What is ABS CNC Machining?
ABS CNC machining is a process that uses CNC equipment to precisely process ABS plastic blanks into custom parts or prototypes through methods such as cutting, boring, and CNC milling. It is a subtractive manufacturing technology that achieves the desired shape by removing excess materials.
In simple terms, you can imagine it as a computer-controlled, extremely precise “engraving knife” that is carving on a piece of ABS plastic, ultimately creating a high-precision part
Understanding the Properties of CNC-Machined ABS
Excellent Toughness
ABS is highly favored in CNC machining, and the core lies in its outstanding balance of strength and toughness.
ABS parts machined by CNC can not only withstand considerable static loads, but also are less prone to brittle fracture when subjected to sudden impact or vibration. Instead, they absorb energy through slight deformation. This characteristic of ABS makes it highly suitable for manufacturing functional prototypes, housings, and tooling fixtures that need to withstand daily wear and tear, assembly stress, or minor impacts.
Superior Dimensional Stability
In precision machining, the dimensional stability of materials is of vital importance, and ABS performs well in this aspect.
ABS is not sensitive to changes in environmental temperature and humidity during machining and subsequent use, and has a low hygroscopicity. Therefore, the expansion or contraction rate caused by environmental changes is very small. This feature ensures that the parts machined by CNC can maintain the precise dimensions and geometries specified at the design stage for a long time, which is an indispensable advantage for assemblies that require strict tolerances and high-precision prototypes.
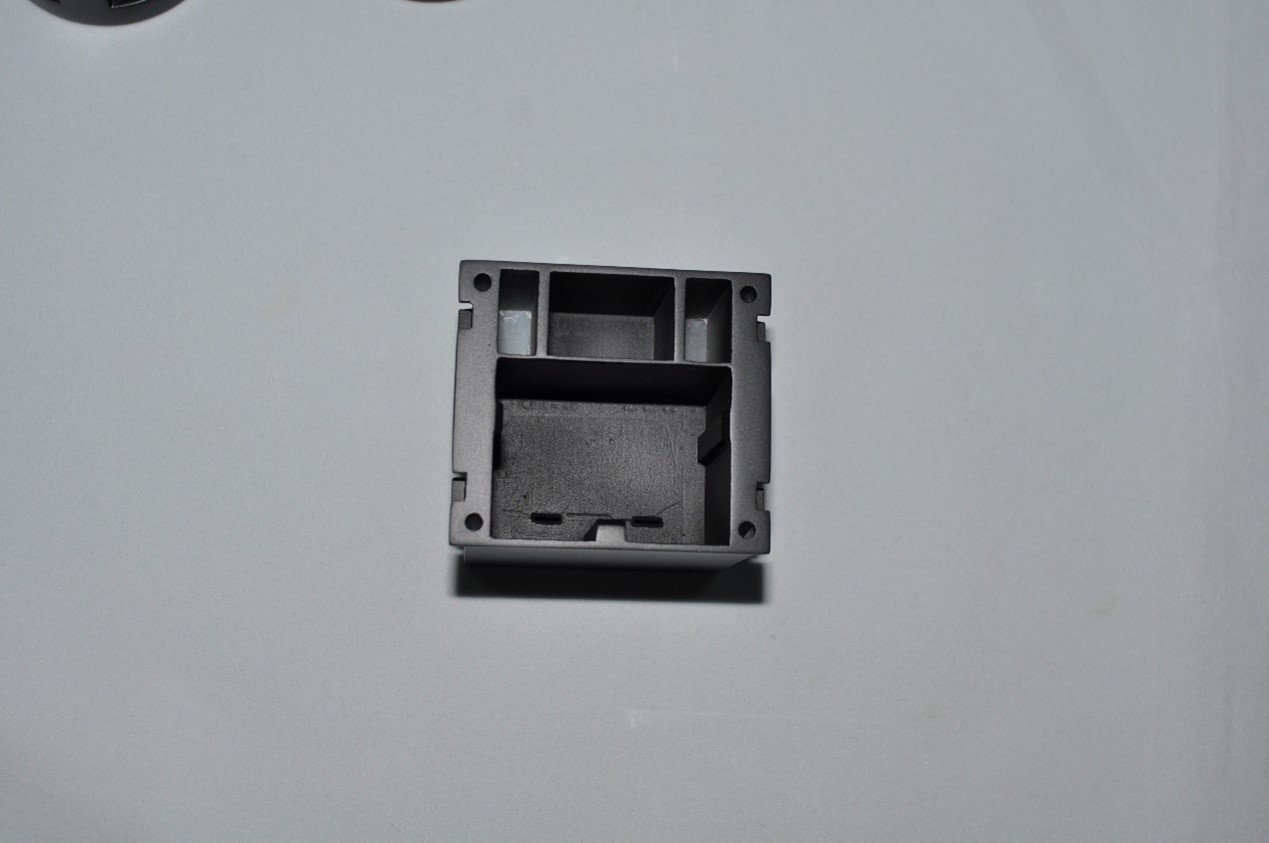

Excellent Surface Finishing
ABS plastic offers unparalleled surface treatment possibilities for CNC-machined parts. ABS plastic itself is a uniform material. After machining, its surface becomes relatively smooth. More importantly, it has excellent adhesion to various paints, coatings, and adhesives.
Whether it is necessary to spray a single color, achieve complex multi-color patterns, or perform metal electroplating to obtain a metallic texture appearance, ABS is an ideal substrate.
Great Machinability
ABS material is relatively soft but also tough, which makes it exhibit excellent cutting performance in CNC machining processes. Machine tools can perform machining at a relatively high feed rate and rotational speed, while the degree of tool wear is much lower than that when machining metal materials.
Under the correct parameters, ABS will produce clean and continuous chips instead of powder or adhered meltules, which is conducive to chip removal and obtaining a smooth machined surface.
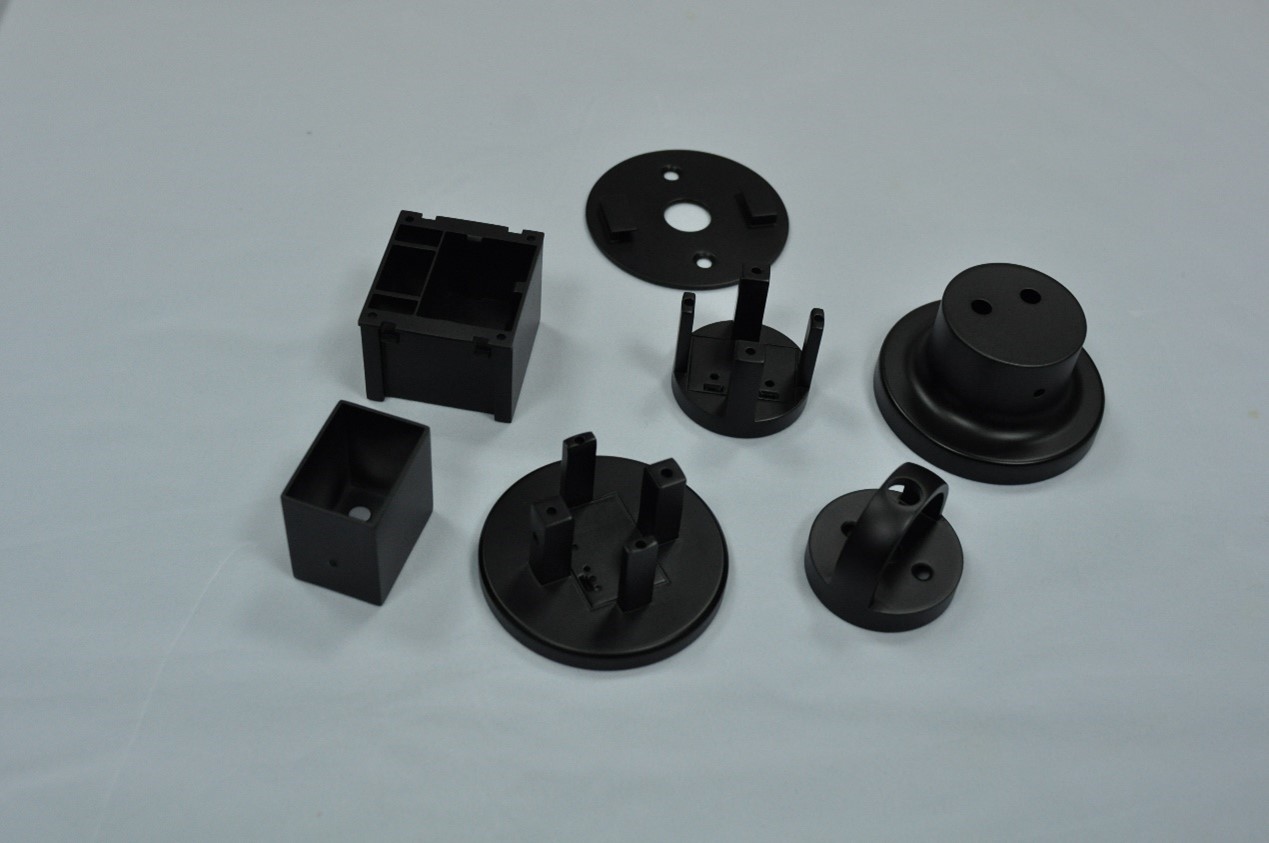

Chemical Resistance
ABS parts machined by CNC have excellent chemical resistance, especially being resistant to dilute acids, dilute alkalis, and various inorganic salt solutions.
ABS is also an excellent electrical insulating material. It does not conduct electricity and is not easily affected by humid environments in terms of its insulating performance. Therefore, it is widely used in the field of electronics and electrical engineering and is often used to process electrical appliance casings, sockets, circuit breaker covers, etc. It can effectively protect internal components and prevent the risk of electric shock, taking into account both safety and functionality.
Benefits of Using ABS Plastic for CNC Prototyping and Parts
Significant Cost-Effectiveness
From the perspective of raw materials, ABS plastic itself is relatively inexpensive. Combined with its easy-to-process characteristics (short machining time and long tool life), the overall manufacturing cost of a single part is highly competitive.
For small-batch production or prototype making, ABS CNC machining is far more economical in cost than mold injection molding. At the same time, it outperforms many 3D printing technologies in terms of performance and appearance, achieving the optimization of cost performance.
Excellent Dimensional Stability
ABS plastic is not sensitive to changes in temperature and humidity during machining and use, and has a low moisture absorption rate. Therefore, it can maintain the long-term stability of its shape and size. This feature is crucial for high-precision prototypes and parts. It ensures that the parts will not undergo significant deformation or dimensional deviation due to environmental changes after machining, guaranteeing the accuracy of assembly and the reliability of functionality.
Lightweight
ABS has a low density and can produce lightweight parts, which is of great significance in fields such as automobiles, aerospace, and portable devices. Through CNC machining, multiple functional components such as clips, hinges, and mounting seats can be easily integrated into a single complex part, reducing assembly requirements, simplifying product design, and enhancing the integrity of the overall structure.
Choosing a Material: ABS, Acrylic (PMMA), or Delrin (POM) for CNC?
ABS
Pros:
An excellent strength-toughness balance
Outstanding machinability
Excellent post-processing capabilities
High cost-effectiveness
Cons:
Poor weather resistance
Moderate heat resistance
Opacity
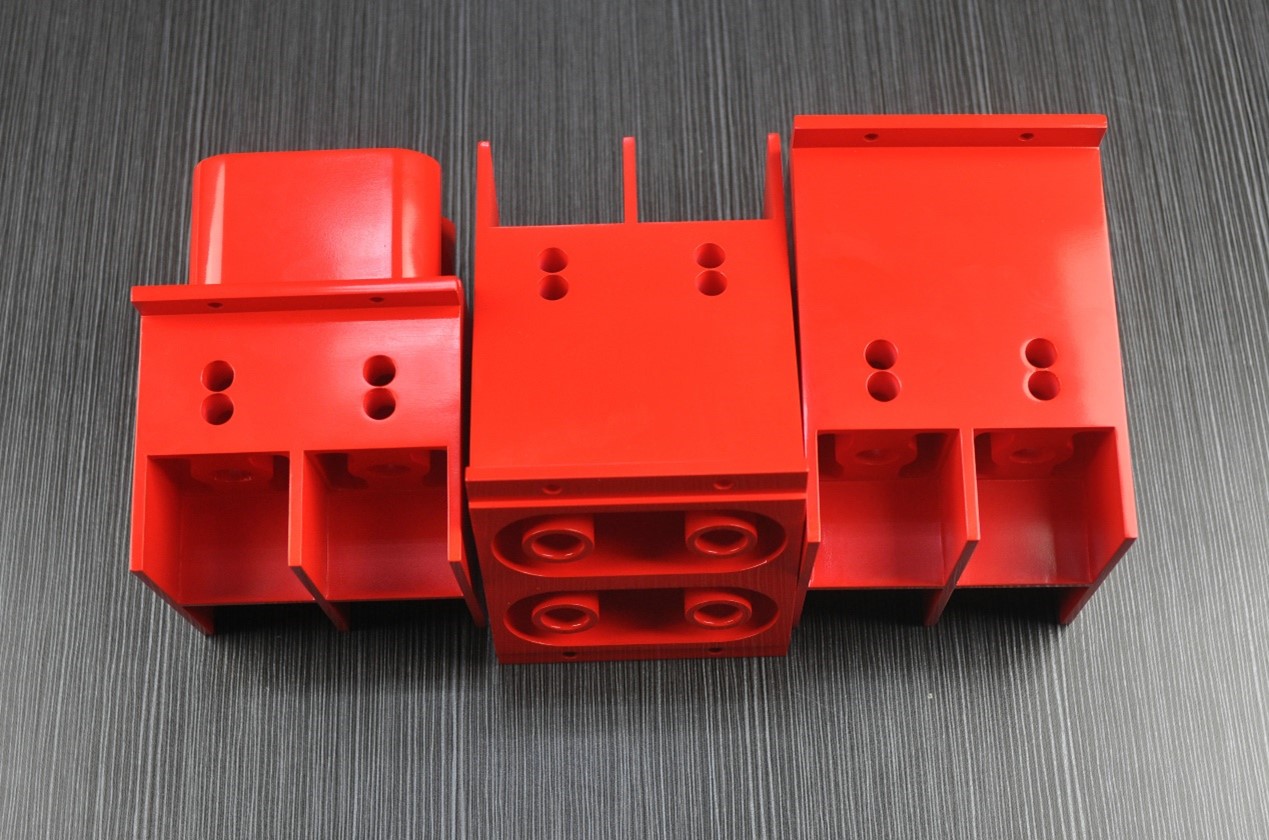

Acrylic(PMMA)
Pros:
Excellent transparency and optical properties
Outstanding weather resistance
High surface hardness and scratch resistance
Cons:
Poor impact resistance
Limited chemical resistance
Susceptibility to cracking and internal stress during machining
Delrin(POM)
Pros:
Excellent rigidity, strength, and wear resistance
Outstanding dimensional stability
Superior machinability
Cons:
Difficulty in bonding and painting
Formaldehyde gas emission at high temperatures
Relatively high cost

ABS vs. Nylon: Choosing the Right Plastic for Your CNC Project
CNC Machinability
ABS is very easy to machine, with clean and neat chips, and can achieve an excellent surface finish.
Nylon has a certain degree of toughness and moisture absorption. During machining, it is prone to generating sticky chips, which may adhere to the cutting tools. Sharp tools and appropriate parameters are needed for control.
Post-processing
ABS is the absolute winner in post-processing. It can be easily bonded, sprayed, and electroplated to achieve a high-quality appearance and special visual effects.
Nylon is difficult to bond and spray, and usually requires special surface treatment (such as plasma treatment) to achieve.
Cost
ABS usually has lower raw material costs and a simpler machining procedure, thus having a clear advantage in projects with tight budgets.
Nylon is more expensive, but the outstanding mechanical properties and durability it offers often prove its value.
CNC Machining vs. Injection Molding for ABS Parts
| Aspect | CNC Machining (ABS) | Injection Molding (ABS) |
| Production Volume | Ideal for low-volume or custom parts | Best for mass production |
| Lead Time | Short — no need for mold fabrication | Long — requires mold design and tooling |
| Initial Cost | Low setup cost | High upfront tooling cost |
| Per-Part Cost | Higher per unit for large quantities | Very low per unit for high volumes |
| Material Waste | More waste due to the subtractive process | Minimal waste; efficient material use |
| Surface Finish | Excellent; can achieve tight tolerances | Very good; surface texture depends on the mold |
| Precision and Tolerances | High accuracy (±0.05 mm typical) | Moderate; depends on mold quality |
| Prototyping Suitability | Excellent for functional prototypes | Less suitable due to high tooling cost |
| Production Speed | Slower per part | Very fast once tooling is ready |
Post-Processing Techniques for CNC-Machined ABS Parts
Painting
Painting is the most commonly used and flexible method to give ABS parts color and a specific surface texture.
Note:
- Adhesion is dependent on surface cleaning and pretreatment.
- Coating thickness affects the dimensional tolerances of parts, requiring special attention for high-precision components.
Electroplating
Electroplating is an advanced treatment process that endows ABS parts with a true metallic appearance and performance, which can greatly enhance the grade and value perception of the products.
Note:
- High cost and complex processes, involving multiple chemical steps.
- Extremely high requirements for initial part design and surface quality, as any defects are amplified after plating.
- The plating affects dimensions, necessitating design allowances.
- Stringent environmental requirements, involving heavy metal treatment.
Bonding
Bonding is an economical and effective method for assembling multiple CNC-machined ABS components into a complex whole.
Note:
- Surface cleaning is critical to success, necessitating an oil-free and dust-free state.
- Testing is mandatory before formal bonding.
Applications for CNC-Machined ABS Parts
Prototyping Verification
Prototype making is the most classic application scenario of ABS CNC machining.
Functional Prototype: A physical model manufactured for testing product design, assembly relationships, and structural rationality. The strength of ABS is sufficient to simulate most of the functions of the final product, allowing engineers to identify design flaws and carry out iterations based on this.
Appearance Prototype: Due to the ease of spraying and polishing of ABS, prototypes with extremely high surface quality can be produced for market display, user research, or investment promotion, and the visual effect can rival that of mass-produced products.
Conceptual Model: In the early stage of a project, quickly transform 3D design drawings into tangible physical objects to facilitate team communication and decision-making.

Consumer Electronics
ABS is widely used in this field due to its excellent strength, insulation, and outstanding appearance treatment ability.
Device Shells: The shells and internal brackets of devices such as smartphones, tablet computers, and smartwatches. CNC machining is suitable for small-batch trial production or customized production.
Electrical Appliance Casings: Control panels and casings of household appliances such as televisions, audio equipment, and remote controls for washing machines.
Connectors and Interfaces: Precision components such as USB port housings and headphone jacks.

Automotive Industry
ABS is used in the automotive field for both prototypes and many final components.
Interior Parts: Dashboard assembly, door inner panels, armrests, etc. These components do not have high requirements for strength and heat resistance, and they need a good appearance.
Functional Components: Fluid pipelines, sensor housings, protective covers, etc.
Prototype Vehicle Parts: Before manufacturing expensive metal molds, CNC machining ABS is used to produce various plastic parts required for the entire vehicle for assembly verification.
Tooling Fixture
By taking advantage of the light weight, strength, and easy processability of ABS, cost-effective fixtures can be manufactured quickly.
Customized Fixtures: Fixtures used on production lines for positioning and fixing metal or other parts during machining. ABS will not scratch the surface of the workpiece, and it is lightweight and easy to operate.
Inspection Fixtures: Specialized gauges or inspection tools used for quickly checking whether the dimensions and shapes of products are qualified.
Robot End Actuators: Grippers, suction cup brackets, etc., used on mechanical arms, which require lightweight components to enhance the robot’s movement speed and efficiency.

Medical Devices
In the medical field, ABS is mainly applied to non-implantable and non-sterile equipment.
Equipment Enclosures and Handles: Prototypes of enclosures and handheld components for medical instruments and diagnostic equipment, as well as small-batch final products. The surface of ABS is smooth and easy to clean and disinfect.
Equipment Components: Drug delivery devices, structural parts of wearable medical devices.

Aerospace Industry
Prototype Components: During the research and development stage of unmanned aerial vehicles and aircraft, they are used to create non-structural parts such as aerodynamic models and cabin models.
Interior and Equipment Covers: Ventilation openings, instrument covers, etc., in the aircraft cabin.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Fuselage and Stand: Utilizing the lightweight and high-strength characteristics of ABS, the fuselage frame, protective cover, and camera gimbal structure of the UAV are fabricated.
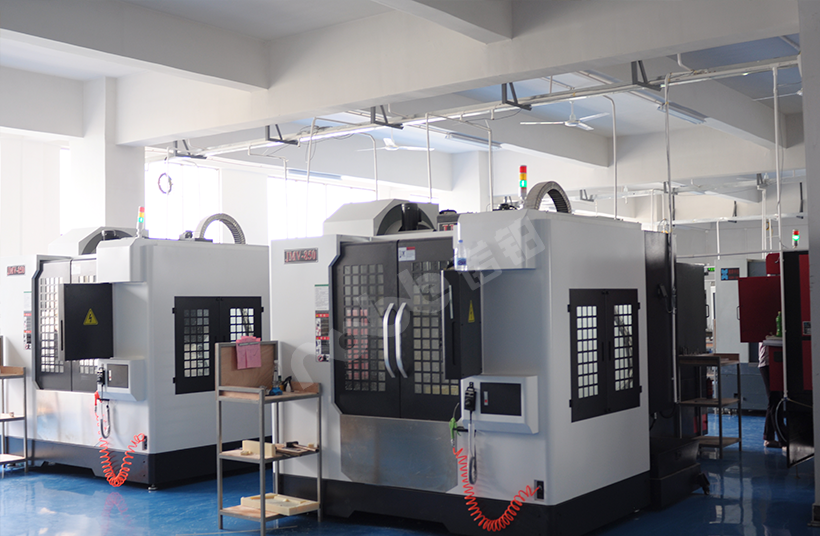

NOBLE’s ABS CNC Machining Service
NOBLE specializes in precision ABS CNC machining to deliver high-quality plastic parts for prototyping and production needs. With advanced multi-axis CNC equipment and extensive material expertise, we can produce complex ABS components with exceptional dimensional accuracy and surface quality.
Our machining capabilities cover milling, turning, drilling, and surface finishing, enabling us to meet diverse design and functional requirements. Whether you need a single prototype or a small-to-medium batch of parts, our experienced engineers ensure fast turnaround, stable quality, and full compliance with your specifications.
We work with various ABS grades, including standard ABS, flame-retardant ABS, and UV-resistant ABS, to support applications across electronics, automotive, medical devices, and consumer products. Each part undergoes strict inspection and quality control to guarantee performance and consistency.
Why Choose Us for ABS CNC Machining:
- Advanced 3-, 4-, and 5-axis CNC machining centers
- Tight tolerances up to ±0.05 mm
- Flexible production — from prototype to volume runs
- Multiple surface finishing options (polishing, painting, plating, etc.)
- Rapid lead times and professional DFM (Design for Manufacturability) support
FAQs
Why is ABS a popular material for CNC machining?
ABS is lightweight, tough, and easy to machine. It offers good dimensional stability, smooth surface finishes, and excellent impact resistance—making it ideal for prototypes, housings, and functional components.
What are the advantages of CNC machining ABS compared to 3D printing?
CNC machining delivers tighter tolerances, smoother surfaces, and better mechanical strength than most 3D printing methods. It’s also suitable for low-volume production and testing of engineering-grade parts.
Can CNC machining achieve tight tolerances with ABS?
Yes. With proper tool selection and machining parameters, CNC machining can achieve tolerances around ±0.05 mm for ABS parts, depending on geometry and equipment precision.
How does CNC machining compare to injection molding for ABS parts?
CNC machining is more cost-effective for prototypes and small batches since it doesn’t require molds. Injection molding is better for mass production due to lower per-unit costs.
What surface finishes can be applied to ABS CNC-machined parts?
Common finishes include polishing, sanding, painting, vapor smoothing, and chrome plating to improve appearance and surface durability.








