Among various manufacturing methods, die casting stands out as one of the most important. With die casting, companies can manufacture robust, precise, and complex metal components efficiently. The automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical device industries make extensive use of these processes.
In this guide, we will explore the workings of die casting, commonly used materials, and how to select the appropriate alloy and surface finish. Additionally, it discusses mold production and criteria for choosing a trustworthy die casting partner. Whether you’re new to manufacturing or looking for improved production solutions, this article offers valuable insights to guide your decisions.
What Is Die Casting?
Die casting is a metal casting process that involves forcing molten metal under high pressure into a mold cavity. The mold cavity is formed using two hardened tool steel dies machined into shape, functioning like an injection mold during the process.
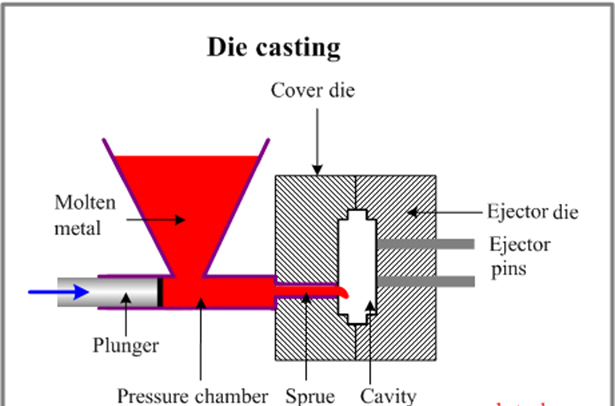
Applications of Die Casting Processes
Die casting is widely used to produce durable and versatile parts, such as engine components and electronic housings. The process offers a variety of material choices, a large build area, and the ability to create intricate, precise, and thin-walled components.
Die Casting in the Automotive Industry
Die casting is commonly applied in the automotive sector, especially for aluminum parts like gearbox cases and engine brackets. Magnesium die casting works well for seat frames and panels, while zinc die casting is suitable for fuel and brake parts.
Die Casting in the Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry depends on die casting to produce high-quality, lightweight parts. Manufacturers prefer this method for its cost efficiency and ability to meet the industry’s exacting standards.
Die Casting in the Medical Industry
Die casting plays a vital role in the medical industry. It ensures the production of lightweight, high-quality parts that meet strict standards, making it the method of choice for critical components.
Die Casting in the Energy Industry
Die casting is a key technique in the energy industry for creating durable, high-precision parts for applications like fuel cells, heat exchangers, and renewable energy systems. It’s popular because it meets the industry’s need for efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Common Die Casting Service
Aluminum die casting Service
Aluminum, a primary material in die casting, is used in cold-chamber die casting with alloys containing magnesium, copper, and silicon. Aluminum die casting is ideal for producing intricate and finely detailed parts, as it is lightweight and has great dimensional stability. It also provides benefits like resistance to high temperatures, excellent conductivity, and corrosion resistance.
Common die-casting aluminum alloys include:
| 360 | A360 | 380 | A380 | 383 | |
| Density | 2.63g/cm³ | 2.63g/cm³ | 2.74g/cm³ | 2.71g/cm³ | 2.74g/cm³ |
| Melting Range(℃) | 557-596 | 557-596 | 540-595 | 540-595 | 516-582 |
| Electrical
Conductivity |
30% IACS | 29% IACS | 27% IACS | 23% IACS | 23% IACS |
| Thermal
Conductivity |
113 W/(m’ K) | 113 W/(m’ K) | 96.2 W/(m’ K) | 96.2 W/(m’ K) | 96.2 W/(m’ K) |
| Ultimate Tensile Strenghth | 300 MPa | 320 MRa | 320 MRa | 320 MRa | 310 MRa |
| Yield Strength | 170 MPa | 170 MPa | 170 MPa | 170 MPa | 170 MPa |
| Hardness | 75 BHN | 75 BHN | 75 BHN | 75 BHN | 75 BHN |
| Fatigue Strength | 140 MPa | 140 MPa | 140 MPa | 140 MPa | 140 MPa |
| Shear Strength | 190 MPa | 190 MPa | 190 MPa | 190 MPa | 190 MPa |
| Elongation | 2.5% | 2.5% | 2.5% | 2.5% | 2.5% |
Zinc Die Casting Service
Zinc alloys are a key material for die casting applications. Zinc casting is favored for its excellent plating qualities, along with added benefits like high impact strength and ductility. It is a popular choice for manufacturers because it is easy to cast with a hot-chamber die casting machine, and its castability minimizes wear on the die. Zinc is often mixed with copper, magnesium, and aluminum, as it is denser than magnesium and aluminum.
Common die casting Zinc alloys include:
| Alloy Grade | Zamak 2 | Zamak 3 | Zamak 5 | Zamak 7 | ZA-8 |
| Density (g/cm³) | 6.7 | 6.6 | 6.7 | 6.8 | 6.9 |
| Melting Point (℃) | 383-386 | 381-387 | 379-386 | 380-386 | 381-387 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m`K) | 109 | 116 | 113 | 113 | 116 |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (10^-6/K) | 26.5 | 27.5 | 26.9 | 26.5 | 26.5 |
| Electrical Conductivity (% IACS) | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 26 |
| Main Chemical Composition | 3.5-4.3% Al 0.02-0.05% Mg 0.035-0.06% Cu |
3.5-4.3% Al 0.03% Mg 0.03% Cu |
3.5-4.3% Al 0.035% Mg 0.035% Cu |
3.5-4.3% Al 0.03-0.06% Mg 0.03-0.06% Cu |
3.5-4.3% Al 0.05-0.5% Mg 0.005-0.03% Cu 0.005-0.03% Ni 0.005-0.03% Fe |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 295 | 255 | 310 | 345 | 380 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 240 | 215 | 230 | 275 | 320 |
| Elongation (%) | 2 | 3 | 6 | 3 | 1 |
| Hardness (HB) | 82 | 70 | 90 | 95 | 100 |
| Main Differences | Contains less Mg and Cu, suitable for larger parts | Contains less Mg and Cu, suitable for larger parts | Contains less Mg and Cu, suitable for larger parts | Contains more Mg and Cu, suitable for complex-shaped parts | Contains Mg, Cu, Ni, and Fe, with higher strength and hardness |
| Main Casting Applications | Automotive, furniture, appliances, and mechanical parts | Electrical, hand tools, toys | Machinery, architectural, and automotive | Automotive, electrical, hardware | Industrial, automotive, electrical |
What to Look for When Selecting Die Casting Alloys
The alloy you choose has a direct effect on how the final product performs and how much it costs to produce. To make the right choice, keep these five points in mind:
1. Mechanical Properties
Choose an alloy that meets the strength, hardness, and durability requirements of the final part. Mechanical performance will vary between alloys.
2. Corrosion Resistance
Think about the environment the part will face. Exposure to chemicals, moisture, or temperature shifts may affect the alloy. Zinc and aluminum offer good natural corrosion resistance, but some alloys may need extra coatings.
3. Thermal Conductivity
If the part needs to manage heat or maintain stable temperatures, consider an alloy with high thermal conductivity. Copper-based alloys are often used when efficient heat transfer is important.
4. Machinability
If CNC machining or other post-processing is needed, make sure the alloy can be machined without too much difficulty. Some alloys are easier to work with, while others may require special tools or techniques.
5. Cost: Evaluate
Look at the total cost, not just the material price. Include production efficiency, machining needs, and finishing steps. Some alloys are more expensive to process, even if the raw material cost is low.
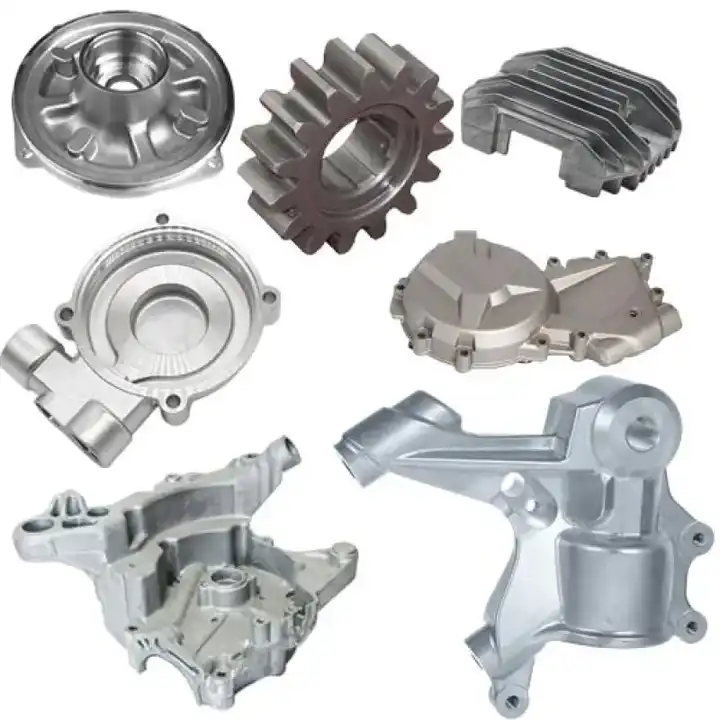

How to Make a Die Casting Mold
A die casting mold has two main parts: the cover side, fixed on a stationary plate, and the ejection side, attached to a movable plate. To produce complex parts with features like holes or threads, some molds include extra components such as slides and cores.
Depending on the part size, a mold may contain multiple cavities to produce several pieces in one cycle. These can be multi-cavity molds, with identical cavities, or family molds, which include different cavity shapes to make various parts at once.
Die casting molds must be strong, heat-resistant, and wear-resistant. They also need good ductility to withstand repeated use. Most are made from hardened tool steel that has been heat-treated. These molds are built to handle thousands of casting cycles per hour and can last up to two million cycles during their lifespan. They also need to endure high clamping forces.
The mold-making process starts with CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and casting-specific simulation tools. Like injection molds, die casting molds need gates, runners, and vents to guide molten metal into the cavity. Ejection pins and locking systems are also needed to release parts and keep the mold closed during casting.
CNC machining is widely used to make die casting molds. The process usually begins with rough cutting the mold shape, followed by heat treatment, then finishing to achieve the final dimensions. For quick-turn or prototype molds, rapid tooling can be used. This may involve CNC machining or methods like Selective Laser Sintering (SLS).
What NOBLE Can Do for Your Product’s Surface Treatment
At NOBLE, we provide a wide variety of surface treatments to enhance your parts. These surface finishes boost appearance, hardness, and resistance to corrosion and chemicals. They also smooth out rough tool paths and cover any marks left during CNC machining. Here are some finishing options that might be the right fit for your custom parts.
| Name | Description | Materials | Color | Texture | |
 |
Anodizing | Anodizing improves corrosion resistance, enhancing wear resistance and hardness, and protecting the metal surface. Widely used in mechanical parts, aircraft, automobile parts, precision instruments, etc. | Aluminum | Clear, black, grey, red, blue, gold. | Smooth, matte finish |
 |
Powder Coating | Powder coating is a type of coating that is applied as a free-flowing, dry powder. Unlike conventional liquid paint, which is delivered via an evaporating solvent, powder coating is typically applied electrostatically and then cured under heat or with ultraviolet light. | Aluminum, Stainless Steel, Steel | Black, any RAL code or Pantone number | Gloss or semi-gloss |
 |
Electroplating | Electroplating can be functional, decorative, or corrosion-related. Many industries use the process, including the automotive sector, in which chrome-plating of steel automobile parts is common. | Aluminum, steel, Stainless Steel | N/A | Smooth, Glossy finish |
 |
Polishing | Polishing is the process of creating a smooth and shiny surface, either through physical rubbing of the part or by chemical interference. The process produces a surface with significant specular reflection, but in some materials can reduce diffuse reflection. | Aluminum, Brass, Stainless Steel, Steel | N/A | Glossy |
 |
Brushing | Brushing is a surface treatment process in which abrasive belts are used to draw traces on the surface of a material, usually for aesthetic purposes. | ABS, Aluminum, Brass, Stainless Steel, Steel | N/A | Satin |
How to Choose the Right Die Casting Manufacturer
Picking a die casting manufacturer isn’t just about price—it’s about finding the right partner for your product. Here’s how to make the right choice:

1. Know What You Need
Start by clearly outlining your project needs. This includes part specifications, order quantity, quality standards, surface treatment, and delivery timeline. Having a clear plan will help you communicate better with suppliers and assess whether they can meet your expectations.
2. Check Their Background
Look for manufacturers with proven experience in die casting. Review their track record, especially in working with the materials relevant to your project. It’s also useful to check what industries they’ve served and whether they’ve produced similar complex parts.
3. See What They Can Handle
Examine the manufacturer’s equipment and production capacity. This includes machine size, available tooling, and support for secondary processes like CNC machining, surface finishing, and assembly. Make sure their facilities match your production scale and technical needs.
4. Ask About Quality
Ask about their quality control systems. Look for companies that follow recognized standards, such as ISO certifications. Also, check their inspection routines, testing procedures, and how they ensure product quality at every stage.
5. Get Engineering Help
See if the manufacturer can support you in the design and engineering phases. A skilled partner can offer suggestions to improve the design for manufacturability, reduce costs, and select the best materials and processes.
6. Talk, Often
Good communication is crucial. Choose a manufacturer that is responsive, open to feedback, and willing to provide updates throughout the project. A cooperative attitude helps avoid delays and misunderstandings.

Final Thoughts
For mass-producing durable and detailed metal components, die casting is a smart choice. When enhanced with CNC machining, it becomes a highly precise and versatile manufacturing solution.
Key success factors include smart material selection, efficient mold design, and proper surface finishing. A good grasp of each step in the process helps you make better decisions and optimize both cost and performance.
NOBLE brings the expertise and capabilities needed to deliver reliable die casting solutions tailored to your project.
Ready to get started? Reach out to us—we’re here to help!








