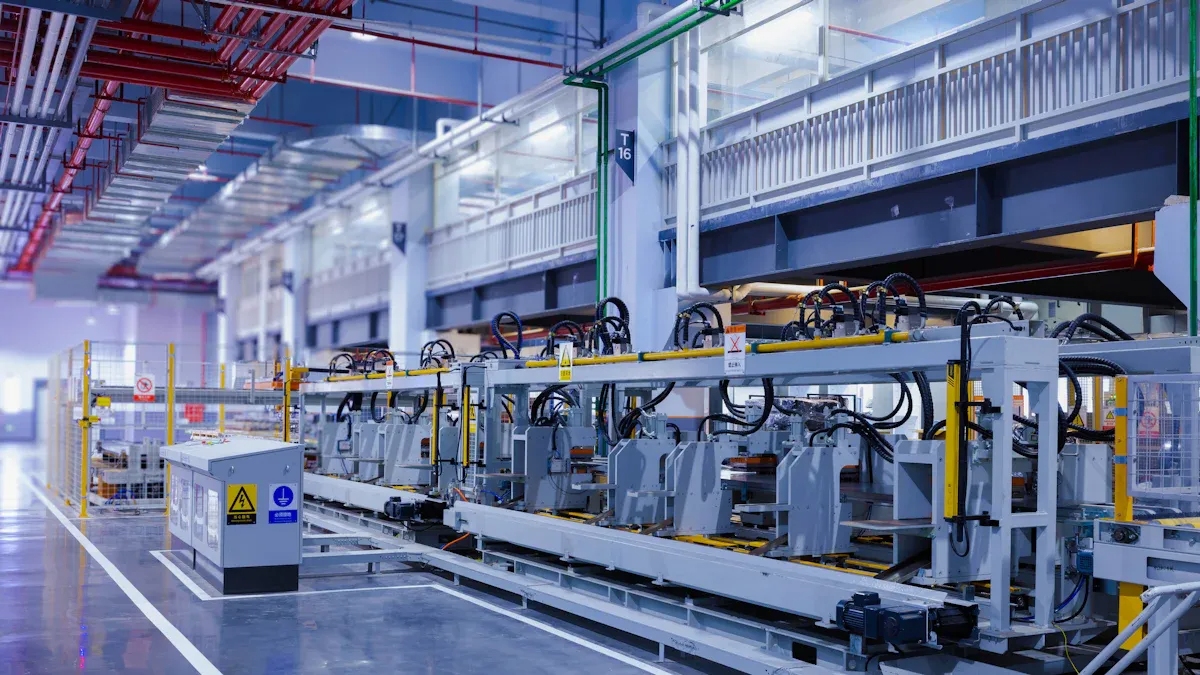
The production of automotive parts is one of the most critical segments within the entire automotive industry. The global layout of assembly lines and modern mass production methods has profoundly impacted this sector. Notably, the majority of parts used on automotive production lines are manufactured near the assembly plants, effectively reducing the cost of transporting parts from the automaker’s central warehouse. The industry keeps growing. In 2024, the market size reached US$454.7 billion, with steady growth ahead.
| Attribute | Value |
| Market Size in 2024 | US$454.7 Billion |
| Forecasted CAGR (2024-34) | 3.9% |
While manufacturing automotive parts for new vehicle assembly remains the industry’s core function, producing replacement parts is equally vital. In other words, every vehicle requires part replacements throughout its lifecycle. This universal reality means demand for automotive parts is nearly equivalent to the demand for brand-new parts installed in new vehicles.

Automotive Parts Manufacturing Overview
Industry Trends
The automotive parts manufacturing sector is currently undergoing a significant transformation. The growing popularity of electric vehicles necessitates a greater focus on producing electric motors and battery systems. Many companies are adopting modern smart factories equipped with robotic arms and artificial intelligence, tools that not only enhance production efficiency but also enable early defect detection.
The following trends warrant attention:
- Demand for eco-friendly automotive parts is surging. Market needs can be met through the use of recycled or biodegradable materials.
- 3D printing enables rapid customization of parts and prototypes, achieving complex structures difficult with traditional methods.
- Rapid advancements in automation and AI allow smart equipment to effectively save time and costs.
- The growing prevalence of autonomous vehicles requires companies to master manufacturing techniques for new sensors and electronic parts.
Common types of automotive parts
When entering automotive parts manufacturing, you’ll encounter a vast array of parts. The most common include:
- Transmission system parts: Gears, wheels, etc.
- Engine parts: pistons, valves, fuel systems, etc.
- Braking systems: calipers, brake discs, brake pads, etc.
- Body and chassis parts
- Electrical/electronic parts: starter motors, spark plugs, etc.
- Suspension and steering parts
- Interior systems: dashboards, seats, etc.
Manufacturers worldwide continuously produce a wide array of automotive parts—both traditional and cutting-edge. If you need precise parts, CNC machining is the way to go, and if you’re after something lighter, aluminum die-cast manufacturers usually have you covered. Custom machining is a favorite for those unique or high-performance parts.
Here’s a quick look at the main groups in the industry:
| Segment Category | Segments / Examples |
| Product Type | Engine Parts, Drive Transmission & Steering, Body Chassis, Suspension & Braking, Equipment, Electrical & Electronic Parts, Others |
| Distribution Channel | OEMs, Aftermarket (online, offline) |
| Vehicle Type | Passenger Cars, Light Commercial Vehicles, Heavy Commercial Vehicles, Two-wheelers, Three-wheelers |
The field is very big, so you have many choices as you grow your business.

Automotive Parts Manufacturing Processes
CNC Machining
When manufacturing automotive parts, CNC machining is nearly the optimal choice. Essentially, you have these high-tech, computer-controlled machines that can precisely cut, shape, and finish metal or plastic. It’s super reliable, and the parts always fit perfectly. Many Chinese automotive parts manufacturers, such as NOBLE, confidently offer CNC machining services, handling everything from small orders to large-scale production runs.
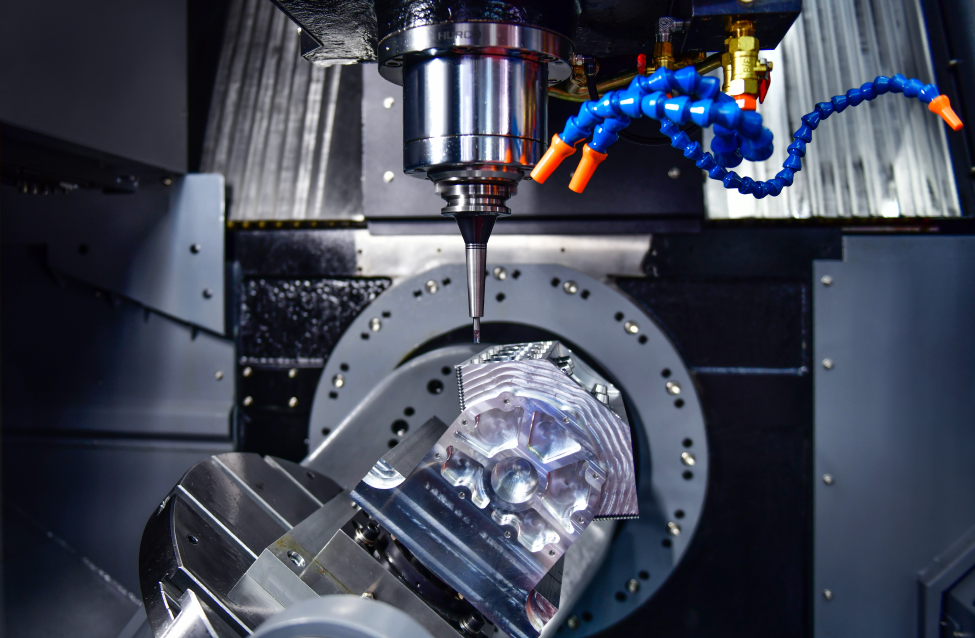
Why should you choose CNC machining for your automotive parts? Let me tell you:
- It’s super fast—machines run non-stop, so production never slows down.
- The parts come out with perfect accuracy, which is crucial for both safety and performance.
- Once you set it up, you can produce the same part again and again with zero errors.
- Your team can focus more on designing and brainstorming new ideas instead of dealing with the nuts and bolts of manufacturing automotive parts.
- And in the long run? It saves you money because the whole process is efficient.
But, there are a few things to keep in mind:
- The machines can be pretty expensive up front.
- Some shapes, like deep holes or undercuts, are tricky to make.
- Complex parts can take longer to finish.
- Not every material works with every machine, so you have to be selective.
- You’ll need skilled workers who know how to operate and fix the machines.
- There can be waste material generated during the automotive parts manufacturing process.
If you really want to set yourself apart, focus on precision and custom machining. Those skills will help you craft special parts for high-performance vehicles.
Injection Molding
If you want to produce large quantities of identical plastic parts, injection molding is your best bet. You simply heat the plastic, force it into a mold, and let it cool. It’s fast and ideal for items like dashboards, buttons, and covers.
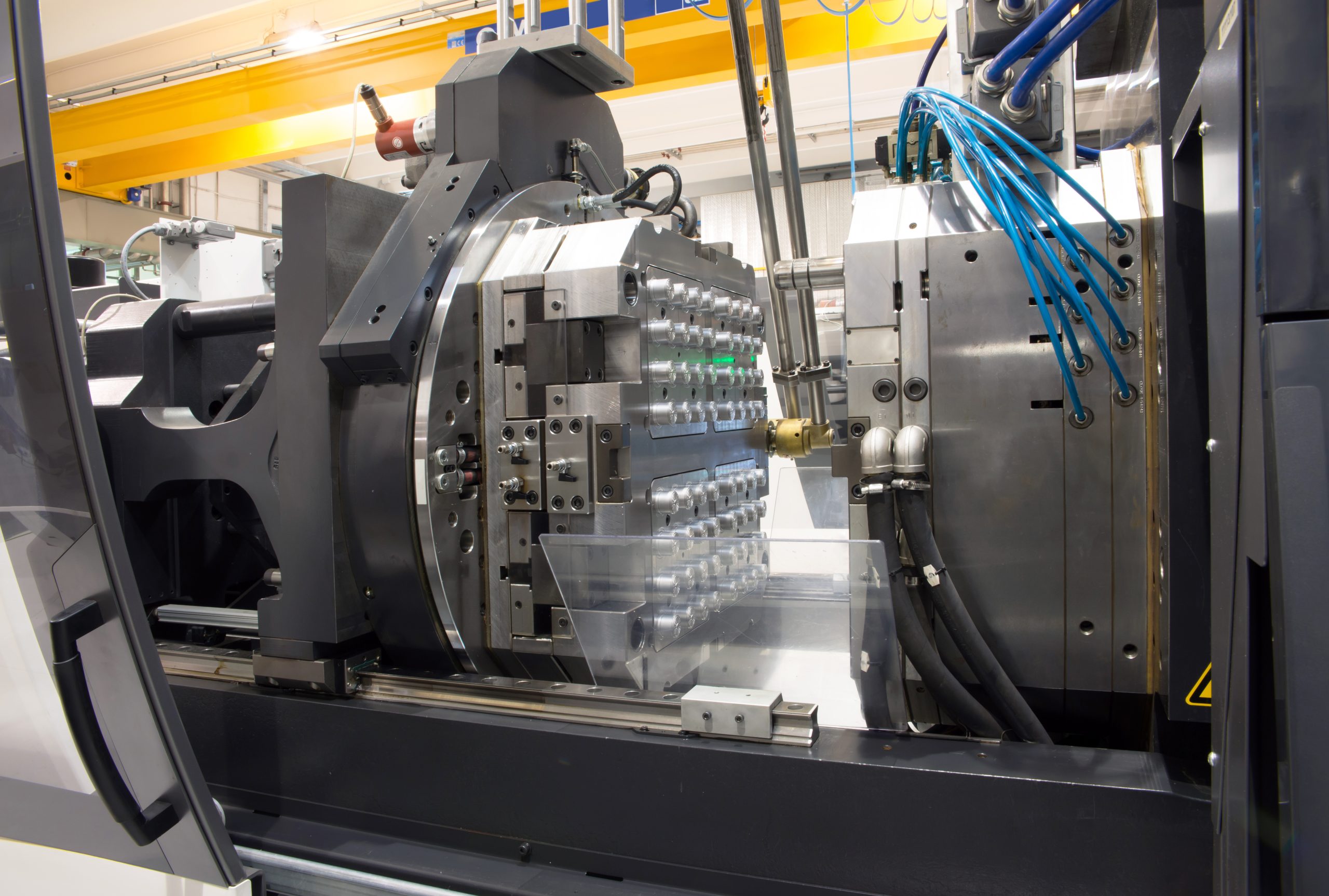
The best part? The more parts you make, the cheaper each one becomes. The table below shows how prices decrease as production volume increases:
| Production Volume | Number of Parts | Mold Cost | Material Cost per Part | Labor Cost per Part | Total Cost per Part |
| Low Volume | 100 | $100 | $0.50 | $3.00 | $4.50 |
| Medium Volume | 5,000 | $2,500 | $0.50 | $2.00 | $3.00 |
| Large Volume | 100,000 | $25,000 | $0.50 | $1.00 | $1.75 |
If you’re manufacturing thousands (or even hundreds of thousands) of automotive parts, the cost per part can drop to $1 to $3. That’s why injection molding is a reliable choice for large automotive parts manufacturing projects.
Quick tip: Want to get into aluminum die casting? You can use the same high-volume approach to reduce costs!
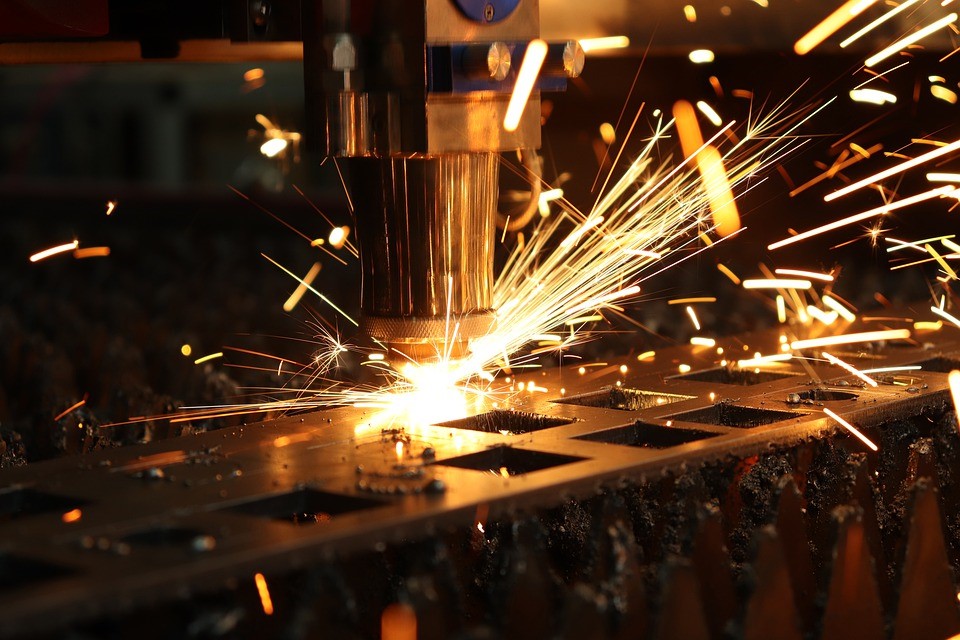

Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet metal fabrication is ideal for creating sturdy, lightweight parts from metal sheets. You can cut, bend, and shape metal to precisely manufacture the automotive parts you need. This is a preferred process in both small shops and large factories.
You’ll find sheet metal fabrication used for:
- Body panels like hoods, doors, and roofs
- Chassis and frame parts
- Heat shields to protect from engine heat
- Fuel tanks
- Brackets and enclosures
Sheet metal fabrication is the preferred choice for numerous automotive parts manufacturers due to its versatility, making it suitable for nearly all vehicle types. If you have a creative vision, you can contact NOBLE to add unique shapes or features to your parts through custom fabrication.
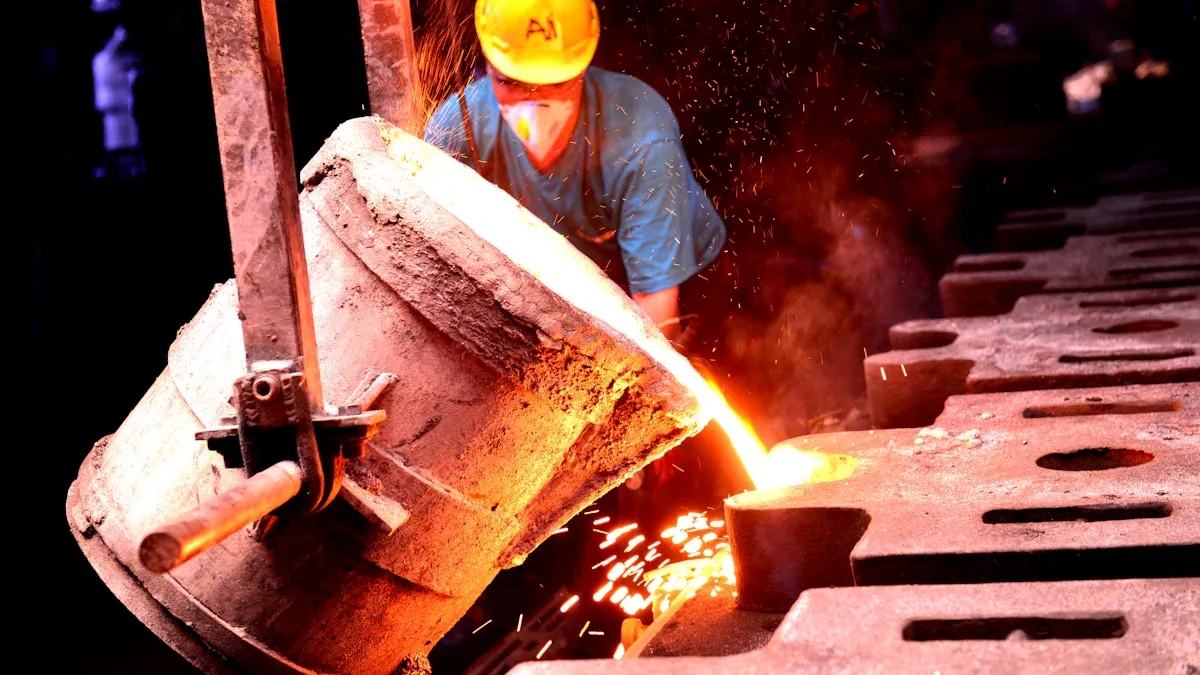

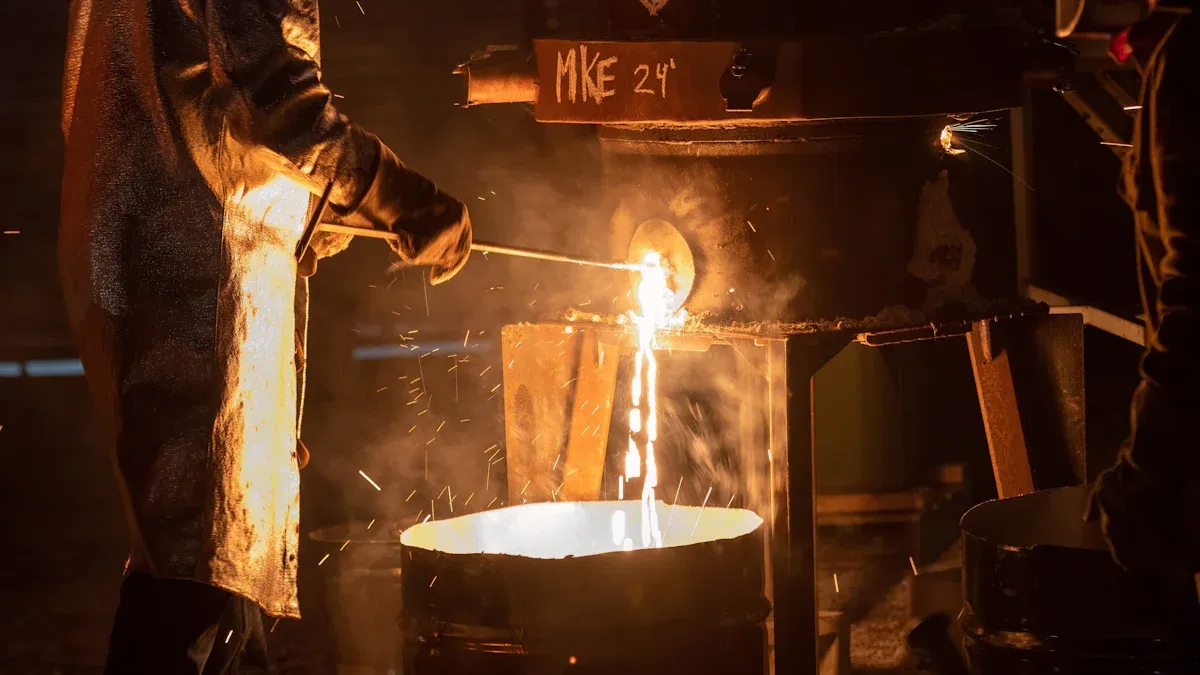
Die Casting
If you need lightweight yet sturdy metal parts, die casting is your best bet. The process of automotive parts manufacturing is straightforward: melt the metal, pour it into a mold, and let it cool. It’s fast and ideal for producing large quantities of parts at once.
Why die casting is awesome for automotive parts:
- You get lightweight parts that help cars burn less fuel.
- It can create complex shapes with tight tolerances.
- You can make thousands of parts in no time, saving you money.
- The parts are tough and built to last.
- Metal recycling is part of the automotive parts manufacturing process, making it eco-friendly.
- You can replace several smaller parts with one large piece, which makes assembling the car easier.
- Die casting works for a variety of parts, from wheels to engine parts to covers.
If you want to dive into aluminum die casting, it gives you the tools to produce high-quality parts for today’s modern vehicles. Die casting gives you the power to create parts that are both strong and precise—exactly what modern car makers and drivers need!

Materials Used in Automotive Parts Manufacturing
So, when manufacturing automotive parts, selecting the right material is a critical decision. The material you choose impacts everything—from strength to weight to the part’s lifespan. Let’s explore the metals and plastics most commonly used in this industry.
Metal
Metals are essential in nearly every vehicle. They’re the backbone of strength and longevity. Here’s a table that shows where each metal works best:
| Metal | Common Uses in Cars | Key Properties |
| Steel | Engine blocks, seats, body panels, suspension | Strong, durable, many grades, cost-effective |
| Aluminum | Wheels, engine blocks, chassis, transmission housings | Lightweight, good for fuel economy, corrosion-resistant |
| Titanium | Brake rotors, wheels, and racing vehicles | Super strong, light, resists rust, high cost |
| Copper | Electrical parts, cooling systems, brake pads | Great for electricity and heat, resists corrosion |
Steel
Steel is everywhere in cars—the frame, body panels, suspension. It’s tough, and there are different types. Some steel bends easily, while other types are extremely resilient. CNC machining or custom fabrication is ideal for shaping steel. It can withstand intense heat, but it’s heavier than other metals.
Aluminum
Aluminum is lighter than steel, helping vehicles save fuel. You’ll find it in parts like wheels, engine parts, and chassis. Many Chinese manufacturers choose aluminum for automotive parts manufacturing because it’s strong yet lightweight. If you plan to produce die-cast aluminum automotive parts, this is an excellent choice.
Titanium
Titanium is ideal for racing vehicles. It’s lightweight, exceptionally strong, and resists corrosion even in harsh conditions. It excels in cutting high-performance parts where weight reduction is critical. Precision machining is essential for working with titanium.
Copper
Copper is the top choice for electrical parts. It excels at conducting both electricity and heat. It’s commonly used in automotive wiring, radiators, and braking systems. Copper resists corrosion, ensuring long-term reliability.
Plastics
Today, while metals remain indispensable in automotive parts manufacturing, plastics are equally hard to ignore—they’re present in numerous vehicle parts. They’re ideal for making cars lighter, which helps improve fuel efficiency. The coolest thing about plastics is their ability to be molded into virtually any shape. This makes them perfect for parts like dashboards, bumpers, and covers. The table below lists some of the most common plastics and their applications:
| Plastic Type | Where You’ll Find It in Cars | Why It’s Used |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Dashboards, bumpers, wire covers | Easy to mold, flame-resistant |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Bumpers, carpet fibers, cable insulation | Durable, lightweight, resists chemicals |
| Polyurethane (PU) | Tires, seats, suspension brushes | Tough, handles wear and tear |
| ABS | Dashboards, wheel covers | Strong, shiny, heat-resistant |
| Nylon | Engine covers, air intake, coatings | Wears well, strong, stable in heat |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | Headlight lenses, sunroofs, bumpers | Hard, clear, resists weather |
Product Development
Prototyping
Prototyping is the process of turning your ideas into tangible objects you can hold in your hands. Start by sketching your automotive part or creating a digital version. Next, select an appropriate material—consider whether it needs to be ultra-strong or lightweight. Also, think about its intended use. If it’s for safety, you’ll need a material that can withstand significant impact.
To create prototypes, consider tools like CNC machining, 3D printing, or vacuum casting before automotive parts manufacturing. These methods let you rapidly build parts with intricate details. Many Chinese automotive part manufacturers rely on these techniques for fast, precise results. For unusually shaped parts, custom machining might be your best option. If needed, contact NOBLE—let us help turn your vision into reality!
Here’s a simple step-by-step guide: First, sketch your idea or create a model. Next, select the appropriate material. Then, build your prototype using CNC or 3D printing. Test its fit and strength—adjust it if anything feels off. Once everything looks good, prepare for mass production by fine-tuning your tools and processes. Finally, thoroughly inspect your prototype for safety and high quality.
Testing & Quality Control
Testing and quality control are crucial for ensuring the safety and reliability of automotive parts. After automotive parts manufacturing, you need to test how parts perform under real-world conditions—think actual vehicles and harsh environments. First, test their performance in high temperatures, low temperatures, and humidity. You’ll also want to check how they handle vibration, pressure, and impact.
Don’t forget electrical performance and safety standards! Visual inspections, precise measurements, and even X-ray testing help uncover any potential issues. Many automakers adhere to this process of automotive parts manufacturing to ensure their products are robust and dependable.
Here is a table of common quality standards:
| Standard | What It Does | Why It Matters |
| ISO 9001 | Manages quality for all products | Keeps customers happy |
| IATF 16949 | Focuses on the auto industry quality | Prevents defects, improves supply |
| ISO 14001 | Manages environmental impact | Reduces waste and emissions |
| ISO 26262 | Checks safety for electronics | Protects drivers and passengers |
| SAE J1739 | Finds possible failures | Makes parts safer and more reliable |
Challenges in Automotive Parts Manufacturing
Cost Management
Handling costs is a big challenge for everyone. You must know where your money goes each day. Watch these main things that affect your costs:
- Raw material prices fluctuate rapidly. Steel, aluminum, and plastic may rise or fall based on market conditions or trade regulations.
- Labor costs encompass not only wages but also benefits and training. Automating processes with robots or CNC machining can help reduce labor expenses. Some companies achieve savings of up to 20% through this approach!
- Safety and emissions regulations require significant investment in research. For example, U.S. companies are heavily investing in new battery technologies.
- The more parts produced in a single run, the lower the cost per unit. Large corporations adopt this approach to reduce expenses and maintain a competitive advantage.
- While new technologies like precision manufacturing may involve higher upfront costs, they deliver long-term savings.
- Supply chain disruptions, such as chip shortages, can delay production and drive up expenses.
Here is a table that shows common costs:
| Cost Area | What It Covers | Typical Range |
| Raw Materials | Metals, plastics | $200,000 – $500,000 |
| Salaries and Wages | Labor and administration | $100,000 – $300,000 |
| Rent or Lease Payments | Factory or workshop space | $50,000 – $150,000 |
| Utilities | Power, water, waste | $10,000 – $30,000 |
| Marketing and Advertising | Trade shows, ads | $5,000 – $25,000 |
| Insurance | Equipment, property, liability | $5,000 – $20,000 |
| Maintenance and Repairs | Machines and tools | $20,000 – $50,000 |
To cut costs, try these strategies:
- Use precision manufacturing and just-in-time inventory to reduce waste.
- Purchase robots for high-frequency repetitive tasks.
- Collaborate with suppliers to secure better pricing.
- Train your team to identify and resolve issues early.
- Use data to monitor your spending and find ways to save.

Competition
There are tons of companies manufacturing automotive parts these days—over 10,000 worldwide! The top 100 suppliers are mainly from places like Japan, China, the U.S., Germany, and South Korea. You’ll be going up against both giant companies and small businesses.
Here are a few big challenges you’ll face:
- Big companies make tons of parts, so their costs are way lower. This is called economies of scale.
- People trust well-known brands, so building your reputation takes time.
- Technology is always changing. You’ll need to keep learning and upgrading your tools.
- Starting your business takes serious money for machines, research, and advertising.
- There are a lot of rules—safety, emissions, patents—you’ll need to follow all of them.
- Building a solid supplier network is tough since the big guys already have established relationships.
- The market is crowded, so you’ll need to carve out a niche—maybe custom machining or focusing on aluminium die-cast automotive parts.

Why Choose NOBLE for Automotive Part Manufacturing
Looking to kickstart or expand your business? You need a partner whom you can count on. NOBLE, a leading manufacturer in China, has built a solid reputation for top-quality products and exceptional service. With over ten years of experience, we combine cutting-edge tech with skilled craftsmanship to help you grow.
Here’s why NOBLE is special:
- Rapid prototyping and small-batch production services to quickly test your ideas and speed up the process of automotive parts manufacturing.
- Precision CNC machining (turning, milling) and custom machining services to ensure every part is spot-on.
- In-house production, so no need to rely on third-party suppliers. We usually deliver projects in just 7-10 days.
- Need a quote? We provide real-time pricing within 24 hours for fast and efficient planning.
- From sheet metal fabrication to injection molding, surface finishing, and aluminum die-cast automotive parts, we’ve got a wide range of services.
- Quality is at the heart of everything we do. With ISO 9001 and ISO 13485 certifications, we put every product through thorough inspection to make sure it’s top-tier.
- Our expert team is always on standby, ready to provide support and advice on all the details.
- Thanks to our global supply network, we can deliver your parts quickly, no matter where you are.
If you want to partner with China’s top automotive parts manufacturer, look no further than NOBLE. From initial prototypes to large-scale production, we provide all-around support and smart solutions to ensure your ideas become a reality. Our precision manufacturing and outstanding service make us the reliable partner you need for success.
Through careful planning, adherence to standards, and continuous learning, you can build a brilliant future in this industry. Below are the key elements for achieving long-term success:
- Upskill your team and teach them new technology.
- Work with schools to find skilled workers.
- Use AI and robotics training for better results.
- Build a culture of quality and teamwork.
Ready to take the first step? Reach out to NOBLE for expert support and start your journey with confidence.
FAQ
What skills do you need for automotive parts manufacturing?
You must know how machines work. Learn about CNC machining and custom machining. It is important to follow safety rules. Practice precision manufacturing every day. Many automotive parts manufacturers in China frequently utilize these skills.
How do you choose the right material for car parts?
Select materials based on their strength, weight, and cost. Steel and aluminum are good for most parts. If you want lighter parts, try the aluminium die-cast automotive parts manufacturer methods. Ask experts if you are not sure.
Why is quality control important in automotive parts manufacturing?
Quality control makes sure your parts are safe and strong. You test each part for fit and strength. Automotive parts manufacturers use strict checks to find problems. Precision manufacturing helps you avoid mistakes and build trust.
Can small businesses compete with big automotive parts manufacturers?
Yes, small businesses can compete with big ones. You can focus on custom machining or give fast service. Use CNC machining for special orders. Many small automotive parts manufacturers in China find their own niche.
What is the first step to start an automotive parts manufacturing business?
Begin with market research to learn about the industry. Write a business plan to guide your steps. Learn about CNC machining and precision manufacturing. Find suppliers and set up your workshop. Talk to other automotive parts manufacturers for advice.










