Injection molding is one of the most versatile and widely used manufacturing methods globally, enabling the mass production of complex plastic, metal, and silicone parts with unmatched precision. As industries evolve, so do the demands for specialized molding techniques.
Which injection molding process is right for your project? What are the unique advantages of different processes? In this guide, we’ll give you a detailed overview of 12 injection molding types, including processes, applications, advantages, and limitations, to help you choose the best solution!
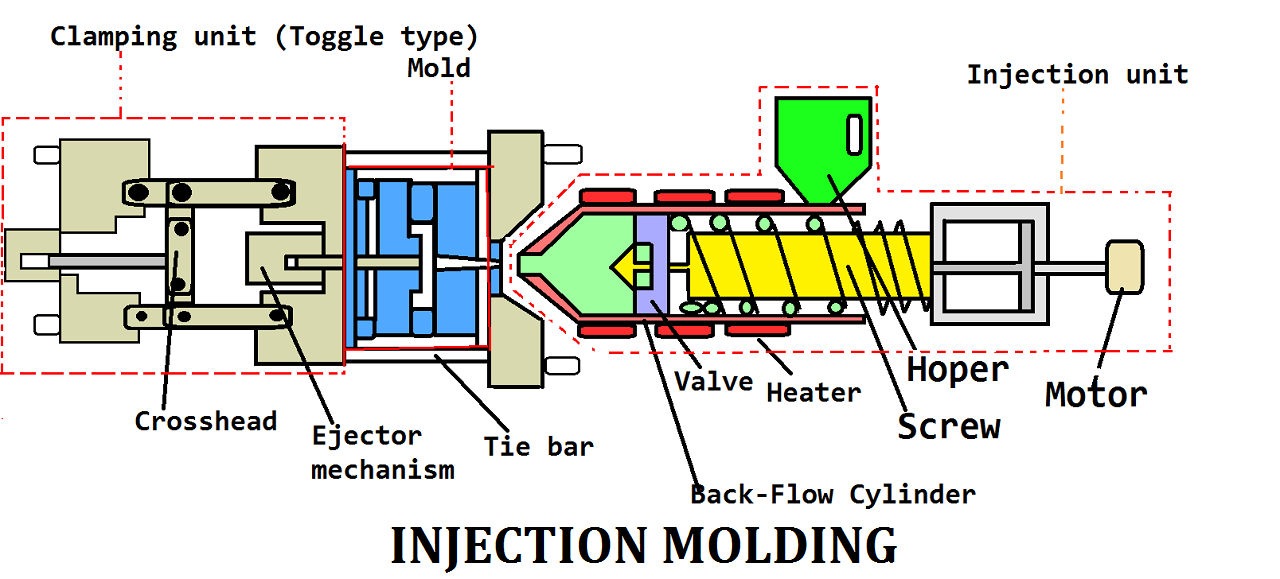
Introduction to Injection Molding
Injection molding involves injecting molten material into a mold cavity, where it cools and solidifies into a desired shape. Originally developed for thermoplastics, the technology now spans metals, silicones, and biodegradable materials. With a global market projected to reach $47 billion by 2030 (QYR Research), understanding the diverse injection molding processes is critical for manufacturers aiming to stay competitive.
Why read this guide?
- Discover how each process addresses unique design challenges.
- Learn which method aligns with your material, volume, and budget needs.
- Gain insights into emerging trends like eco-friendly molding and micro-manufacturing.
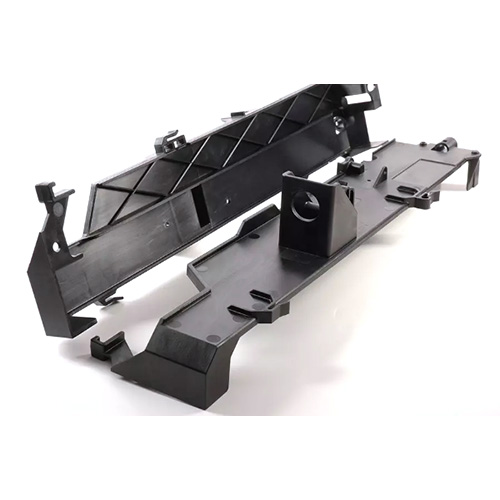

12 Types of Injection Molding Processes
1. Conventional Injection Molding
Conventional injection molding is a tried-and-tested technique for producing plastic parts. In this method, thermoplastic pellets are heated and injected into a mold, where they solidify into the desired shape. This process excels in mass production, making it invaluable for industries that require consistent, large quantities of molded items.
Applications:
- Automotive dashboards
- Electronic housings
- Consumer goods
Advantages:
- Highly efficient production cycle, often as short as 15 seconds per item
- Ideal for large-scale manufacturing, producing batches in the tens of thousands
Limitations:
- High initial cost for mold production
- Once a mold is made, making design revisions is challenging and costly
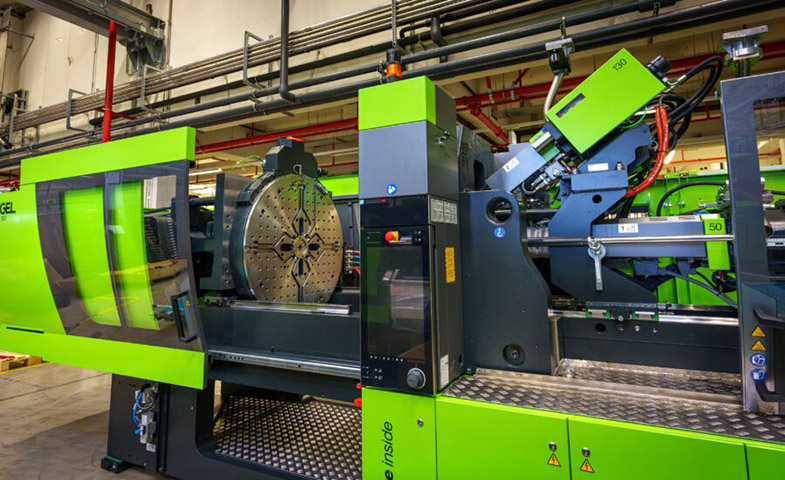

2. Two-Shot Injection Molding
The two-shot injection molding process, often referred to as multi-material molding, involves injecting two different materials (or colors) into a single mold in a sequential manner. This method uses specialized rotating molds to combine the materials, which creates parts with multiple properties or colors. The approach is especially beneficial when functionality and aesthetics are equally important.
Applications:
- Toothbrush grips
- Automotive buttons
- Multi-color consumer electronics
Advantages:
- No need for additional post-molding steps such as painting or bonding
- Combines beauty and functionality (for example, soft-touch components)
Limitations:
- Mold complexity leads to a 30-50% increase in production costs
- Requires exact material alignment for proper functioning
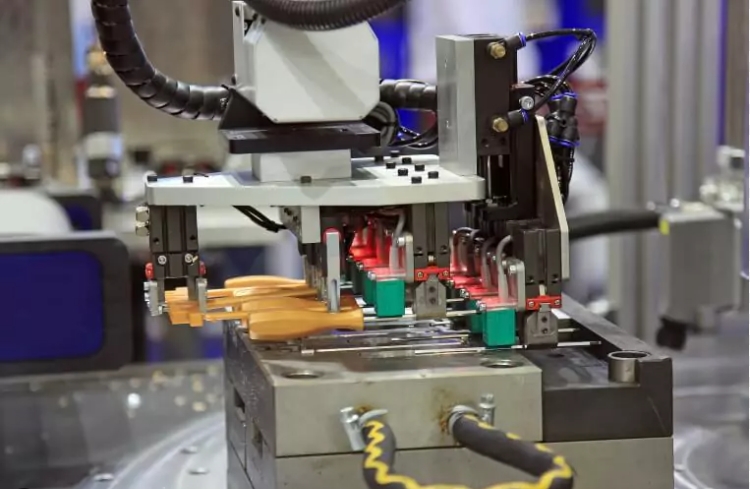

3. Insert Molding
Insert molding, also called metal insert injection molding, involves the insertion of metal or plastic parts into a mold before injecting molten plastic around them. This process encapsulates the inserts, combining the rigidity of metal with the versatility of plastic, resulting in stronger, more functional parts.
Applications:
- Electrical connectors with brass terminals
- Reinforced tool handles
Advantages:
- Combining the strength of metal with the flexibility of plastic
- Simplifies assembly by eliminating the need for additional fasteners, like screws
Limitations:
- The precise placement of inserts is crucial, requiring small tolerances
- There’s a risk of the inserts shifting during the injection process
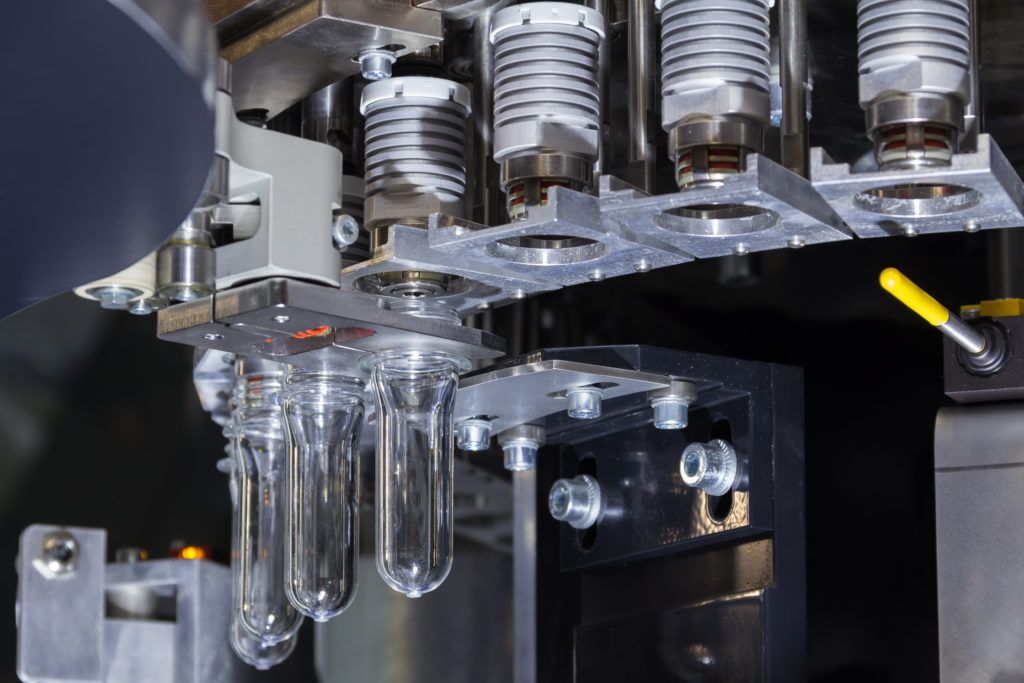

4. Gas-Assisted Injection Molding (GAIM)
Gas-assisted injection molding, or GAIM, is an innovative molding technique where inert gas (usually nitrogen) is injected into molten plastic. This process creates hollow areas inside the molded part, reducing the material consumption and enhancing the strength of the final product. It’s particularly useful for producing lighter, yet durable components.
Applications:
- Frames for furniture
- Automotive door panels
- Components with thick walls
Advantages:
- Material use is reduced by 20-40%
- Prevents sink marks from forming in thick sections
Limitations:
- Specialized gas injection equipment is necessary
- Suitable only for certain part geometries, such as tubular or ribbed designs

5. Micro Injection Molding
Micro injection molding, or micro molding, is the technique used to produce extremely tiny parts—typically under 1 gram—using specialized equipment and molds. This method is essential for applications where high precision and small sizes are critical.
Applications:
- Medical catheters
- Micro-optics for devices
- Components for wearable technology
Advantages:
- Enables the production of highly detailed, miniaturized parts
- Supports the use of biocompatible materials, such as PEEK, for medical implants
Limitations:
- Mold costs can be significant due to the intricate details involved
- The cycle time is slower, sometimes taking up to 2 minutes to produce parts with micro-scale features
![]()
6. Liquid Silicone Rubber Molding (LSR)
Liquid silicone rubber molding, often referred to as LSR injection molding, involves mixing two liquid silicone components, injecting them into molds, and then heat-curing the mixture to produce parts that are both flexible and long-lasting. This technique is especially useful when high performance in extreme conditions is required.
Applications:
- Medical seals
- Baby bottle nipples
- Kitchen products
Advantages:
- Can endure extreme temperature fluctuations, from -50°C to 250°C
- Hypoallergenic and FDA-compliant, ensuring safety in sensitive applications
Limitations:
- Material costs can be 3 to 5 times higher than thermoplastics
- Requires the use of vacuum systems to remove air bubbles during the injection process
7. Reaction Injection Molding (RIM)
Reaction injection molding (RIM) is a molding process where liquid polymers, such as polyurethane, are combined and injected into a mold, where they chemically react and cure. This process is known for producing large, lightweight, and impact-resistant parts.
Applications:
- Automotive bumpers
- Industrial equipment housings
- Insulation panels
Advantages:
- Allows for the production of large parts weighing up to 50kg
- Offers outstanding impact resistance
Limitations:
- The cycle time can be long, ranging from 5 to 10 minutes
- Works only with low-viscosity materials

8. Structural Foam Molding
Structural foam molding, also known as foam injection molding, is a specialized process wherein a chemical foaming agent is added to molten plastic. This causes the plastic to expand, resulting in a product with a porous interior, thereby reducing both its weight and material usage.
Applications:
- Pallet trays
- Construction formwork
- Industrial containers
Advantages:
- A weight reduction of 10-30% per part
- Reduced clamp force requirements, which subsequently lead to energy conservation
Limitations:
- The surface finish might need a bit of post-processing
- It is primarily suitable for functional, non-aesthetic applications
9. Co-Injection Molding
Co-injection molding, also known as multi-layer injection molding, involves injecting two different materials sequentially into a mold, creating parts with multiple layers. This allows for a combination of properties, such as a rigid inner core and a soft outer layer, for improved performance.
Applications:
- Food packaging, especially for barrier layers
- Dashboards in automotive applications
Advantages:
- Allows for the combination of different material properties, such as rigidity and UV resistance
- Can cut material costs by using recycled materials for the core layer
Limitations:
- The molds required are more complex, often with multiple runners
- Risk of delamination between the layers

10. Thermoset Injection Molding
Thermoset injection molding, also known as thermoset plastic molding, involves injecting thermoset plastics (e.g., epoxy) into molds, where they are cured under heat to form irreversible bonds. This process results in parts with strong thermal and dimensional stability, perfect for high-temperature environments.
Applications:
- Electrical insulators
- Circuit breakers
- Appliance handles
Advantages:
- Can withstand temperatures up to 575°F
- Maintains excellent dimensional stability
Limitations:
- The material cannot be remelted and recycled
- The curing process is slower, taking between 3 and 8 minutes

11. Metal Injection Molding (MIM)
In metal injection molding (MIM), a blend of metal powder and binder is injected into a mold, followed by a debinding process and sintering, which results in dense, high-strength metal parts. MIM is particularly suited for industries requiring parts with complex geometries and tight tolerances.
Applications:
- Surgical tools
- Aerospace fasteners
Advantages:
- Capable of producing complex geometries, including internal threads and fine details
- Offers strength similar to that of machined metal parts
Limitations:
- Sintering shrinkage may lead to dimensional changes of ±0.3%
- High energy consumption during sintering

12. Biodegradable Plastic Molding
Biodegradable plastic molding, or eco-friendly injection molding, involves using biodegradable substances like PLA and PHA. These materials are molded using conventional injection molding techniques but offer a more sustainable alternative to traditional plastics.
Applications:
- Disposable cutlery
- Compostable packaging
- Agricultural films
Advantages:
- Breaks down in 6 to 12 months in industrial composting conditions
- Decreases dependency on fossil fuels in the production of plastics
Limitations:
- Costs can be 20-50% higher than those of conventional plastics
- Limited mechanical strength makes it unsuitable for heavy-duty or load-bearing applications
Choosing the Right Process: Key Considerations
To ensure you choose the best injection molding process for your project, take some time to understand its unique needs. By doing so, you and your engineers can develop a customized solution that’s perfect for your parts.
| Factor | Questions to Ask |
| Volume | Is the project low-volume (100-1,000 units) or mass production (10,000+ units)? |
| Material | Does the part require flexibility, heat resistance, or biocompatibility? |
| Budget | Can you afford high mold costs upfront for long-term savings? |
| Lead Time | Is rapid prototyping needed, or is the timeline flexible? |
| Sustainability | Are eco-friendly materials or energy-efficient processes a priority? |
Why Partner with NOBLE for Injection Molding?
1. Cutting-Edge Capabilities: Precision and Innovation in Every Part
Machines: With tonnages ranging from 20T to 1800T, all parts from micro to large components can be processed.
Tolerances: Achieve ±0.05mm precision for mission-critical components that require utmost accuracy.
Materials Expertise: Extensive experience in handling plastic materials such as ABS, PEEK, PE, etc.
2. Cost-Effective Solutions: Maximizing Value, Minimizing Costs
Prototyping: Get functional prototypes in just 5-7 days, so you can move forward with your project quickly.
Bulk Discounts: Enjoy volume pricing for large orders.
Tooling Optimization: Our AI-powered Moldflow analysis helps minimize defects and ensures optimal production.
3. End-to-End Service: Complete Solutions, From Design to Delivery
Design Support: We provide expert DFM (Design for Manufacturing) consultations to optimize your product for efficient production.
Post-Processing: Offering a range of surface treatment services and full assembly for a complete product.
Global Compliance: Certifications such as ISO 9001, ISO 13485 (medical), and FDA-510K ensure reliability in global production.

Future Trends in Injection Molding
- Smart Molding: With IoT integration, machines now offer real-time data and insights, helping to fine-tune the molding process for better outcomes.
- Circular Economy: Embracing a circular economy by focusing on closed-loop recycling of post-consumer plastics to reduce environmental impact.
- Hybrid Materials: The rise of hybrid materials—blending plastics with carbon fiber and nanomaterials—enables stronger, more versatile products.
Conclusion
Whether it’s conventional thermoplastics or cutting-edge metal and biodegradable techniques, injection molding provides unparalleled versatility for modern manufacturing. By choosing the right method for your project, you can maximize cost-efficiency, product quality, and environmental sustainability.
Let’s Get Started!
Reach out to NOBLE today for a free consultation and discover how our injection molding capability can make your vision a reality!







