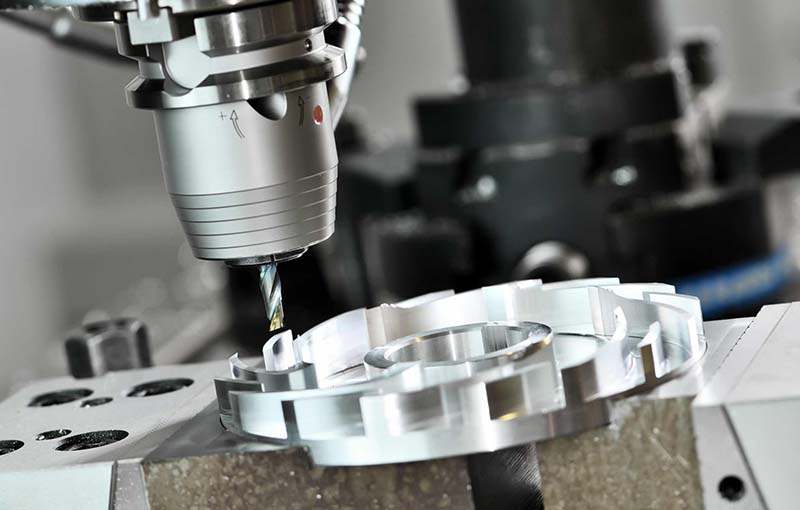
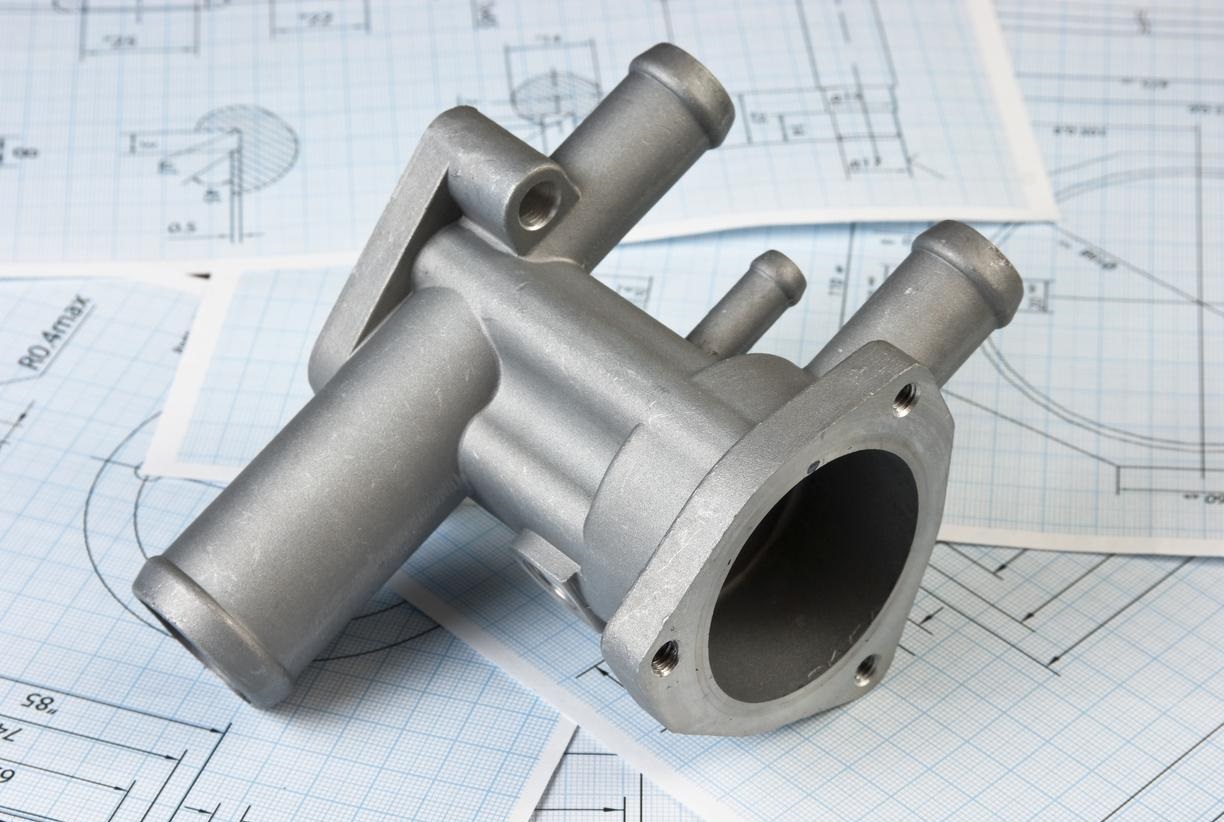
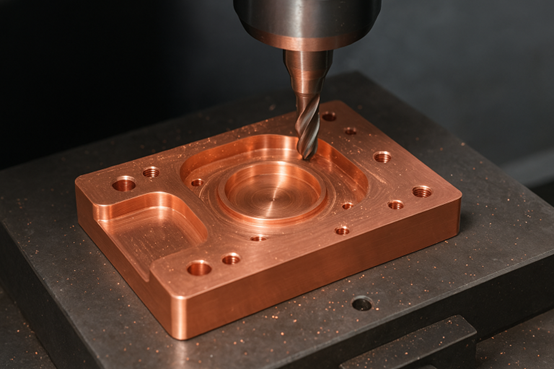
What Is Brass CNC Machining?
Brass CNC machining refers to the use of CNC milling, CNC turning, and drilling techniques to cut, shape, and refine brass material. Brass is a copper-zinc alloy known for its excellent machinability, corrosion resistance, and electrical conductivity. When combined with CNC technology, manufacturers can achieve high precision and smooth finishes, even for the most complex designs.
How Brass CNC Machining Works
Design and CAD Modeling
The process starts with making a digital drawing. Engineers or designers use CAD software to draw the part they want. At this step, they decide all the details, like the exact size, the location and size of holes, and the shape of the curves. Once the drawing is done, it is changed into a special code that the CNC machine can read. This code tells the machine how to move its tools and how much material to remove. Unlike old methods where workers had to measure and adjust by hand, the CNC machine follows the design automatically.

Tool Selection and Setup
When machining brass, it is important to use sharp and accurate tools. Before starting, you should check and compare different tool types, sizes, and materials. For example, carbide tools can make clean and sharp cuts, while diamond-coated tools last longer and are more durable. After choosing the right tools, the next step is to set them up correctly in the CNC machine. The operator must adjust the cutting speed and feed rate carefully. If the speed is too high, the brass may get too hot and soften or even melt. If the speed is too low, the tool may drag and leave rough surfaces. The brass piece must be tightly clamped in place to keep the process safe, stable, and accurate..
Sharp Cutting and Finishing
Once everything is set up, the CNC machine begins to follow your digital design to cut the brass. The sharp tools rotate at high speed and carefully slice the metal into the exact shapes and sizes that were planned. When the cutting process is complete, the part usually needs a finishing touch to improve its appearance and texture. This can be done by brushing the surface to create a softer, matte look or by polishing it. Because brass is a relatively soft metal, it must be handled with care during finishing to avoid scratches or dents.

Post-Processing Operations
After the CNC machine completes the cutting process, the next important step is cleaning and deburring the brass parts. This involves removing any leftover dust, small chips, or sharp edges that may remain on the surface. By smoothing out these rough spots, the part becomes safer to handle and looks more refined.
Once cleaning is done, the part goes through a quality inspection. If small adjustments are needed, they can be made at this stage to improve accuracy and performance. In some cases, a protective coating may also be applied to shield the brass from oxidation or wear.
The Types of Brass Materials for CNC Machining
C2600
C2600 brass contains about 70% copper and 30% zinc. This alloy has very good ductility, meaning it can be stretched or shaped without breaking. It also has excellent deep drawability, making it a good choice for forming complex shapes.

C2680
C2680 brass has about 65% copper and 35% zinc, which is why it’s also called 6-4 brass. Like C2600, it has great ductility and deep drawability, so it’s easy to work with when making detailed or stretched parts.
C2801
C2801 has higher strength but slightly less ductility. It’s commonly used for structural components and parts that need to be tough and durable. Because of its strength, it’s often selected for industrial applications where both performance and resistance to wear are important.
C3602
This alloy is based on 60/40 brass (C2801) but has lead added to improve machinability. The lead makes it much easier to cut, allowing for fast machining speeds and very smooth surface finishes.
Brass H59
An economical brass material characterized by high strength and hardness. It maintains excellent pressure processing properties during heat treatment and demonstrates good corrosion resistance. As such, it is frequently utilized in the manufacture of various mechanical parts, welded components, and hot-punched and hot-rolled parts.
Brass H90
Similar in performance to H96 but with higher strength, H90 can be plated with metal or enameled. It is commonly used in the manufacture of products such as case bands and bimetallic strips.

Types of Brass CNC Machining Processes
CNC Turning
CNC turning is one of the most common processes in brass machining. It involves rotating the workpiece on a lathe and cutting it with a tool, and is suitable for machining rotary parts such as shafts and discs.
The turning process features high precision and good surface quality, and is often used to manufacture precision parts such as valves and joints. The turning process has relatively high machining efficiency and low cost.
CNC Milling
CNC milling is used to process the planes, curved surfaces, or complex cavities of brass parts. It achieves multi-dimensional cutting by rotating the milling cutter and moving the workpiece.
The milling process has good flexibility and can handle various irregular structures, such as molds and heat sinks. It is suitable for medium and small batch production, and the surface roughness can be controlled within an optimal range.
CNC drilling is mainly used for hole processing, where precise hole positions are formed by cutting on brass workpieces with drill bits.
Drilling technology is suitable for high-precision hole system processing, such as electronic component brackets or pipe fittings. It can achieve continuous multi-hole operation with high efficiency and stable hole wall quality, and supports automated production.
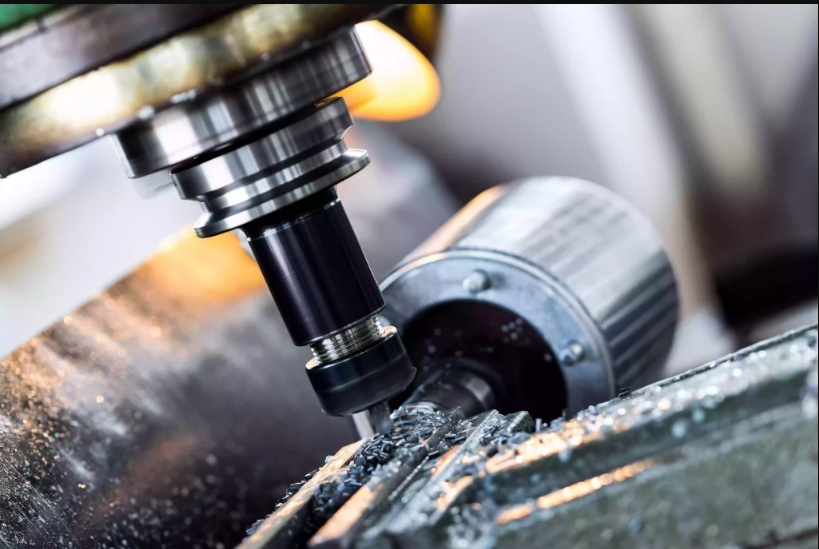

Why Choose Brass for CNC Machining?
Brass is a popular material in many industries because it is both strong and easy to work with. Compared to stainless steel, brass is softer, so machines need less force to cut it. This makes the cutting tools last longer and helps reduce the cost of making parts.
Brass can be shaped and polished to have a very smooth surface, so it often needs little extra work after machining to look nice. Its combination of strength, ease of cutting, and good appearance makes it a smart choice for making many kinds of parts.
Advantages of Brass CNC Machining
High Precision
CNC machining allows brass parts to be produced with very tight tolerances. This level of accuracy is especially important for custom components where every measurement must be exact.

Excellent Machinability
Brass is easier to cut and shape than many other metals. This reduces the time required for production and lowers manufacturing costs, making it a cost-effective choice for complex parts.
Corrosion Resistance
Brass naturally resists rust and oxidation, which makes it ideal for parts used in outdoor environments or in marine applications. This ensures the components remain durable and reliable over time.
Electrical Conductivity
Brass is commonly used in electrical components and connectors because it conducts electricity very well. This makes it reliable for applications where efficient electrical flow is essential.
Aesthetic Appeal
Brass has a natural, shiny, golden look that makes it ideal for decorative or luxury items. Its attractive appearance adds visual value while still providing strength and durability.
CNC Machining Brass Surface Finishes
After CNC machining, brass parts often need finishing to improve either their appearance or their performance. There are different finishing options you can choose depending on the use of the part:
Powder Coating
Powder coating involves covering the brass part with a layer of dry powder, which is then heated to form a protective coating. Powder coating improves the resistance of brass against corrosion and wear, making the part stronger and more durable in harsh conditions.

Polishing
Polishing is done to improve the look of the brass part. By using an abrasive polishing wheel or disc, impurities and small surface marks are removed. This gives the brass a smooth, reflective, and shiny surface, making it more attractive for decorative purposes.

Electroplating
Electroplating is a process where the brass part is dipped into an electrolyte solution to coat its surface with a thin layer of another metal. During this process, an electric current is applied, causing metal molecules from the solution to bond onto the brass surface.
Depending on the requirement, metals such as nickel, chrome, or even gold can be used. This not only improves the visual appeal by giving the part a glossy or reflective finish but also adds protective qualities, such as better resistance to corrosion, improved hardness, and longer service life.

Brushing
Our brushing technique uses abrasive belts over the material to create diverse patterns that match the parts’ structure and color.
Common Applications of Brass CNC Machining
Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, brass is widely used to make components such as sensors, radiators, fittings, and connectors. One of the main reasons it is preferred is that brass is easy to machine, allowing manufacturers to produce parts quickly and with high accuracy. The durability of brass ensures that these parts can withstand long-term use under demanding conditions, making them reliable for vehicles.

Aerospace
In aerospace, where precision and safety are critical, CNC-machined brass is an excellent material for producing high-accuracy components. Common examples include fasteners, electrical connectors, and small fittings that must perform consistently even in extreme environments.
Brass offers both reliability and a long service life, which are essential qualities for aerospace applications where failure is not an option.

Medical Devices
Brass is used in medical devices and surgical tools because it provides both high accuracy and long-lasting durability. Its ability to be precisely machined makes it suitable for components that require exact measurements and reliable performance during medical procedures.
Electronics
Brass is highly valued in electrical applications because of its excellent electrical conductivity combined with natural resistance to corrosion. This makes it one of the best materials for manufacturing electrical terminals, connectors, switches, and other related components that need both performance and durability.
Brass can also be polished to enhance the visual appeal of electronic devices, giving them a high-quality and professional look.
Consumer Products
In consumer products, brass is popular for decorative hardware, musical instruments, and household fixtures. Its attractive appearance, ease of machining, and ability to hold a polished or shiny finish make it ideal for items that need both functionality and visual appeal.
Musical Instruments
Brass instruments like trumpets and saxophones need very precise parts. CNC machines are used to shape mouthpieces, valves, and tuning slides so they fit perfectly in the instrument.
Because every piece is made to exact measurements, the instrument produces clear and rich sounds. Even small dents can affect the music, but brass is strong and durable, which helps the instrument stay in tune for a long time.
CNC-Machining Brass Tips
Choose the Right Tool
Use sharp, high-speed steel or carbide tools to achieve clean cuts and smooth surfaces. Avoid dull tools to prevent tearing the material.

Use Proper Speeds and Feeds
Brass cuts well at moderate speeds. Too fast can cause chatter, too slow can reduce efficiency. Adjust spindle speed and feed rate based on the alloy and part size.
Apply Lubrication
Use cutting fluid or oil to reduce heat, improve surface finish, and extend tool life.
Minimize Tool Pressure
Brass is soft, so excessive force can deform parts. Use light cuts and multiple passes for deeper features.
Watch for Burrs
Brass can produce small burrs when cutting edges or holes. Plan for deburring or use chamfered edges.
Secure the Workpiece
Make sure brass parts are clamped firmly to avoid vibration, which can affect precision and surface quality.
Plan for Polishing
Even though brass machines easily, some applications may need polishing or finishing to achieve the desired shine or smoothness.

Why Partner With Us for Brass CNC Machining Services?
Our company specializes in high-quality brass CNC machining, offering custom solutions for clients worldwide.
With advanced 5-axis CNC machines and skilled engineers, we guarantee precision, efficiency, and competitive pricing.
Whether you need rapid prototyping, small-batch production, or large-scale manufacturing, we deliver consistent results tailored to your project needs.
- BrassParts with Tight Tolerances: We implement strict quality management to ensure consistent high quality on your brass
- Material Options: Over 50 brass materials and a wide range of surface finishes for your choice.
- Fast Lead Time: Not only do we have a digital CNC machining services platform that provides a faster ordering process, but we also own domestic workshops and state-of-the-art machinery to accelerate the production of your prototypes or parts.
- 24/7 Engineering Support: No matter where you are, you can get our 24/7 engineering support all year round. Our experienced engineer can provide you with the most appropriate solution for your part design, material selection, surface finishing options, and even lead time.
FAQs of Brass CNC Machining
What is the Tolerance Range for Brass?
Brass parts can achieve very tight tolerances, typically ranging from ±0.005 to ±0.020 inches. Using sharp tools and slower cutting speeds can improve precision even further. For many applications, a tolerance of ±0.001 inches is sufficient.
Is Brass CNC Machining More Expensive Than Other Materials?
Brass may cost more per kilogram than some other materials like aluminum, but it can save money over time. Brass is easier to machine, which means fewer tool changes, faster production, and less material waste.
How Does Brass’s Composition Affect Its Machinability?
Brass is mainly made of copper and zinc, which gives it a balance between softness and strength—it is softer than steel but stronger than plastic. The addition of lead further improves machinability by making the material easier to cut.
What industries commonly use brass CNC machining?
Industries include automotive, aerospace, electronics, medical devices, and consumer products, where precision, durability, and appearance are important.
How do I choose the right cutting tools for brass CNC machining?
Sharp carbide or high-speed steel tools are ideal. Leaded brass cuts easily, while harder alloys may require slower speeds and more durable tools.