In the realm of modern manufacturing, sheet metal processing stands as a cornerstone, providing the backbone for diverse industries ranging from automotive and aerospace to electronics and construction. The ability to transform flat sheets of metal into intricate components and structures through precise techniques such as cutting, bending, and forming is essential for achieving both functional excellence and aesthetic appeal in end products.
What is called sheet metal?
Sheet metal is metal that is formed into thin, flat pieces. Sheet metal is generally produced in sheets less than 6 mm. It is one of the fundamental forms used in metalworking and can be cut and bent into a variety of different shapes. Thicknesses can vary significantly.
What is the purpose of sheet metal?
Sheet metal is used to hold architectural and structural components together, so they keep their shape. Sheet metal cladding is used to cover large areas such as rooftops or partitions. Sheet metal is also frequently used in combination with other materials to make walls, floors, and ceilings.
How is sheet metal fabrication?
The manufacturing process starts with selecting metal and cutting it into the desired size and shape. The metal is then formed into its final product through various techniques, such as rolling, extruding, and bending. The end product can vary from simple flat panels to complex three-dimensional structures.
The Importance of Sheet Metal Machining
Sheet metal, known for its strength, versatility, and cost-effectiveness, is favored across industries where durability and precision are paramount. Whether it’s creating complex automotive parts, robust HVAC systems, or intricate electronic enclosures, mastering sheet metal processing techniques is crucial for meeting design specifications, maintaining quality standards, and optimizing production efficiency.

What is Sheet Metal Forming?
Sheet stock is procured in a flat state and cut, then formed into its final state through a series of progressive steps. For a typical sheet metal project, the first step is equivalent to sheet cutting, where a shear, laser, waterjet, plasma, or punch press is used to create the internal holes and edge features of the part. This process is also known as blanking.
Once the blank is produced, the next step is to form sheet metal using various tools, but most commonly, some sort of brake. A brake press can be manual or automated and uses die inserts to create a desired angular bend, forming the two-dimensional sheet into a three-dimensional object. Sheet metal forming can bend the part in multiple directions, creating simple parts such as brackets up to highly complex geometries, which may require custom die tools. Once the tools are in place, making subsequent sheet parts in production is very cost-effective. This makes sheet metal fabrication and forming ideal for low to high volume production.

Sheet Metal Machining Materials Available at NOBLE
Various materials are available for CNC machines, giving you options for rapid prototyping and custom production runs of complex parts. We provide instant quotes on more than 150 metals and plastics for your manufacturing needs, and you can even compare prices on different processed materials.
Below are some common materials and models for your reference:
.jpg)
Aluminum
| Aluminum 6061-T6 | 6061 aluminum is a versatile alloy with excellent machinability, weldability, and corrosion resistance, used in aerospace, automotive, and more. |
| Aluminum 7075-T6 | Aluminum 7075-T6 is used in high-strength applications like aerospace, military, and automotive due to its strength, lightness, and corrosion resistance. |
| Aluminum 5052 | This alloy offers excellent corrosion resistance, formability, and weldability, making it ideal for marine, automotive, and CNC machining applications. |
| Aluminum 6063 | 6063 aluminum is perfect for CNC machining architectural elements, window frames, furniture, and irrigation parts, offering great surface finish and corrosion resistance. |
| Aluminum 6061 | 6061 aluminum is used in aerospace, automotive, and marine industries for its strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability, ideal for custom CNC machining. |
| Aluminum 2024 | Aluminum 2024 is used in aerospace and military applications for its high strength, fatigue resistance, and extreme condition endurance, ideal for CNC machining. |
| Aluminum 5083 | Aluminum 5083 is used in marine, transportation, and industrial applications for its corrosion resistance and strength, ideal for shipbuilding and CNC machining. |
| Aluminum 6082 | Aluminum 6082 is used in structural applications like bridges and cranes for its strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability, ideal for CNC machining parts. |
| Aluminum 7075 | 7075 aluminum is used in aerospace, military, and sporting goods for its strength, light weight, and fatigue resistance, ideal for CNC machining. |
| Aluminum ADC12 (A380) | Aluminum ADC12 (A380) is used in automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing for its fluidity, castability, and corrosion resistance, ideal for CNC machining components. |
Stainless Steel
| Stainless Steel SUS201 | SUS201 stainless steel is used in kitchen utensils, food processing, automotive parts, and architecture for its moderate corrosion resistance, strength, and formability. |
| Stainless Steel SUS303 | SUS303 stainless steel is used in automotive, aerospace, and machinery for its excellent machinability and moderate corrosion resistance in components like fasteners and gears. |
| Stainless Steel SUS304 | SUS304 stainless steel is used in kitchen equipment, chemical containers, piping, and architecture for its high corrosion resistance and good formability. |
| Stainless Steel SUS316 | SUS316 stainless steel is ideal for marine, chemical, medical, and food production equipment due to its superior corrosion resistance, especially against chlorides. |
| Stainless Steel SUS316L | SUS316L stainless steel is ideal for medical implants, pharmaceutical equipment, and marine environments, offering high corrosion resistance and low carbon content for welding. |
| Stainless Steel SUS420 | SUS420 stainless steel is used in cutlery, surgical instruments, valves, and gears for its high hardness and moderate corrosion resistance. |
| Stainless Steel SUS430 | SUS430 stainless steel is used in kitchen appliances, automotive trim, and decorative architecture for its good corrosion resistance and formability. |
| Stainless Steel SUS431 | SUS431 stainless steel is used in pump shafts, marine hardware, and aircraft components for its high strength, corrosion resistance, and toughness. |
Titanium
| Titanium Grace 2 | This commercially pure material offers excellent corrosion resistance and moderate strength, used in marine, chemical, and medical applications for its formability. |
| Titanium Grace 5 | Used in automotive parts, this material’s high strength, low density, heat resistance, and wear resistance improve performance and handle complex conditions. |
| Titanium Grace 9 | It balances strength, corrosion resistance, and formability, making it ideal for aerospace, automotive, and marine applications requiring moderate strength and lightweight properties. |
| Titanium Grace 12 | It offers superior corrosion resistance in aggressive chemical environments, used in chemical processing and heat exchangers where strength and resistance are crucial. |
| Titanium Grace 23 | This low-impurity Grade 5 version offers improved ductility and toughness, ideal for medical implants and aerospace applications needing higher toughness and biocompatibility. |
| Titanium Ti-15-3 | This high-strength alloy is used in aerospace and military applications, offering exceptional strength and corrosion resistance at high temperatures, ideal for turbine blades and airframes. |
Titanium Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-6Mo |
This high-performance alloy is used in automotive, aerospace, and military industries, offering excellent strength, fatigue resistance, and thermal stability in high-temperature environments. |
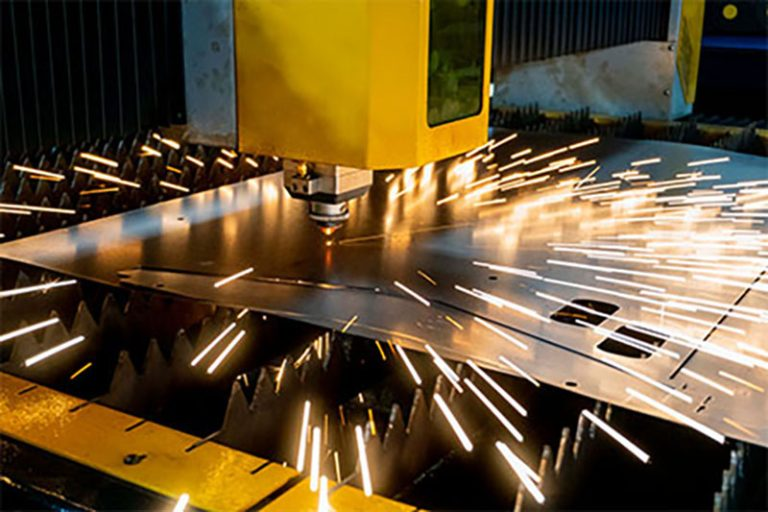

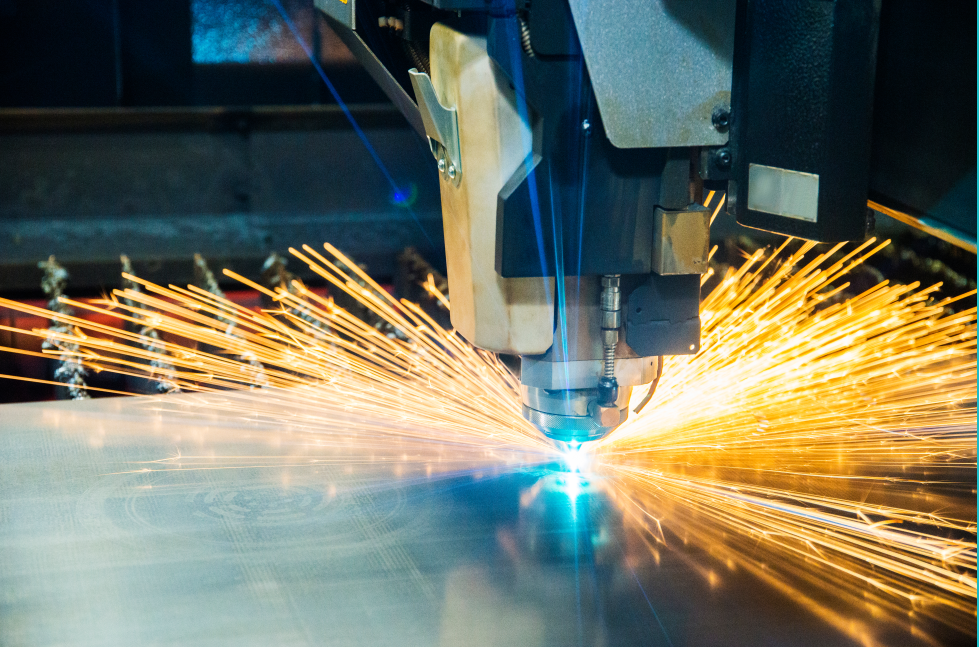
Essential Techniques in Sheet Metal Machining
1. Sheet Metal Cutting Techniques
Shearing: This traditional method involves using shear forces to cut straight lines in sheet metal, ideal for high-volume production where precision is key.
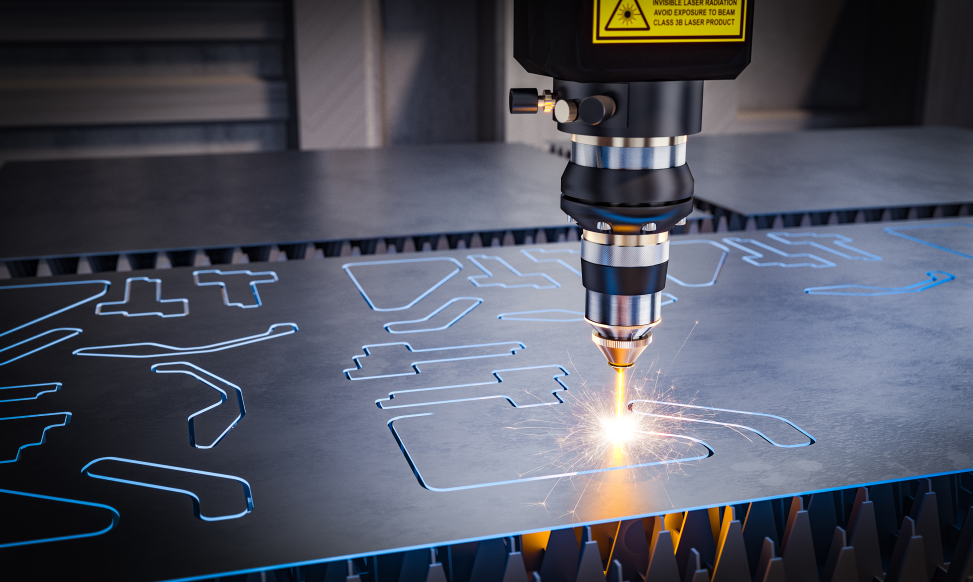
Laser Cutting: Utilizing focused laser beams, this technique offers unparalleled precision and flexibility for cutting intricate shapes and patterns in various metals.
Waterjet Cutting: By employing a high-pressure stream of water mixed with abrasive particles, waterjet cutting is suitable for materials sensitive to heat, delivering clean edges without affecting material properties.
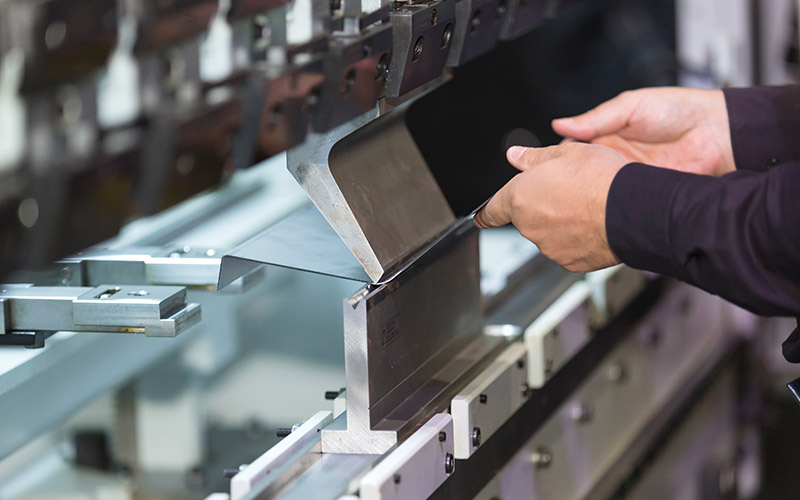

2. Sheet Metal Bending and Forming
Press Brake: Using a press and die set, press brake bending allows for precise angular bends in metal sheets, making it indispensable for creating components with specific geometries.
Roll Bending: This technique employs rollers to curve metal sheets into cylindrical or conical shapes, offering versatility in producing pipes, tubes, and curved components.
Deep Drawing: Ideal for creating three-dimensional shapes, deep drawing involves pulling a sheet metal blank into a die cavity to form seamless and structurally robust components.
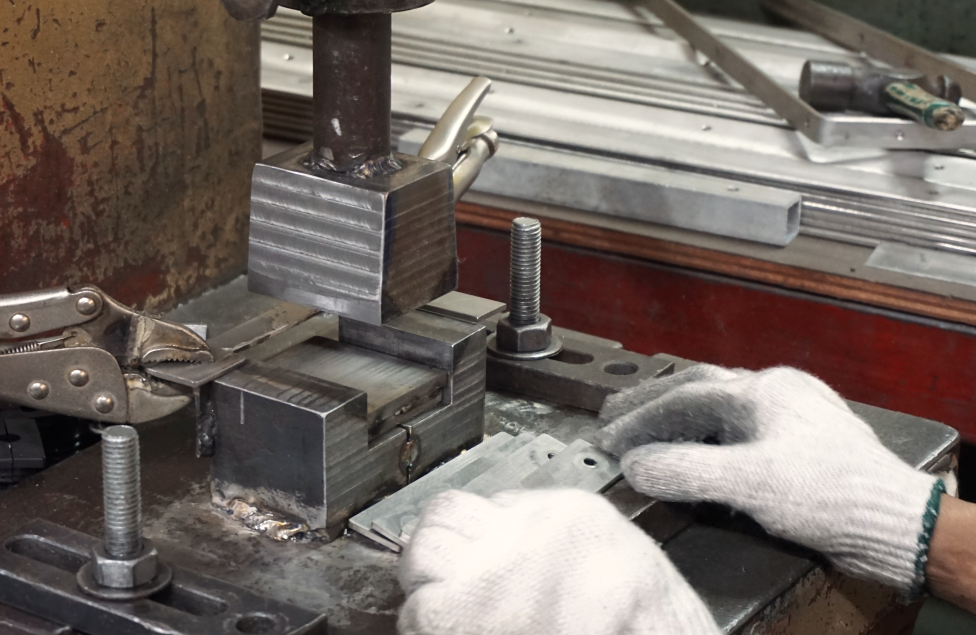

3. Sheet Metal Riveting
Welding: By fusing metal sheets using heat, welding creates strong, permanent joints suitable for structural applications in industries like automotive and construction.
Fastening: Techniques such as riveting, screwing, and bonding with adhesives provide options for creating temporary or detachable joints, offering flexibility in assembly and maintenance.

Tips for Optimizing Sheet Metal Machining Efficiency
1. Material Selection and Preparation
Choosing the right metal alloy based on mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness is crucial for achieving desired product performance and longevity.
2. Design for Manufacturing (DFM) Principles
Implementing DFM principles early in the design phase helps minimize material waste, reduce manufacturing complexities, and optimize assembly processes, ultimately lowering production costs and lead times.
3. Tooling and Equipment Maintenance
Regular maintenance and calibration of cutting tools, dies, and molds ensure consistent quality and precision in sheet metal processing operations, extending equipment lifespan and minimizing downtime.
4. Quality Control Measures
Implementing stringent quality control measures throughout the manufacturing process—from raw material inspection to final product testing—ensures adherence to design specifications and customer expectations.
5. Embracing Technological Advancements
Incorporating advanced technologies such as automation, robotics, and computer-aided design (CAD) software enhances production efficiency, accuracy, and scalability in sheet metal processing operations.
Trends Shaping the Future of Sheet Metal Machining
1. Sustainability Initiatives
Increasing focus on sustainability drives innovations in eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient manufacturing processes, and recycling programs aimed at minimizing environmental impact.
2. Digital Transformation
Integration of digital technologies such as IoT-enabled equipment monitoring, AI-driven predictive maintenance, and cloud-based data analytics enhances operational visibility, efficiency, and decision-making capabilities.
3. Additive Manufacturing (AM)
The adoption of AM technologies, such as metal 3D printing, revolutionizes sheet metal processing by enabling complex geometries, rapid prototyping, and on-demand production capabilities.
4. Customization and Personalization
Growing consumer demand for personalized products drives customization trends in sheet metal processing, prompting manufacturers to offer tailored solutions and flexible manufacturing processes.

Conclusion
Mastering sheet metal machining involves a blend of craftsmanship, technological innovation, and strategic foresight. By leveraging advanced techniques, adhering to best practices, and embracing emerging trends, manufacturers can enhance product quality, streamline operations, and remain competitive in an increasingly dynamic global marketplace.
Whether you’re a seasoned industry professional or exploring new opportunities in sheet metal processing, staying informed about evolving techniques, optimizing production workflows, and embracing technological advancements will be key to unlocking new possibilities and achieving sustained success in this essential field of manufacturing.

.jpg)








