What is injection molding?
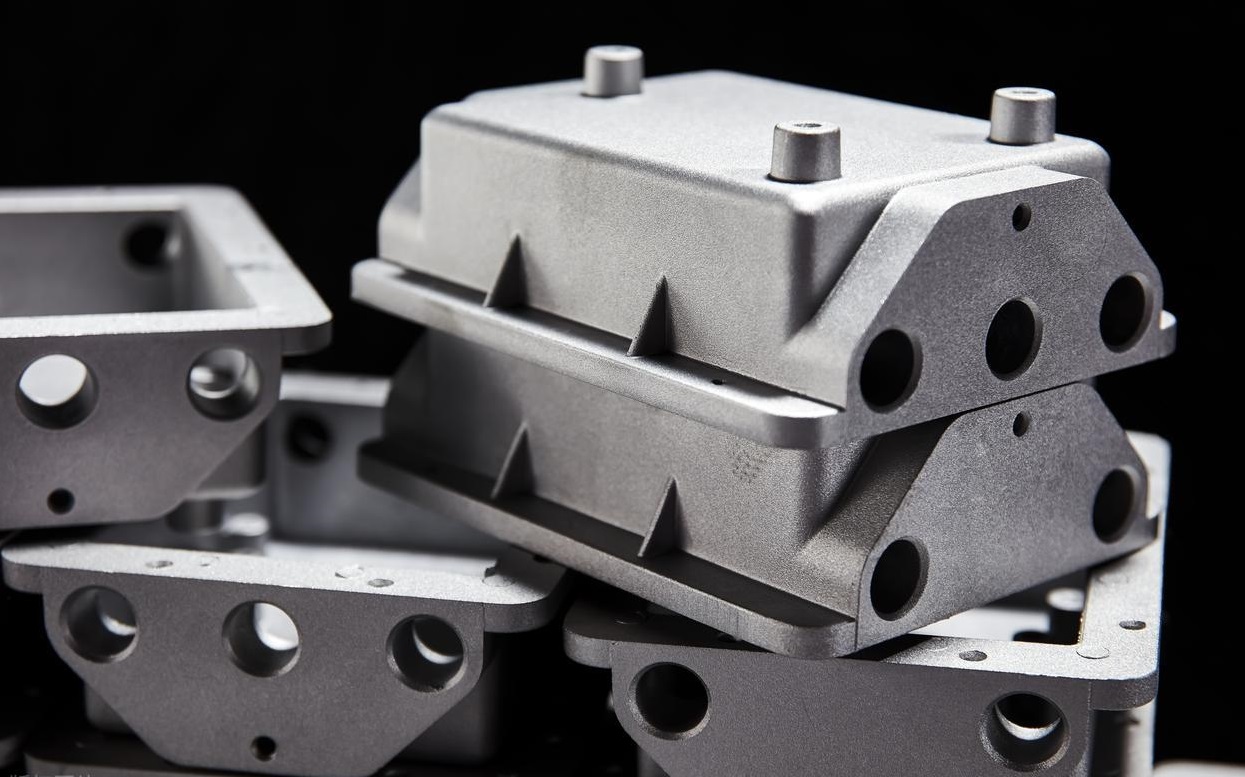
Injection molding, also known as injection mold forming, has entered every corner of our lives with its high efficiency, precision, and large-scale production capabilities. It features fast production speed, high efficiency, automation, and the ability to produce various shapes, from simple to complex, and multiple sizes, ranging from small to large, with precise dimensions and wide coverage. It can be applied to automotive interior parts, appliance shells, medical devices, and daily necessities. In the following, we will introduce the entire production process of injection molding in detail.
How does injection molding work?
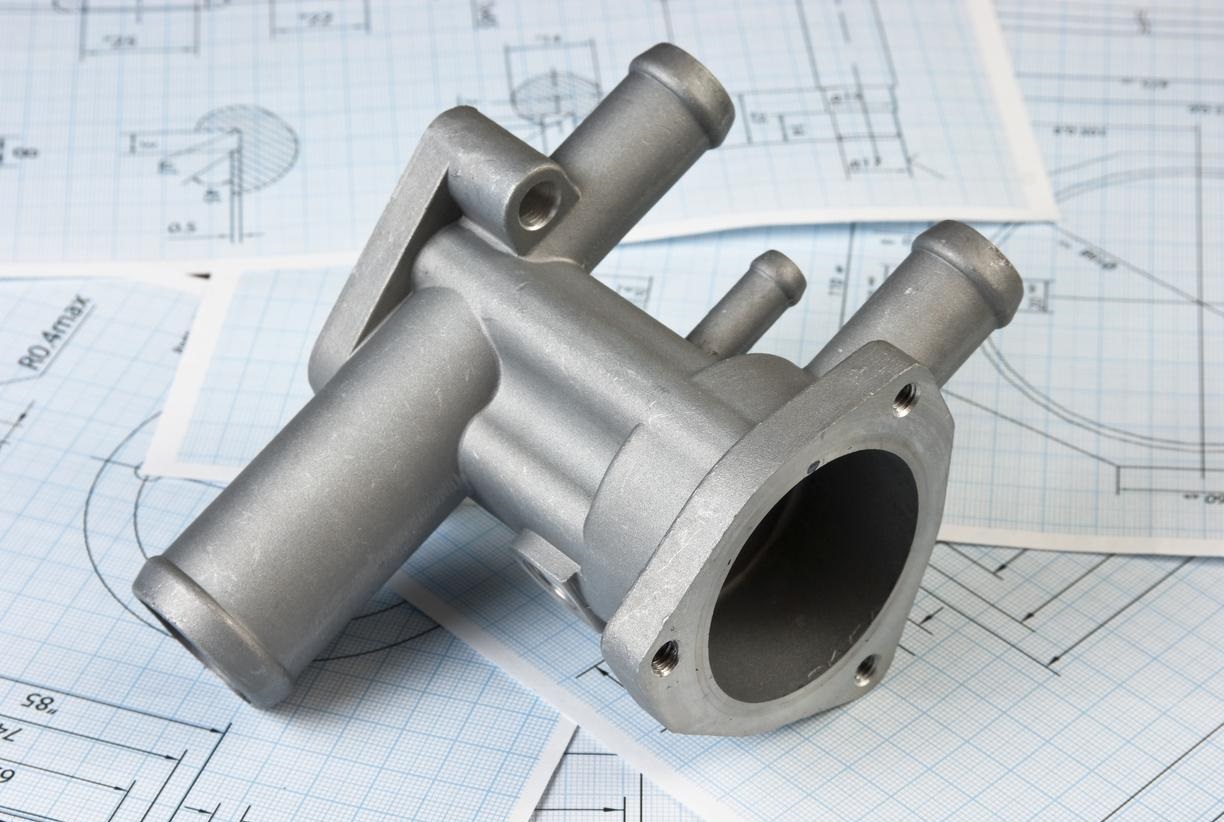
Injection molding is the most common manufacturing process for producing plastic parts. Injection molding machines use plastic raw materials and various molds to produce parts of various sizes, durable or disposable, for numerous industries and applications. Its working principle is that the injection molding machine feeds raw materials into a mold, which is the negative mold for the final part and consists of two parts: the injection mold (A) and the ejector mold (B). The space between the two parts is the mold cavity, into which the material is injected.
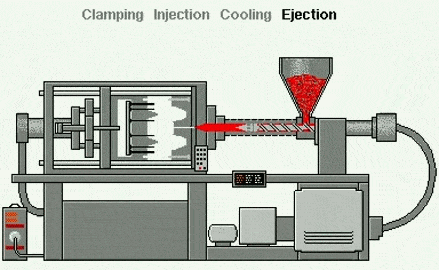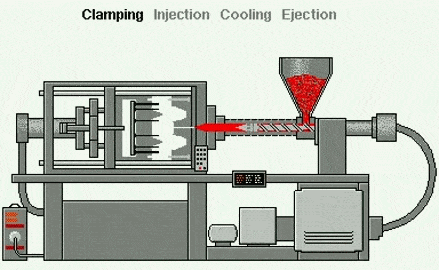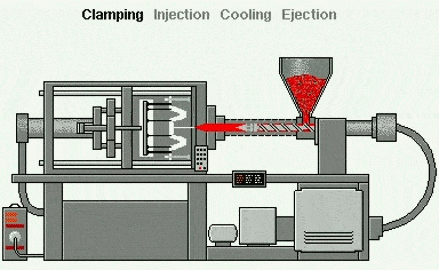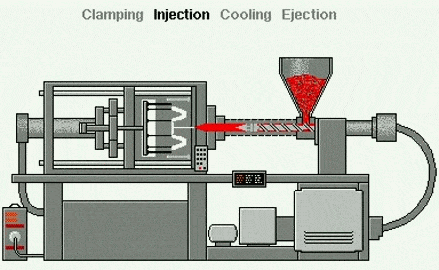
Injection molding is a molding process—unlike subtractive (cutting) techniques (such as CNC machining) or additive processes (such as 3D printing), which use molds as molding devices. This method is suitable for materials such as thermoplastics, which are heated to a molten state and then injected into a metal mold, where they cool and take shape within the mold or cavity. The process can be divided into:
1. Plastic Particle Feeding:
Small plastic particles (plastic pellets) are poured into the hopper. These particles are usually thermoplastics—plastics that soften when heated.
2. Plastic Melting:
The plastic pellets pass through a heated barrel with a rotating screw.
3. Injection Molding:
As the screw rotates, it pushes plastic pellets forward while the heater melts them into a thick molten liquid.
4. Injection Molding:
Once the molten plastic has accumulated to a certain point, the screw injects it into a metal mold cavity under high pressure. The mold is shaped exactly like the desired final part (e.g., a bottle cap, phone case, or car dashboard).
5. Cooling:
Inside the mold, the plastic cools and solidifies. Cooling channels within the mold help accelerate the cooling process.
6. Mold Opening:
After the plastic has solidified, the mold opens into two halves.
7. Ejection:
Ejector pins push the finished product out of the mold.
8. Repeat:
The mold closes, and the entire process is repeated—typically every few seconds—making injection molding ideal for mass production.

Common injection molding process types
Insert Molding
Insert molding is the process of molding thermoplastic material around a preformed component to create a finished part that incorporates multiple materials.
Our plastic injection molding process uses precise machinery to shoot molten resin into a mold to become a final production-grade thermoplastic part.

Covering plastic, metal, and rubber over each other via chemical bonding, our overmolding reduces assembly time and gives our parts greater strength and flexibility.
![]()
Liquid silicone rubber (LSR) is a thermoset process to produce a high volume of pliable, durable, intricate, and precise silicone rubber parts. This process first mixes two compounds (generally consisting of the base-forming silicone and the platinum catalyst).

The Metal Injection Molding (MIM) process combines the design flexibility of Plastic Injection Molding with the strength and integrity of wrought metals to offer cost-effective solutions for highly complex part geometries.
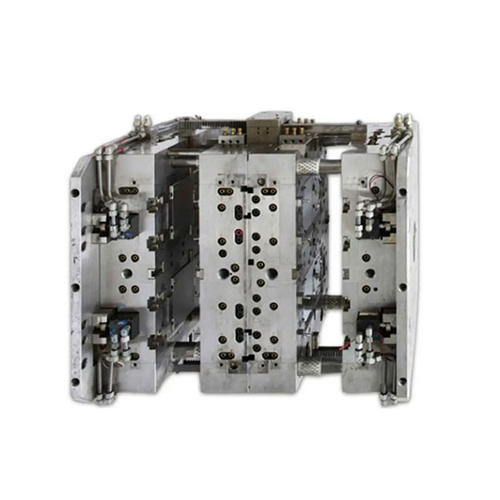

With our experience and advanced machinery, we excel at designing and manufacturing a series of plastic injection molds adjusted to your tolerance and cost.
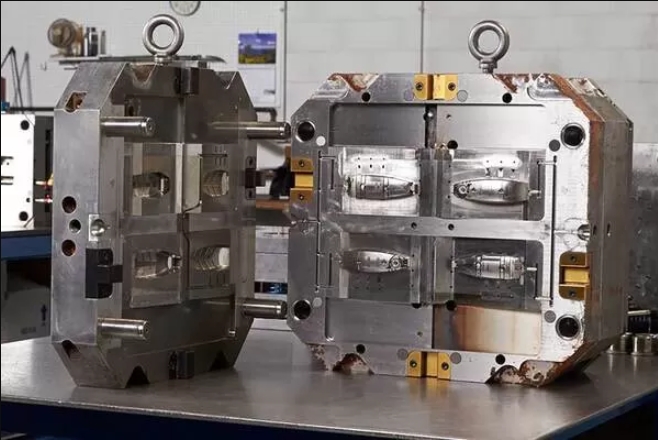

Multi-Shot Injection Molding
Multiple types of plastics are injected into the same mold at different stages to produce parts with different colors, textures, or material properties in one cycle. Due to its diverse types and strong functionality, it is widely used in car dashboards and button housings.
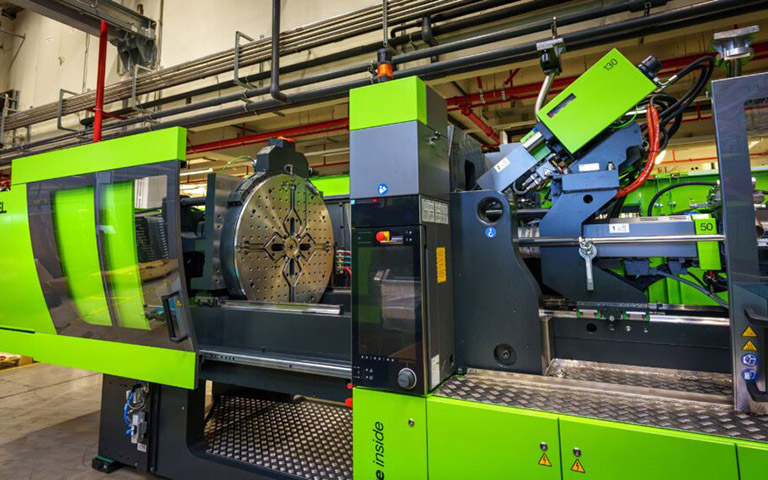

Two-Color Injection Molding
Two different colors of plastic are injected into the mold in one cycle. The two colors are injected at different stages, or two separate injection units are used to create parts with two colors or materials. It is widely used in consumer goods, car buttons, and mobile phone cases for its aesthetic appeal and enhanced functionality.
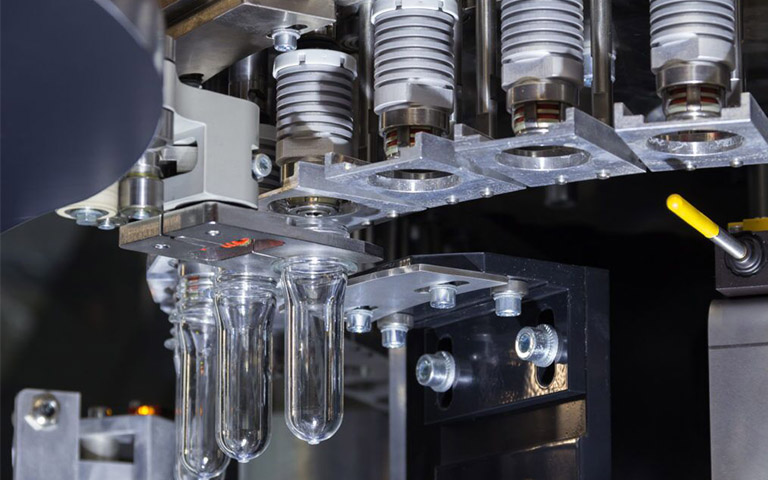

Gas-assisted Injection Molding
Nitrogen or other inert gases are injected into the molten plastic during molding. This gas creates an internal cavity, which reduces material usage and makes the part lighter without increasing strength. It is widely used in automotive door panels and mobile device housings due to its energy-saving, improved part weight, and surface finish.

It mixes reactive elastic or thermosetting materials and injects them into the mold, where they undergo a chemical reaction and harden. Due to its characteristics of producing flexible and hard parts, it is widely used in automobile bumpers and industrial product shells.

It uses thermoplastic materials that can be melted and reshaped multiple times, heating them until they are melted, and then injecting them into the mold to solidify. Because it is recyclable and cools quickly, it is widely used in plastic consumer products and medical equipment parts.
Advantages of Injection Molding
Injection molding is the best option for mass-producing plastic parts. After all, there’s a reason why so many manufacturing companies around the world use it to produce precision parts. NOBLE engineers summarize the following six advantages of using injection molding technology:
High Efficiency
Injection molding is a highly efficient process; once the mold is made, large-volume orders can be produced quickly.
Affordable Price
Injection molding is one of the most cost-effective methods for producing large quantities of parts, especially suitable for mass production. Although mold design and manufacturing may take some time, the entire process becomes very economical and efficient afterward.
High-Volume Production
Injection molding with steel molds can facilitate the production of millions of parts.
Good Surface Finish
With the proper treatment, injection-molded parts emerge from the mold with a smooth finish that requires no further refinement.
High tensile strength
Injection-molded parts may be reinforced by adding fillers to the liquid resin, improving tensile strength.
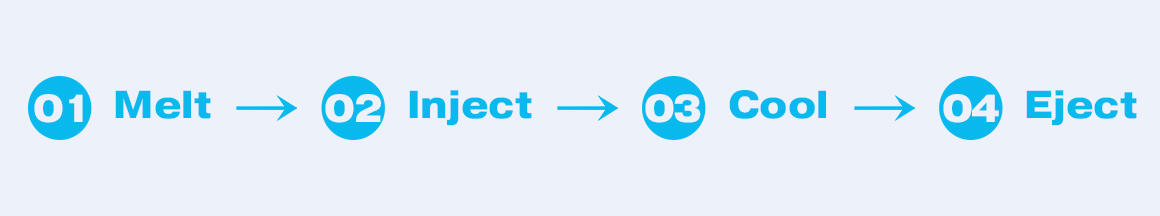
Parts Production Process Using Injection Molding
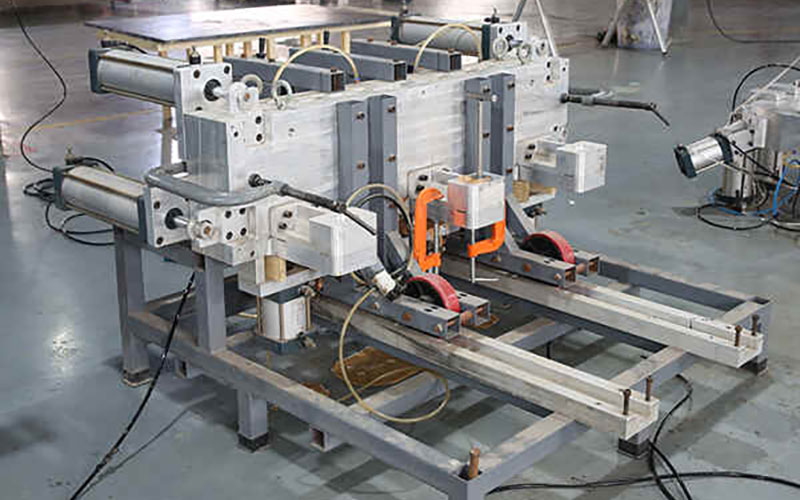
1. Mold Design& Manufacturing
Molds and injection molding machines have a very close relationship. The injection molding machine is the foundation of production, while the mold is the carrier that gives shape to the product. The design and manufacture of the mold are the cornerstone of the entire process. Its quality directly determines the quality, production efficiency, and cost of the final product.
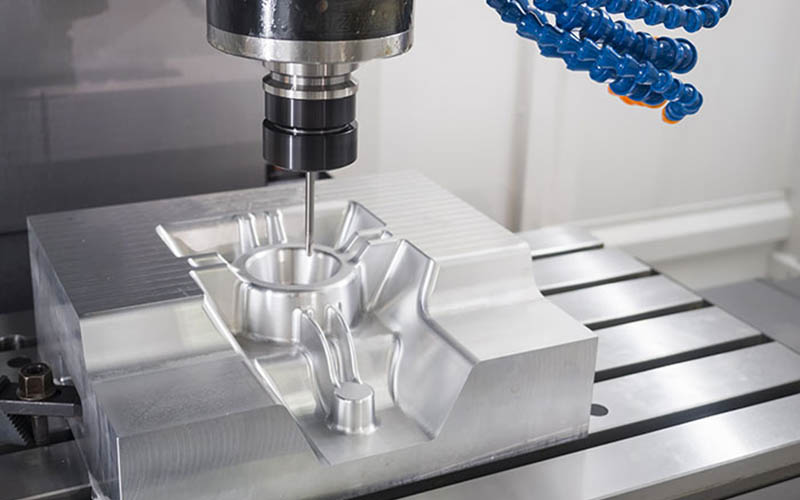

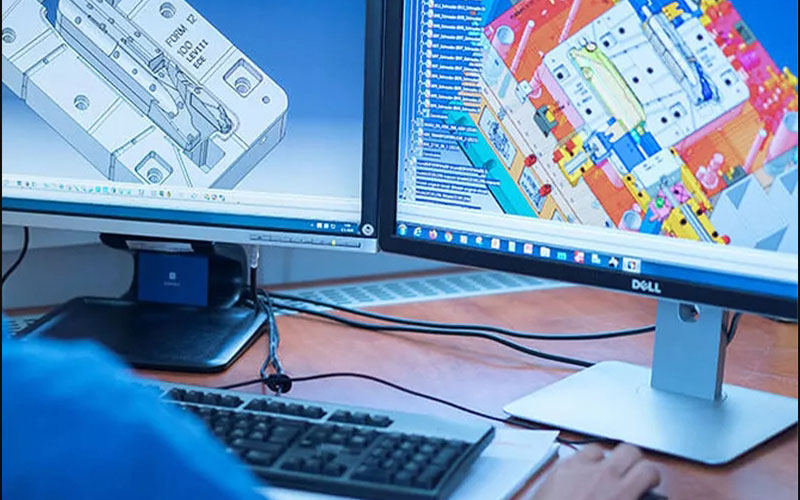
1.1Product Analysis and Design:
Everything stems from the requirements of the final product. Engineers need to comprehensively consider the functions, appearance, structure, and assembly relationship of the product. At this stage, software modeling is required, which is a crucial step. Simulated analysis of injection molding is also necessary to predict the filling, holding pressure, cooling process, and various possible defects during the injection molding process, to optimize the product structure and mold design.
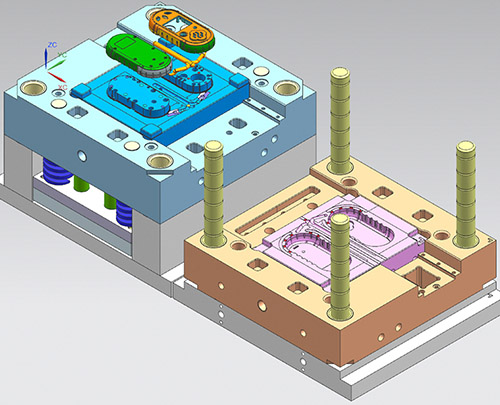
1.2Mold Structure Design:
The mold itself is a complex and precise design. The designer needs to plan the mold cavity and mold core to form the inner and outer surfaces of the product. The gating system, including the main runner and injection port. The cooling system: designing waterways inside the mold to rapidly lower the mold temperature and shorten the molding cycle.
The ejection system: after the product cools and solidifies, a pin, push plate, etc., is needed to smoothly remove it from the mold.
The exhaust system: to remove air from the cavity during the melt filling process.The lateral core-pulling structure: this is mainly for products with inverted structures or holes, and additional design is needed to assist in demolding. Before opening the mold, a lateral movement is performed to achieve demolding.
Mold material selection and machining: The commonly used materials include P20, H13. This can be selected based on the product’s price, mold lifespan, and product structure.
2. Raw material preparation and pre-treatment
2.1 Selection of plastic types:
Choose the appropriate plastic based on the product requirements. Each type of plastic has different characteristics, such as ABS being relatively tough, PP being lightweight, PC having good transparency, good impact resistance, and PA being wear-resistant.
2.2 Raw material pre-treatment:
involves drying the plastic raw materials in a dryer for several hours to remove their trace moisture. If the moisture is not removed, it will cause bubbles in the product under the influence of the high mold temperature. If the product has other color requirements, color matching is also necessary. Color matching is usually achieved by adding color masterbatches or color powders to obtain the desired color.
3. Injection molding process
This is the most crucial step. The product can only be produced after a complete injection molding cycle.
1. Clamping and locking the mold, as the name suggests, means closing the mold.
2 . Injection, that is, the screw in the barrel rotates under the drive of the system to transport, compress, and plasticize the plastic particles. After the plasticization is completed, the screw stops working and injects the plasticized molten material at high speed into the closed mold cavity.
3 . Pressure retention, the mold cavity is filled, the injection speed slows down, and it begins to enter the pressure retention stage. The screw continues to maintain a certain pressure until the product is formed.
4 . Cooling: After injection and pressure retention, the product begins to cool and solidify in the mold. Because the cooling in the mold requires a long time, it accounts for at least half of the entire production cycle.
5 . Molding opening and ejection: After the product cools and solidifies, the mold opens, and the ejection system starts to operate, pushing the product out from the mold core.
4. Post-processing and refinement
When the product is taken out of the mold, there are usually some accessories attached to it, which require further machining.
4.1.Water gate removal:
After the product is formed and the pouring system solidifies, the excess water gate needs to be separated from the product. For small products, the trimming might have been completed during the ejection process, while for complex products, manual trimming of the water gate is required.
4.2 Post-processing:
Depending on the product’s requirements, additional processing may be necessary.
4.3De-burring:
After the product is formed, the surface, especially at the parting line or the pin position, may have burrs or rough edges, which need to be removed.
4.4Screen printing / Spraying:
According to the product’s usage requirements, it may be necessary to have the logo of the screen printing company or surface painting.
4.5Ultrasonic welding:
Multiple injection-molded products are combined using ultrasonic welding to form a complete integral part.
4.6Assembly:
Assembled with other parts.
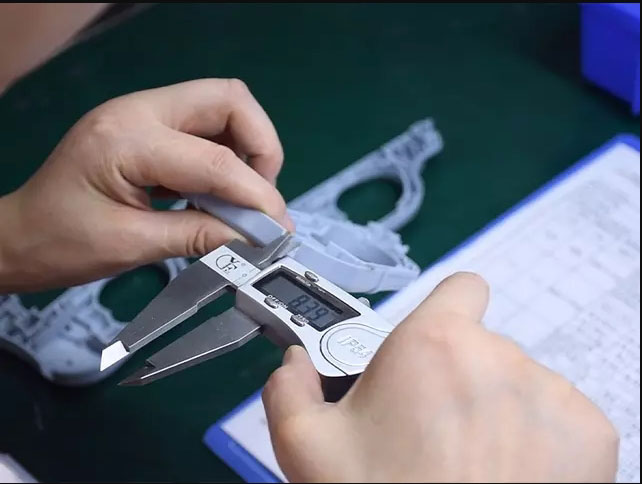

5. Quality inspection and control are an important part of injection molding production.
1. First-piece inspection:
Before starting mass production, we need to conduct a comprehensive inspection of the first piece, including dimensions, appearance, and functionality. We must ensure that all parameter settings are correct and that the product is qualified before mass production, and that the parameters are correct.
2. In-line inspection and sampling inspection:
During mass production, regular inspections are also required. We need to focus on appearance defects (such as missing materials, shrinkage) and key dimensions to ensure that the product is qualified.
3. Precision measurement:
During the inspection process, we need to use precision instruments such as calipers, micrometers, and three-coordinate measuring machines to conduct strict inspections of dimensions and geometric tolerances.
4. Performance testing:
Tensile strength, impact strength, and other performance requirements need to be tested as per the requirements.
Injection molding defects are problems that arise during the production process of plastic products due to factors such as process parameters, mold design, or material properties. For these defects, there are also a series of corresponding measures.
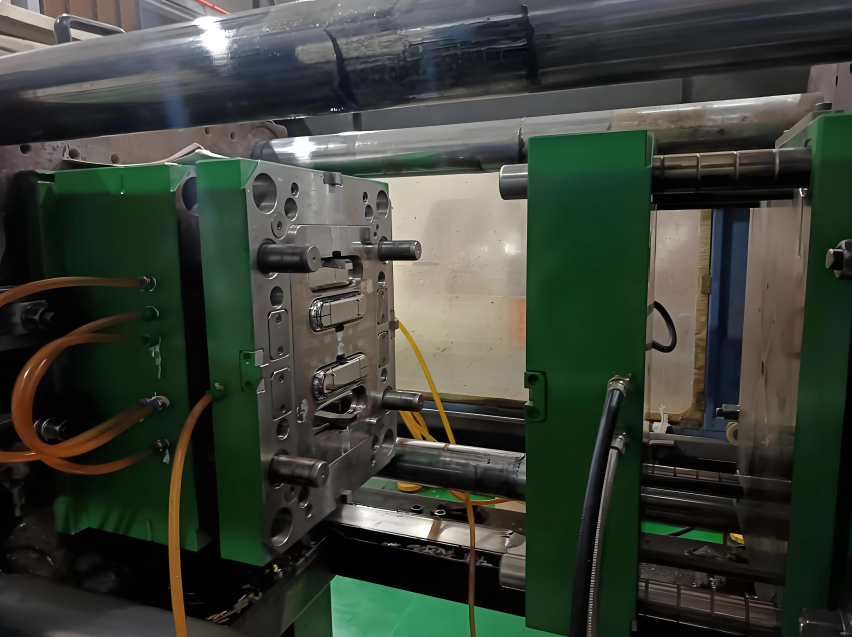

Common Defects and Solutions in Part Injection Molding
Injection molding defects are problems that arise during the production process of plastic products due to factors such as process parameters, mold design, or material properties. For these defects, there are also a series of corresponding measures.
1. Injection Molding Parts Appearance-related defects
1. 1Material shortage:
The common causes of material shortage include insufficient injection pressure, too slow injection speed, too low material temperature, slow melt flow rate at the bottom, poor mold exhaust, preventing the residual air in the mold cavity from being discharged, insufficient feeding quantity, insufficient material supply in some corners of the barrel, too small gate or flow channel size, excessive melt resistance, and thus inability to pass through.
2.1 Flying Edge :
The main manifestation is the presence of excessive burrs at the edges of plastic parts, mainly occurring at the parting surface of the mold, the mating surface of the slider, or the gap of the ejector pin. The cause of the flash is excessive injection pressure, insufficient clamping force, which causes the gap in the mold cavity to be expanded by the melt, high material temperature reduces the viscosity of the melt, allowing it to penetrate the mold gap, foreign substances on the parting surface of the mold, wear resulting in excessive mating gap, improper gate position, causing the melt to impact the mold and generating stress.
3.1 Silver Lines:
The symptoms are that silver-white filament-like stripes appear on the surface of injection-molded parts, which often occur in plastics such as ABS, PC, and PMMA.The causes of silver streaks: The raw materials contain moisture or volatile substances. During the injection process, these substances will volatilize into gases and cannot be expelled, resulting in their remaining on the surface of the plastic parts. Excessive material temperature causes the raw materials to decompose and produce gases. The surface roughness of the mold cavity is insufficient, causing the melt to flow unevenly.
4.1 Depression:
The main manifestation is surface depressions on the plastic parts, which are commonly seen in cases where the wall thickness dimensions are inconsistent, near the ribs or injection ports.
The cause of the depression is the inconsistency in the wall thickness of the plastic parts. There is a significant difference in the uniformity of the wall thickness, and the cooling speed in the wall thickness area is slow. During injection molding, the molten material does not have enough thickness to shrink completely, the holding pressure time is insufficient, the pressure is not enough, the mold temperature is too high, and the cooling speed of the plastic parts is slow, increasing the shrinkage rate.
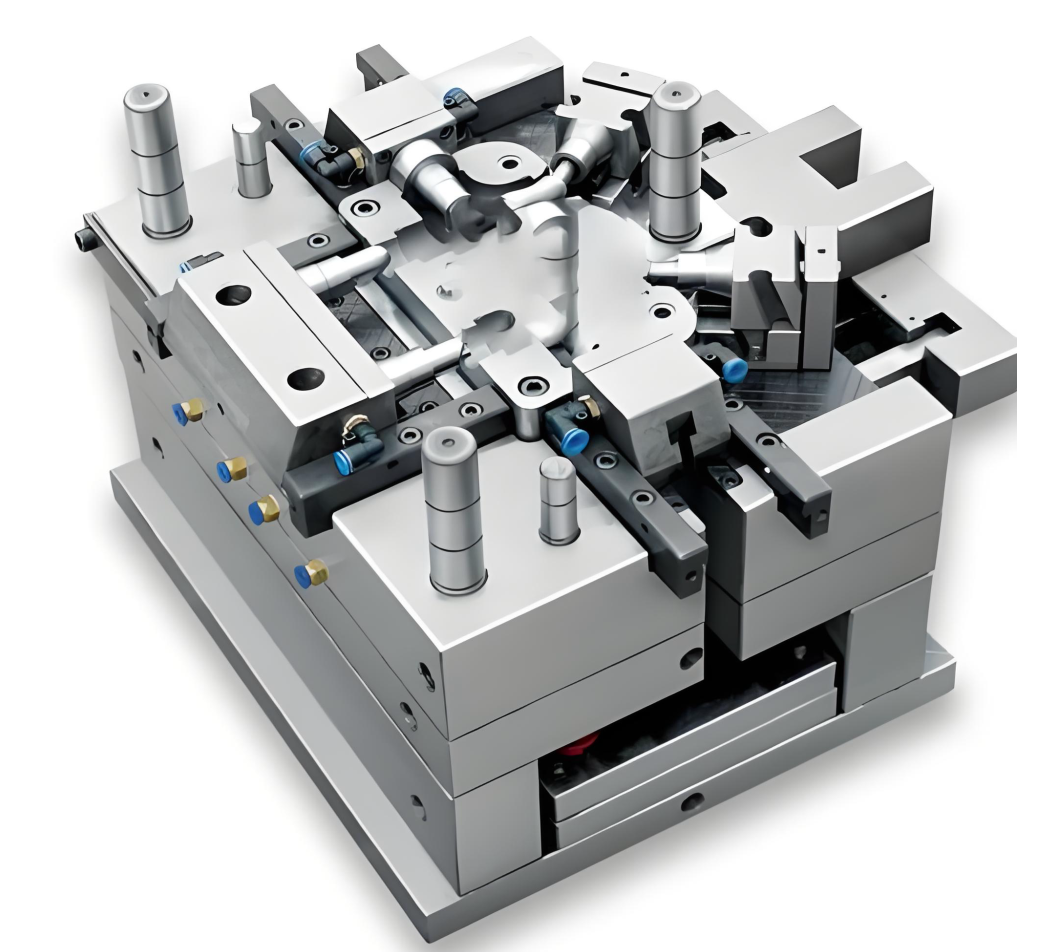
2. Injection Molding Parts Dimension and Precision Defects
2.1Excessive/Insufficient Dimension
The main manifestations are as follows: The actual size of the plastic parts exceeds the tolerance range specified in the drawing, being either larger or smaller than the required size. The reasons for the size deviation are: The deviation in the mold cavity size causes the size deviation of the plastic parts; the unstable injection molding process parameters lead to fluctuations in the shrinkage rate; the unstable raw materials due to different production batches result in differences in material properties; and the inconsistent cooling causes inconsistent shrinkage.
2.2Transformation
The main problem is that the plastic parts bend after cooling and cannot maintain the shape as designed in the drawing. The causes are as follows: The cooling speeds of different areas of the plastic parts are not uniform, which leads to differences in shrinkage and stress generation. The position of the injection port is improperly set, causing stress concentration during the filling of the molten material and concentrated stress during the mold ejection process, resulting in deformation during ejection.
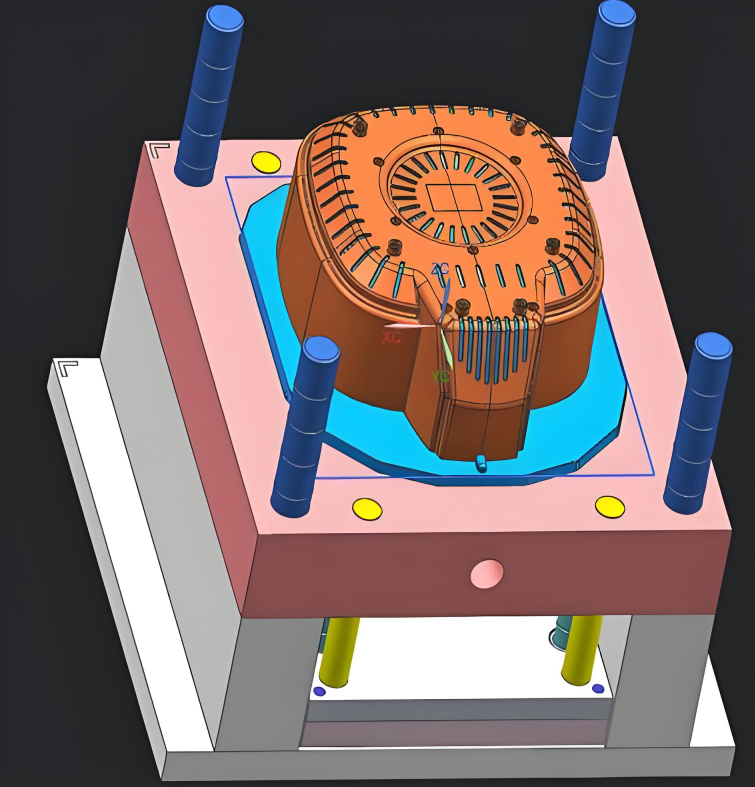
3. Injection Molding Parts Structural and Performance Defects
3.1Welding Line
The main manifestation is that the melt flows in the mold cavity and forms lines, which affect the appearance of the plastic part and are often distributed at the injection port.T he main manifestation is that the melt flows in the mold cavity and forms lines, which affect the appearance of the plastic part and are often distributed at the injection port.
3.2Bubbles
The main manifestation is the presence of air bubbles in the interior of the plastic parts, which are commonly found in the thick-walled areas and at the injection port positions. The cause is that the moisture in the raw materials will volatilize into gas and get trapped inside the plastic parts. The cavity exhaust is not smooth, and during injection, the molten material wraps the air and forms bubbles.

4. Brittle Fracture:
Solution:
Strictly dry the raw materials to remove the moisture. By reducing the injection speed, increasing the mold temperature, and prolonging the holding time, the gas can be discharged more effectively. The main manifestations are poor toughness of the molded parts, which are prone to cracking. This is commonly seen in brittle plastics such as PC, PMMA, and PS.
Causes:
Decomposition of raw materials or the introduction of impurities leads to the breakage of molecular chains; excessive internal stress during injection molding, such as rapid cooling or excessive pressure, roughness of the mold cavity surface causes micro-cracks on the surface of the molded parts; and insufficient or ineffective content of toughening agents in the raw materials.
Injection Molding Tolerances and Standards
There are many injection molding manufacturers in mainland China, and NOBLE has many years of experience in injection molding. It can provide the most efficient and economical solutions to meet your unique needs with unparalleled injection molding accuracy so that you can get impeccable, high-quality injection molded parts or prototypes in advance. We can also achieve special tolerances if you indicate the requirements in the drawing.
| Mold Class | Purpose | Shot Life | Tolerance | Lead Time |
| Class 105 | Prototype Testing | Under 500 cycles | ± 0.02mm | 7-10 days |
| Class 104 | Low-volume Production | Under 100.000 cycles | ± 0.02mm | 10-15 days |
| Class 103 | Low-volume Production | Under 500.000 cycles | ± 0.02mm | 10-15 days |
| Class 102 | Medium-volume Production | Medium to high production | ± 0.02mm | 10-15 days |
| Class 101 | High-volume Production | Over 1,000,000 cycles | ± 0.02mm | 10-18 days |
Commonly used materials for injection molding
These are common molded plastics offered by our injection molding services. After knowing the basics of materials such as common grades, brands, advantages, and disadvantages, choose the appropriate injection molding material according to your application requirements.
Tooling Material:
Before the injection molding process starts, for low or high-volume production, a high-tolerance CNC-machined tooling is needed. Most commonly used materials include:
| Tool Steel: | P20, H13, S7, NAK80, S136, S136H, 718, 718H, 738 |
| Stainless Steel: | 420, NAK80, S136, 316L, 316, 301, 303, 304 |
| Aluminum: | 6061, 5052, 7075 |
Plastic Materials:
Plastic injection molding service comes with a wide range of materials with different properties, including impact strength, rigidity, thermal resistance, chemical resistance, etc.
| ABS | Nylon (PA) | PC | PVC |
| PU | PMMA | PP | PEEK |
| PE | HDPE | PS | POM |
Additives and Fibers:
Standard plastic materials may not meet the custom injection molding parts requirements. In this case, additives and fibers can be added to improve aesthetic and functional properties, providing additional features for your injection-molded parts.
| UV | absorbers | Colorants |
| Flame | retardants | Glass fibers |
| Plasticizers |
Surface Finishes for Injection Molding
Injection molding includes injection mold tooling, plastic injection molding, and more. The surface treatment of the mold is usually completed during the production process. After the injection molding is completed, we will carry out certain surface treatments on the finished product as per your requirements.
Glossy
A grade finish is made using a diamond buffing process and yields shiny surfaces on injection molded parts.
Semi-glossy
B-grade finishes use grit sandpaper to produce parts with a slightly rougher finish than grade A parts. Custom molded plastic parts that undergo B-grade finishing have a matte surface texture.
Matte
C-grade finishes use grit sanding stones to produce a rough, uneven surface. Injection plastic parts that undergo C-grade finishing have a matte surface texture.
Textured
D grade finishes use grit and dry glass beads or oxide to produce a very rough textured finish. Depending on the type of material used, products can have a satin or dull finish.
Applications of injection molding
Since injection molding can achieve high precision at good manufacturing speeds without changing the material’s structure, it is becoming more familiar with the ever-expanding range of machines, control systems, and tools used for injection molding. NOBLE is committed to providing precision machining services for all walks of life. Our injection-molded precision parts are found in all walks of life, including.

Automation Equipment
NOBLE Rapid Prototyping service allows you to quickly and easily create automated functional prototypes to test and optimize your design, select the right process, reduce costs, and shorten project cycles. On-demand services can produce automated parts with a high level of accuracy.
Automotive
Our low-volume manufacturing services are the ideal manufacturing solution for on-demand automotive parts

Medical Devices
Medical supplies manufacturers, tech startups, and research labs benefit significantly from the prototyping solutions we provide.
Robotics
Our industrial-grade robotics prototyping and parts manufacturing services aid in the continuous evolution of the robotics market.

Why choose NOBLE for custom injection molding services?
Injection molding is an excellent choice for the mass production of plastic parts. Every year, so many high-tech companies worldwide choose NOBLE for injection molding parts processing. What makes so many customers choose us? NOBLE is a Sino-British joint venture with independent R&D, production, and sales capabilities. We have extensive experience in injection molding processes and can provide a full range of services for your new projects, including design, manufacturing, assembly, inspection and testing, and packaging.
Material Versatility
NOBLE offers more than 200 materials to choose from, including commodity and engineered resins, helping you find the right balance between performance and cost, and identifying alternative material options to help reduce overall manufacturing costs.
High Efficiency
With certified domestic factories and a strong supply chain system, we can accelerate product development cycles and complete the production of your injection molded parts as quickly as possible.
Comprehensive Capabilities
We offer a range of injection molding services, from design and prototyping to tooling and production. Our comprehensive capabilities allow us to provide complete solutions for our clients’ needs.
Consistency and High Quality
Owing to certified factories, conducting in-process inspections and dimensional verification after production guarantees the custom molded parts are consistent in quality, regardless of the complex shape, with high precision.
Competitive Price
Provide you with high-precision custom injection molding services at competitive prices, from prototype design to production, and tailor-made injection molding solutions for you, ensuring that you get high-quality injection molded parts. Our talented team can provide value-added injection molding solutions that exceed your budget.
Quality Assurance
We have a rigorous quality assurance process to ensure that every injection-molded part we produce is of the highest quality. Our team inspects each molded part to ensure it meets our stringent quality standards.

NOBLE’s superior injection molding quality inspection service
NOBLE’s experienced engineers have the expertise and experience to meet your specific needs, can undertake complex and challenging injection molding projects, and strictly implement our demanding quality inspection process to ensure that you get low-cost and high-precision injection molded parts.
- Material Certificate
- Free DFM Design Feedback
- Weekly Mold Progress Report
- Trial Mold Parameter & Video Supplying
- T1 samples Inspection Report
- Inspection Report Before Shipment